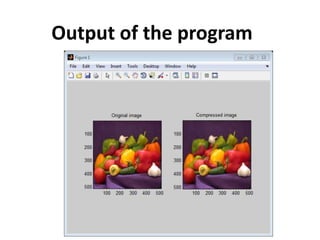
The document discusses image compression techniques. It introduces compression goals of minimizing file size while maintaining quality. It then covers compressing grayscale images using global thresholding and Huffman encoding. The document demonstrates this method on a "mask" image, outputting the compression ratio and bits per pixel. It also covers compressing color images using wavelet-based methods like SPIHT. The quality of the compressed "wpeppers" image is assessed using MSE and PSNR metrics.




![wcompress
• %--------------------------------------------------------------
• % Compression and uncompression of a truecolor image
• % and computed MSE and PSNR error values.
• % Compression parameters are the same as those used for example 3,
• % but using the 'spiht_3d' method give better performance yet.
• %--------------------------------------------------------------
• X = imread('wpeppers.jpg');
• [cr,bpp] = wcompress('c',X,'wpeppers.wtc','spiht','maxloop',12)
• Xc = wcompress('u','wpeppers.wtc');
• delete('wpeppers.wtc')
• D = abs(double(X)-double(Xc)).^2;
• mse = sum(D(:))/numel(X)
• psnr = 10*log10(255*255/mse)
• % Display the original and the compressed image
• subplot(1,2,1); image(X); title('Original image'); axis square
• subplot(1,2,2); image(Xc); title('Compressed image'); axis square](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/two-dimensionaltruewaveletcompression-130216142357-phpapp01/85/Two-dimensional-true-wavelet-compression-5-320.jpg)



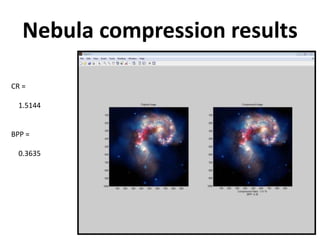
![Compression code
• load mask;
• image(X)
• axis square;
• colormap(pink(255))
• title('Original Image: mask')
• meth = 'gbl_mmc_h'; % Method name
• option = 'c'; % 'c' stands for compression
• [CR,BPP] =
wcompress(option,X,'mask.wtc',meth,'bpp',0.5)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/two-dimensionaltruewaveletcompression-130216142357-phpapp01/85/Two-dimensional-true-wavelet-compression-10-320.jpg)
![Uncompression code
• %%%%here is the uncompression part
•
•
• option = 'u'; % 'u' stands for uncompression
• Xc = wcompress(option,'mask.wtc');
• colormap(pink(255))
• subplot(1,2,1); image(X);
• axis square;
• title('Original Image')
• subplot(1,2,2); image(Xc);
• axis square;
• title('Compressed Image')
• xlabel({['Compression Ratio: ' num2str(CR,'%1.2f %%')],
...
• ['BPP: ' num2str(BPP,'%3.2f')]})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/two-dimensionaltruewaveletcompression-130216142357-phpapp01/85/Two-dimensional-true-wavelet-compression-11-320.jpg)