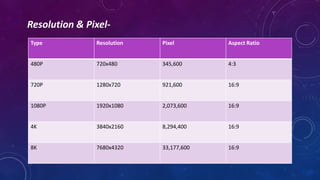
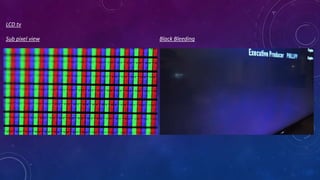
The document discusses the history and evolution of television technology in India, starting from its introduction in 1959 with Doordarshan and its role in education and community development. It covers various types of display technologies including CRT, LCD, LED, and OLED, detailing their characteristics such as size and resolution. Additionally, it provides specifications like resolutions from 480p to 8k and highlights the advancements in television technology over the years.