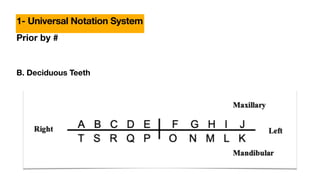
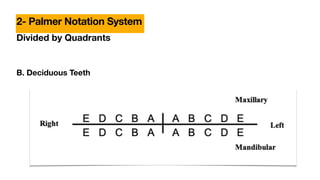
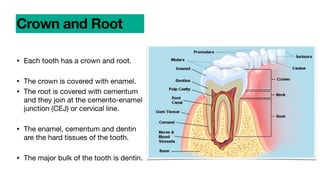
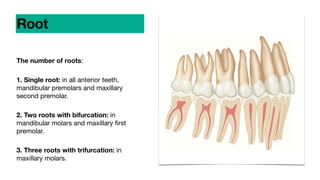
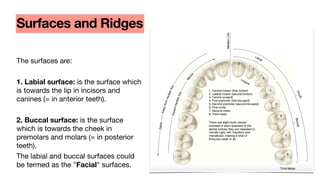
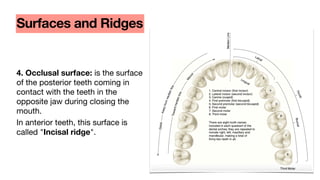
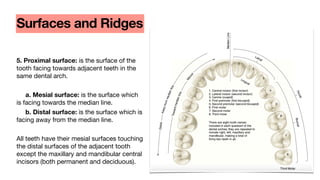
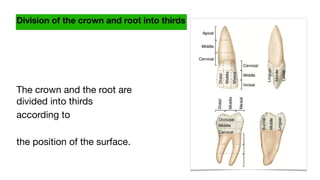
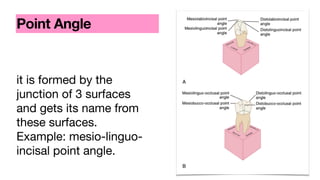
This document discusses dental anatomy and different tooth numbering systems. It introduces the universal, Palmer, and FDI numbering systems for identifying permanent and deciduous teeth. It also describes the basic anatomy of teeth, including the crown, root, surfaces, and divisions. Key parts are identified such as the cemento-enamel junction, pulp chamber, and anatomical and clinical crowns. The number of roots in different teeth and the surfaces and ridges are outlined. Line angles and point angles are also defined.