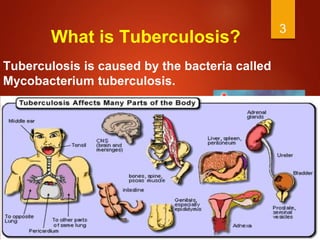
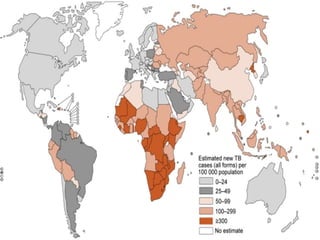
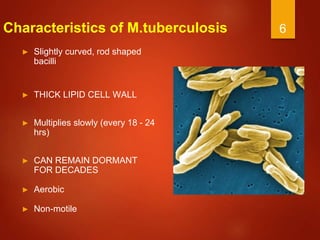
Tuberculosis is caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. It remains a serious global health issue, infecting around a quarter of the world's population and causing millions of deaths every year, especially in India. The bacteria has a thick lipid cell wall, grows slowly, and can remain dormant in the body for decades. Symptoms include cough, appetite loss, breathing difficulty, fever, and chest pain. Diagnosis involves tuberculin skin tests, interferon-gamma release assays, and sputum cultures. Treatment consists of a multi-drug regimen including isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol over several months.