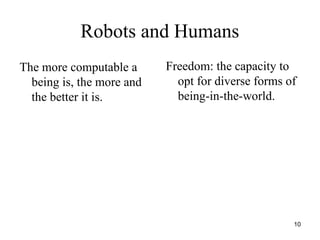
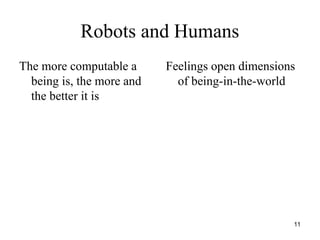
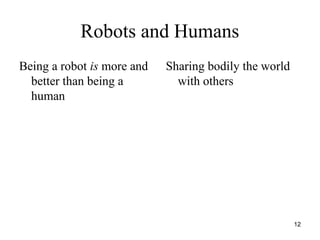
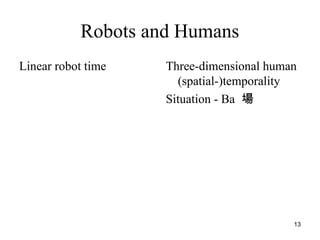
The document discusses robo-ethics, highlighting the integration of robots into society and the implications for human interaction, self-awareness, and ethics of care. It suggests that robots may soon become ubiquitous like cars, raising questions about their use, societal risks, and social opportunities. Additionally, it emphasizes the cultural significance of robots in Japan and the need for new ethical frameworks to accommodate the changing landscape of human-robot relationships.









![28
Conclusion
Cosima Wagner writes in her book
„Robotopia Nipponica. Research on the
Acceptance of Robots in Japan“ (2013):
"[...] "social robots" illustrate the "negotiation
character of the creation and use of
technological artefacts" (Hörning), which
for example includes the rejection of
military applications of robot technology in
Japan.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tsukuba2015final-240827152241-4aff16df/85/tsukuba2015_finaladalahpowerpointbaguus-ppt-28-320.jpg)









