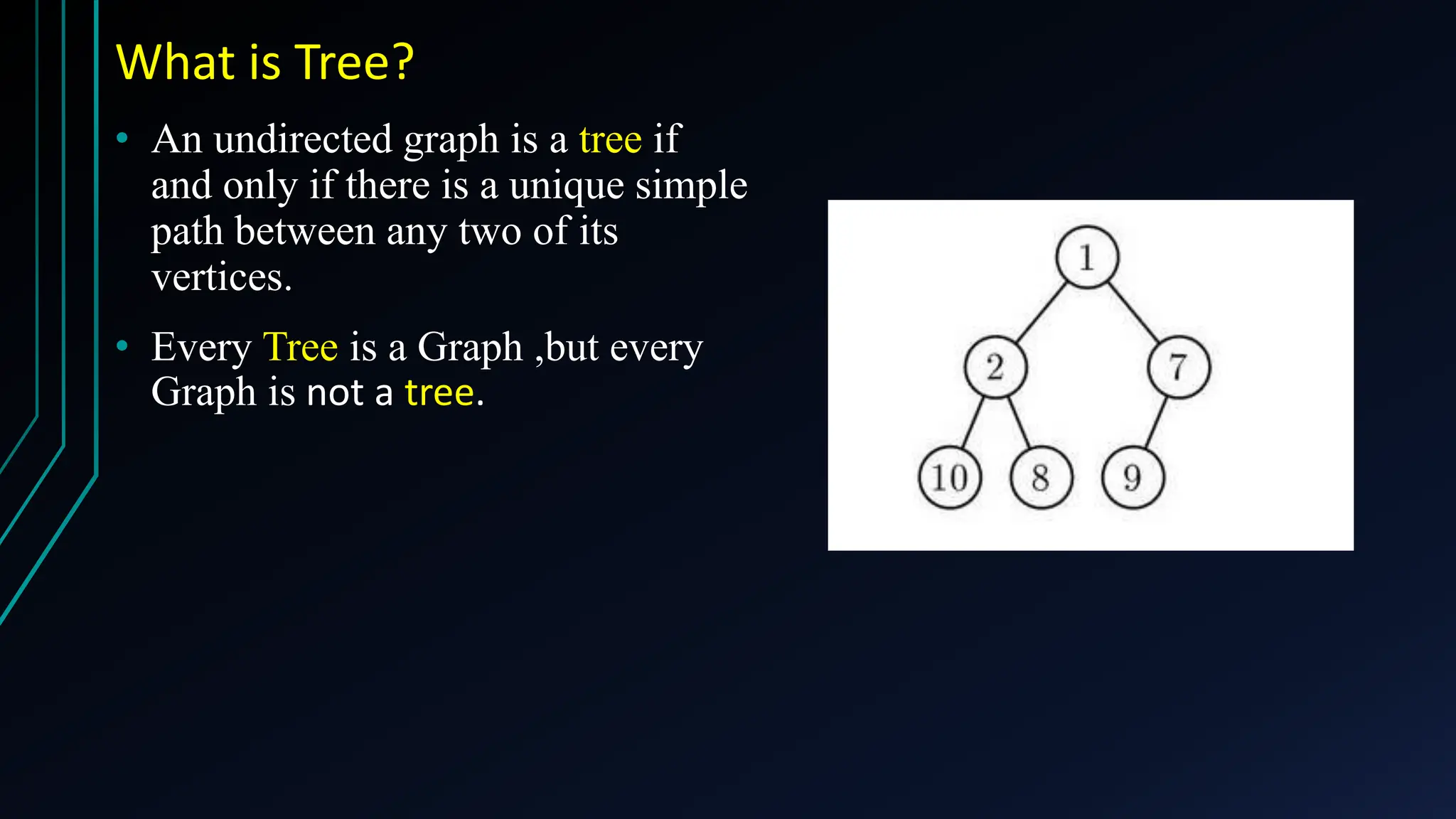
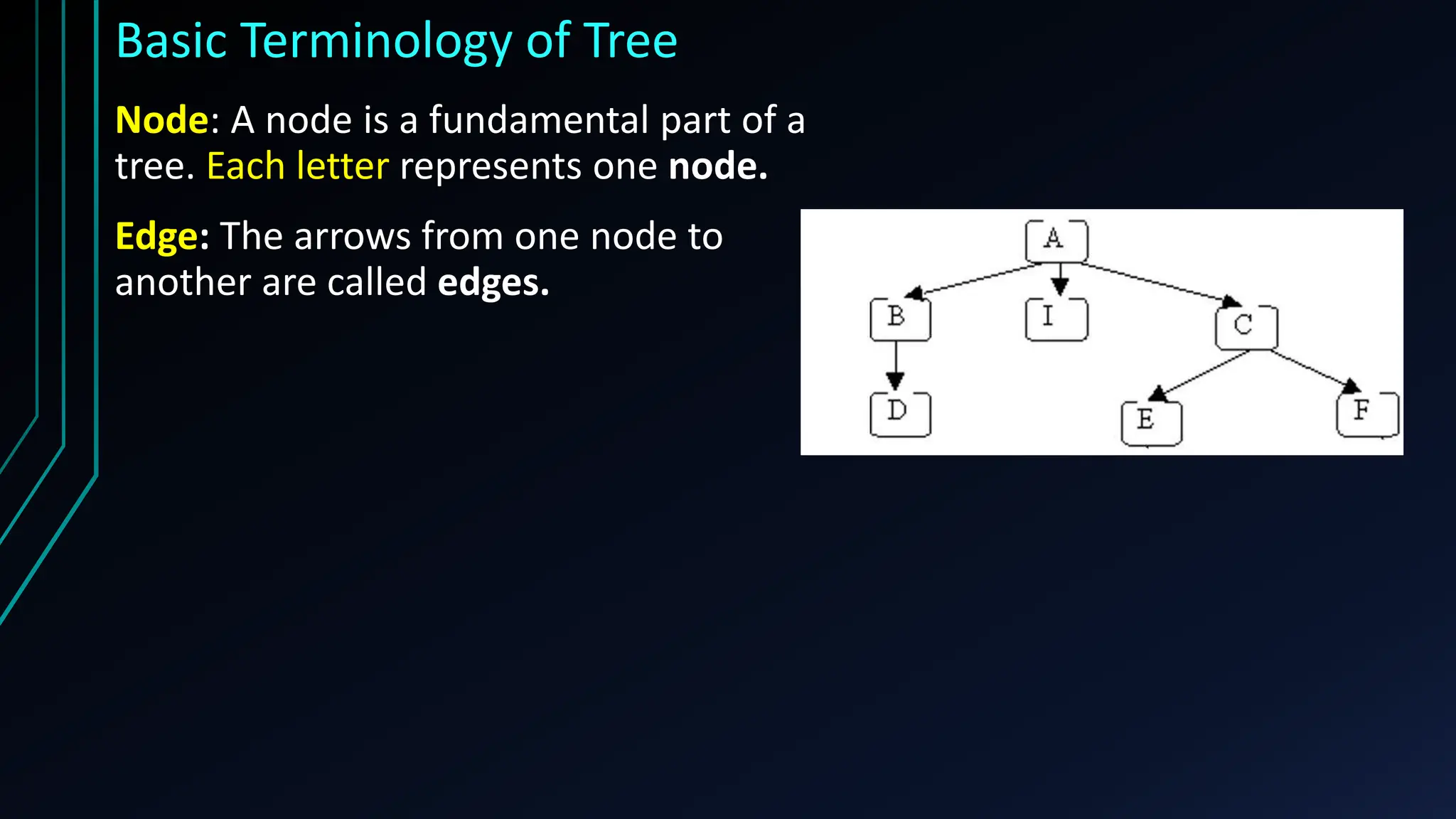
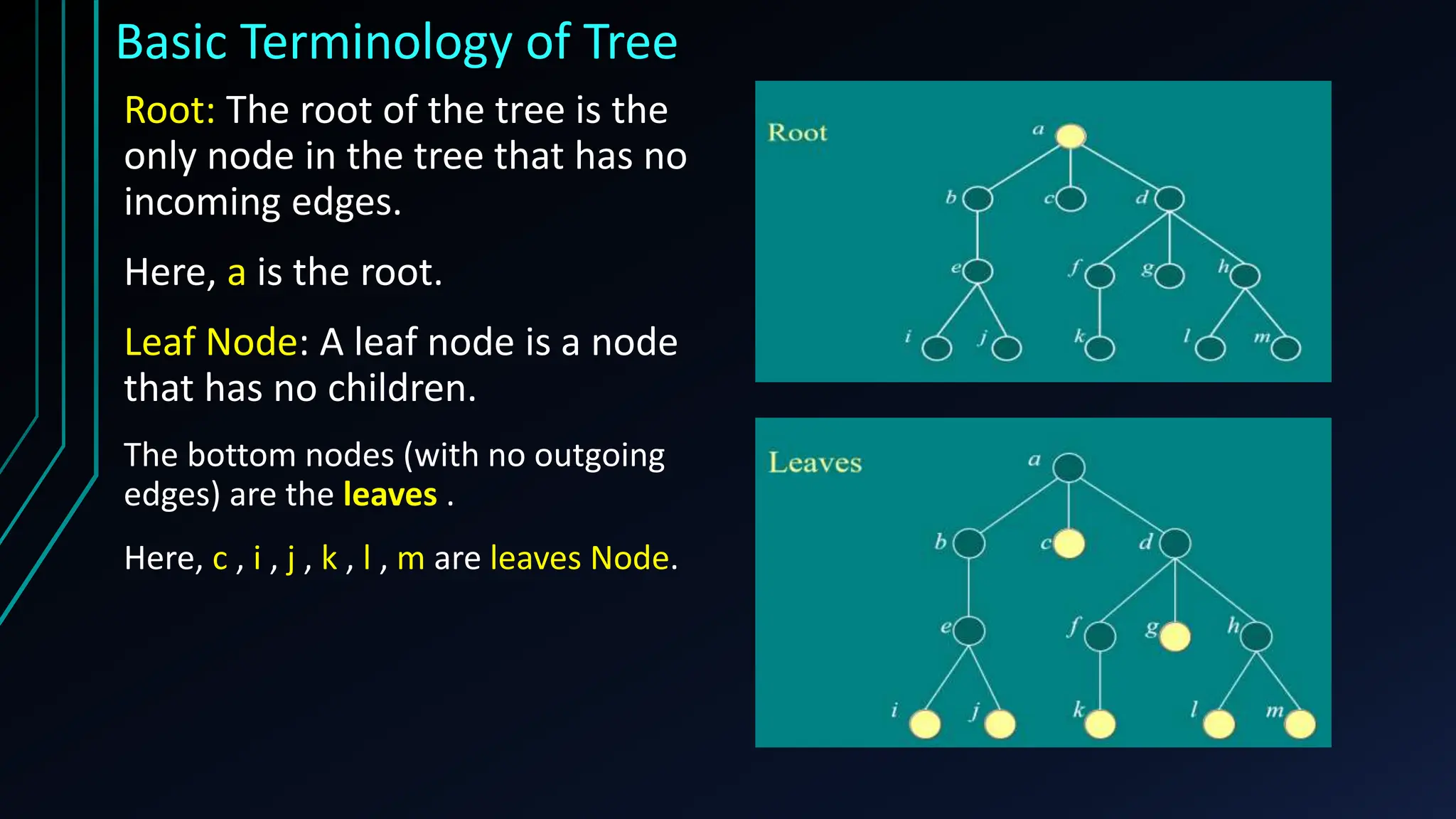
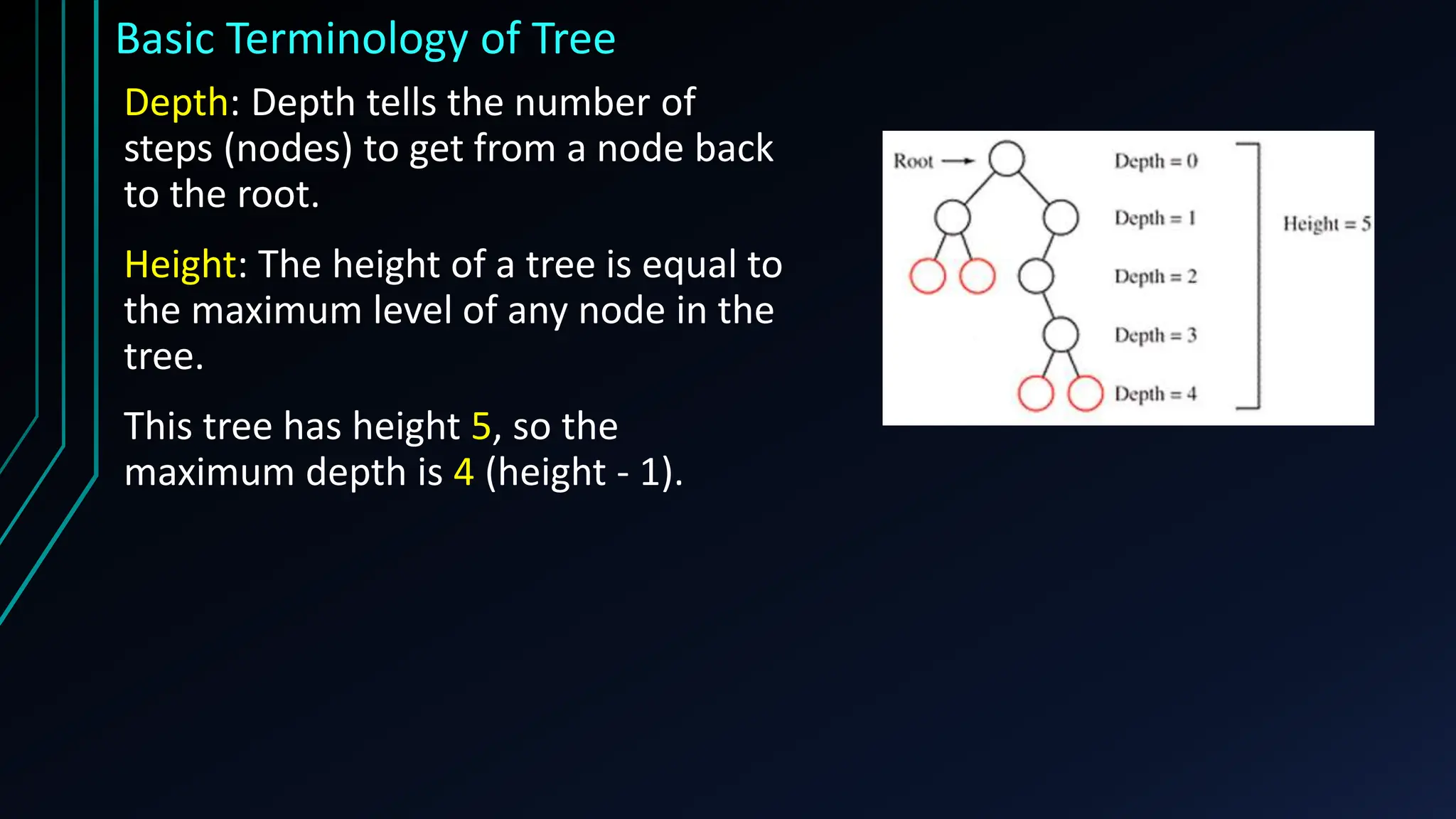
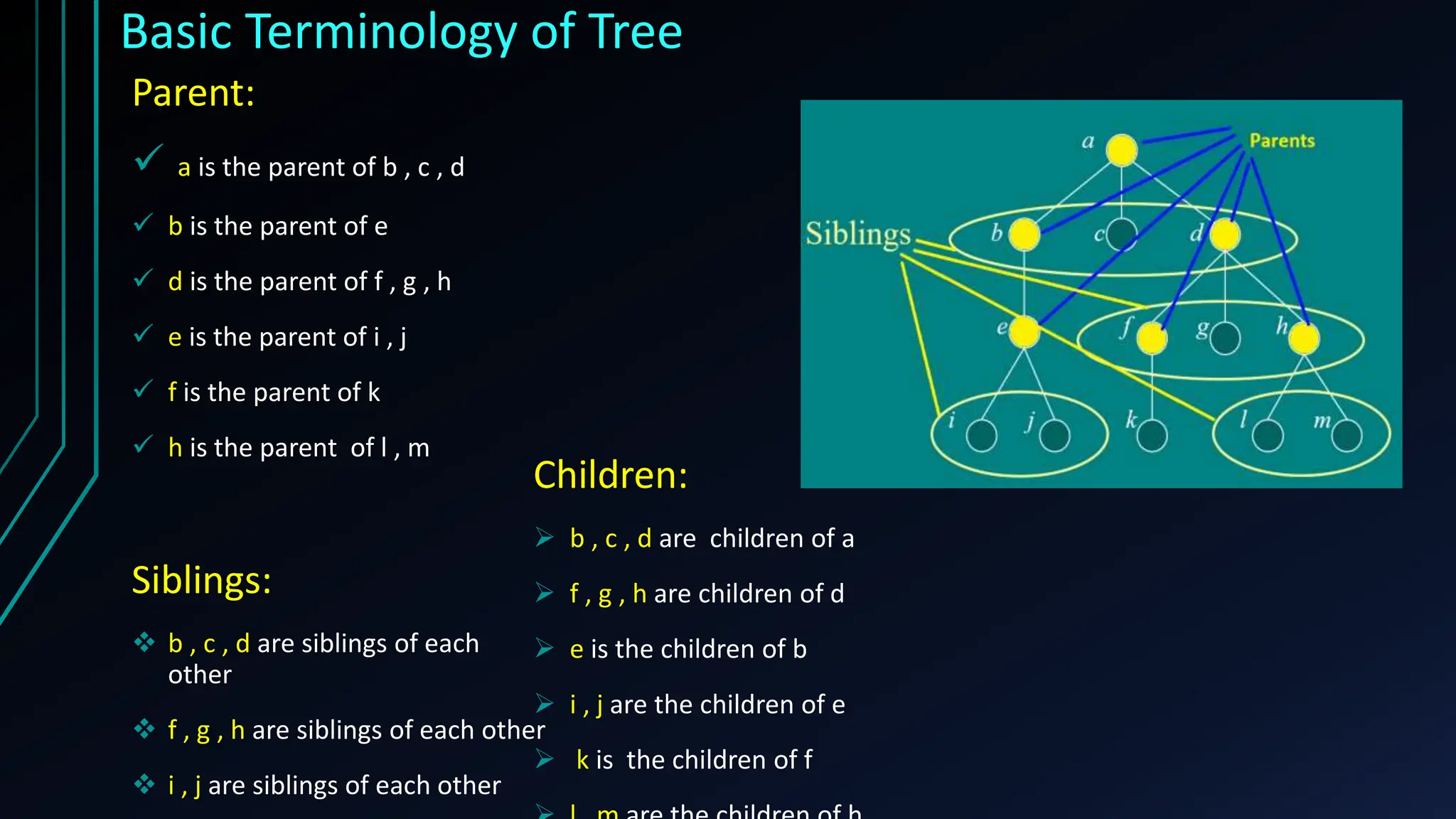
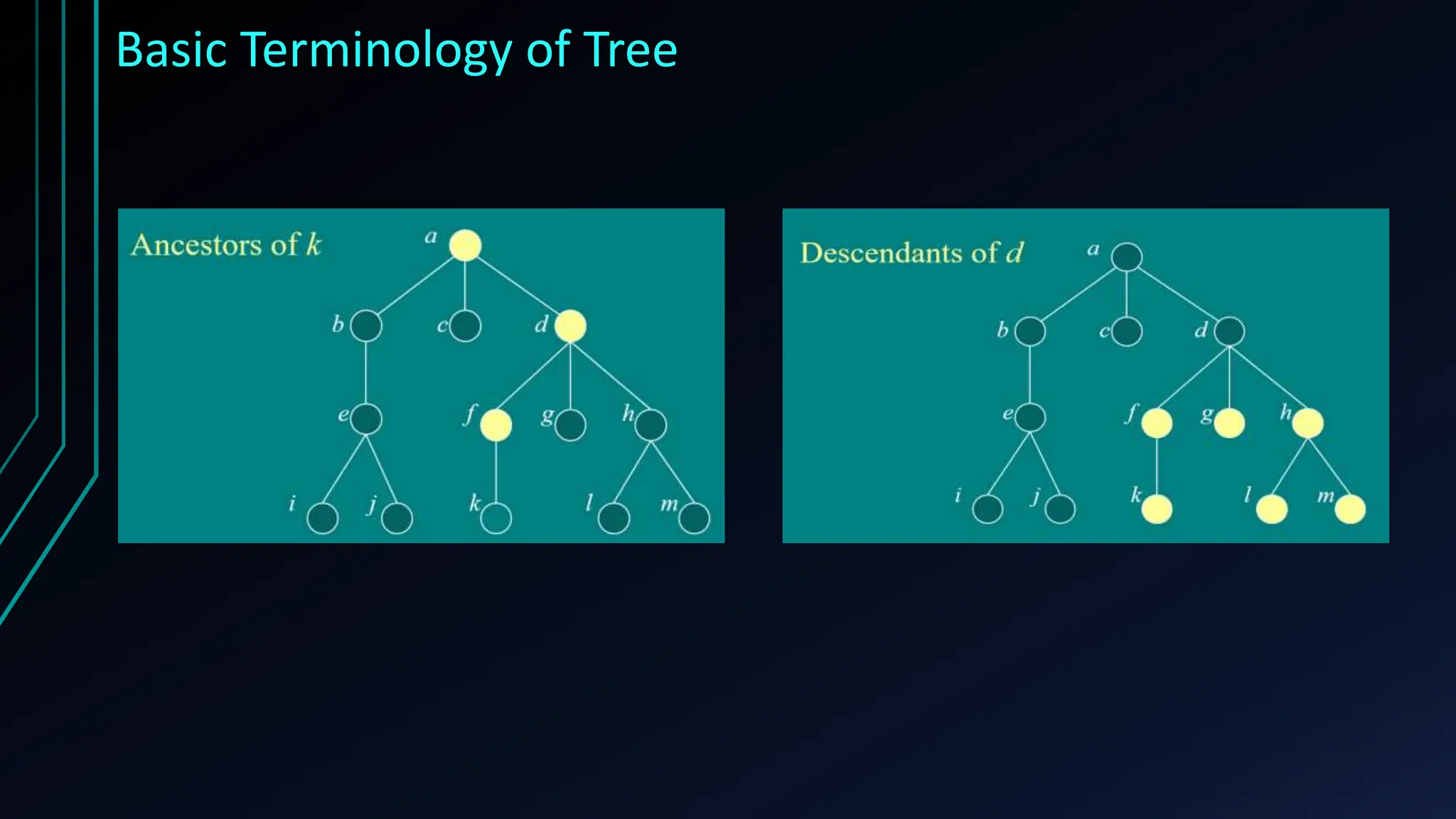
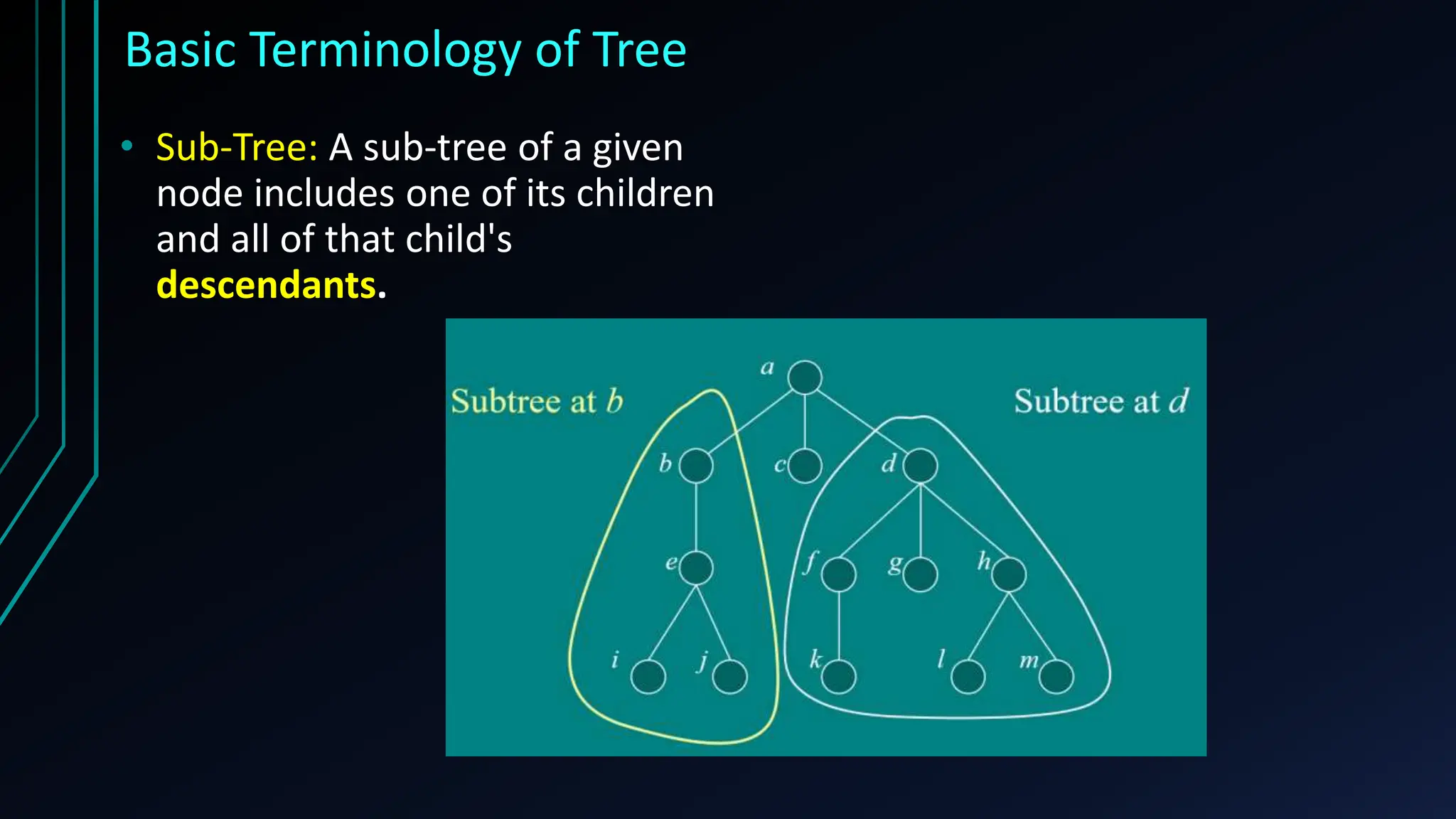
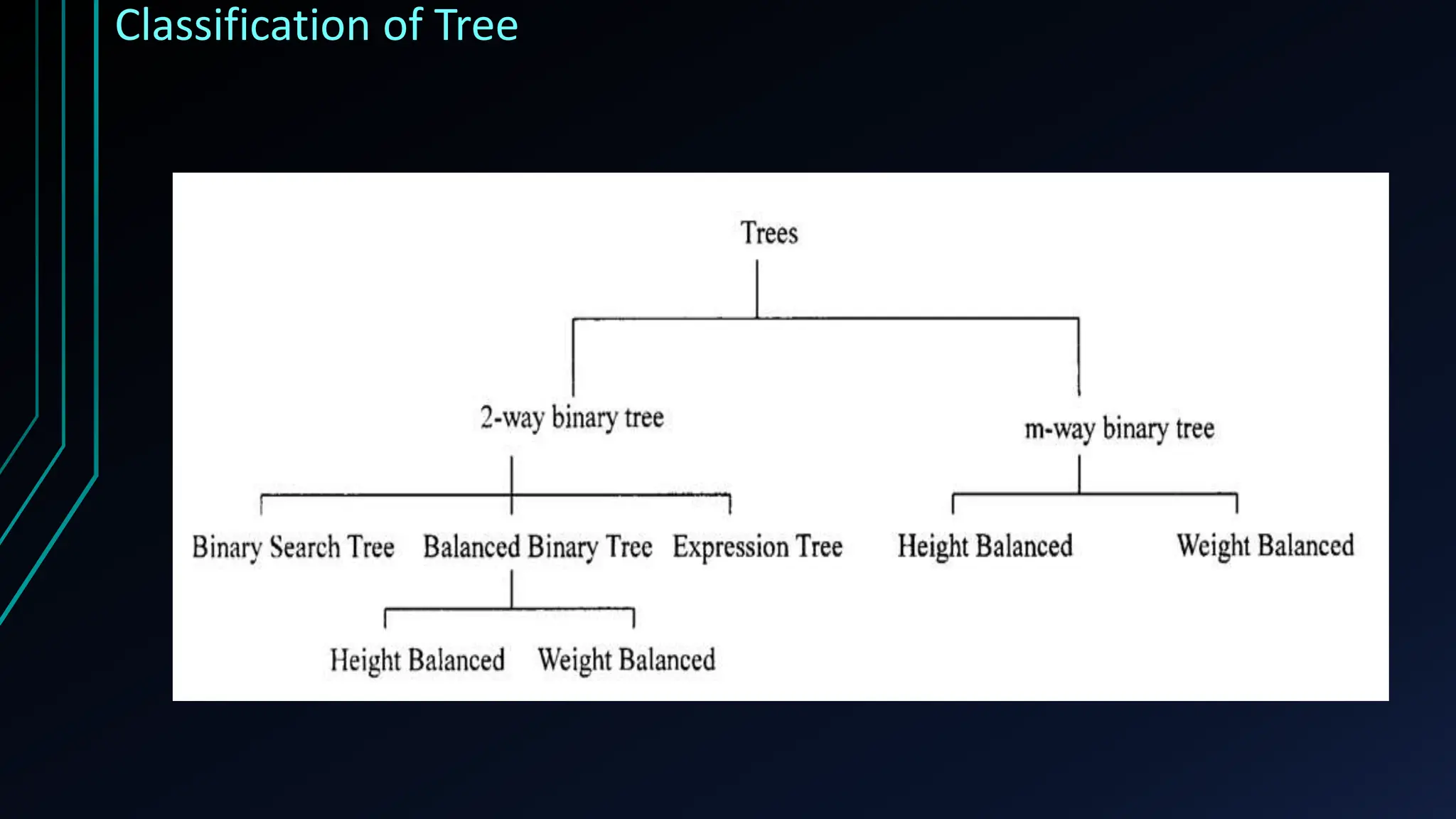
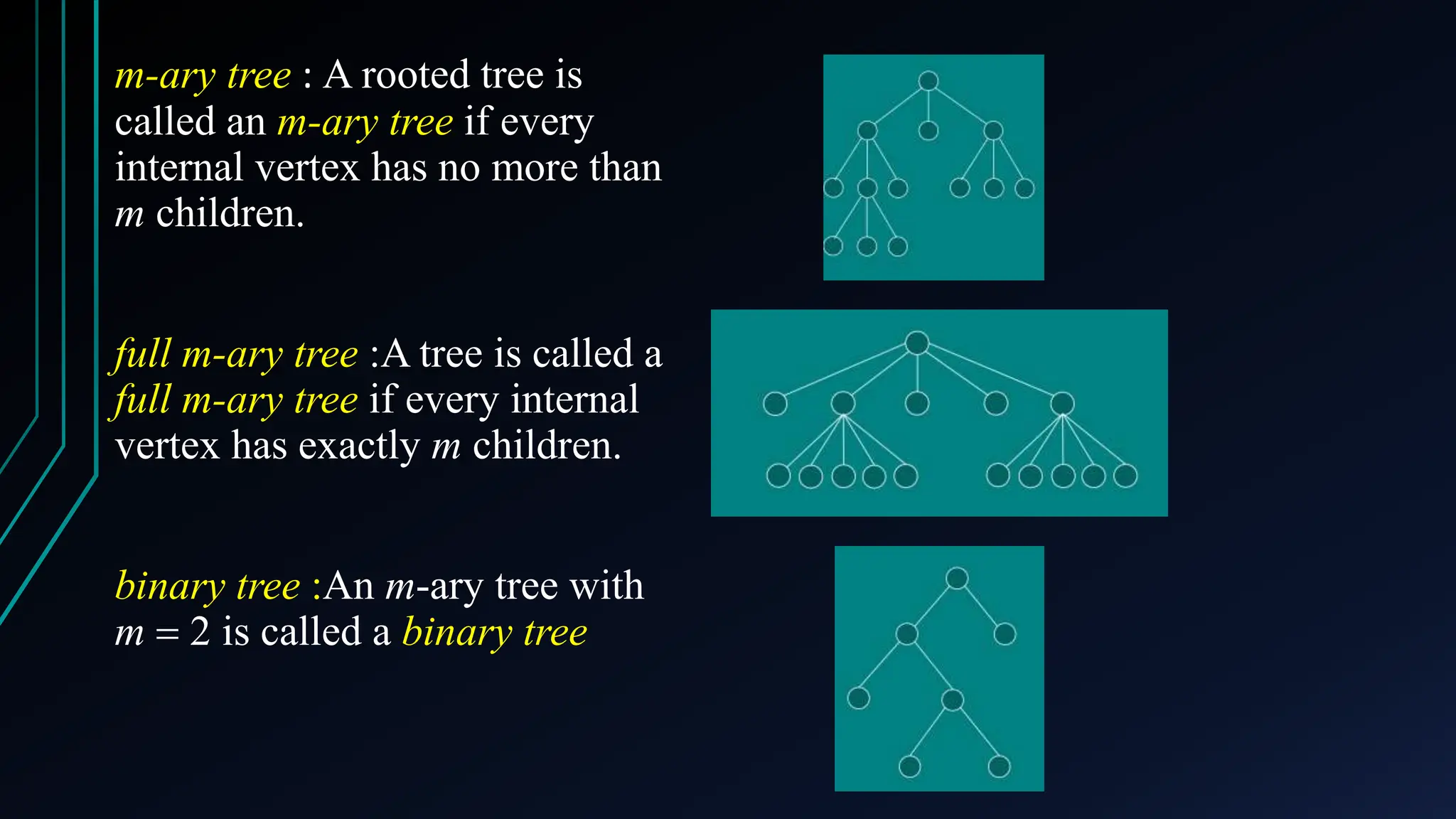
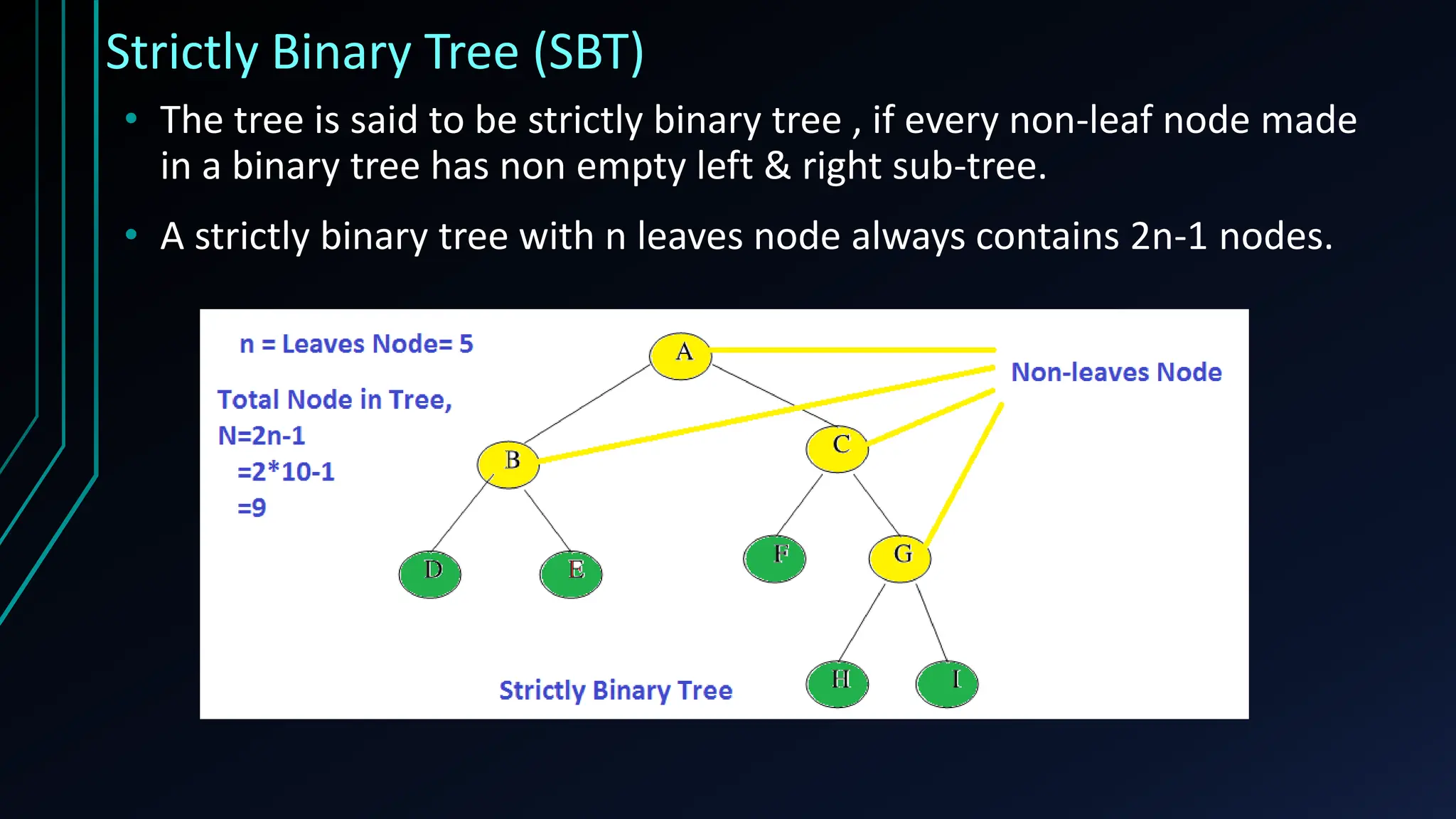
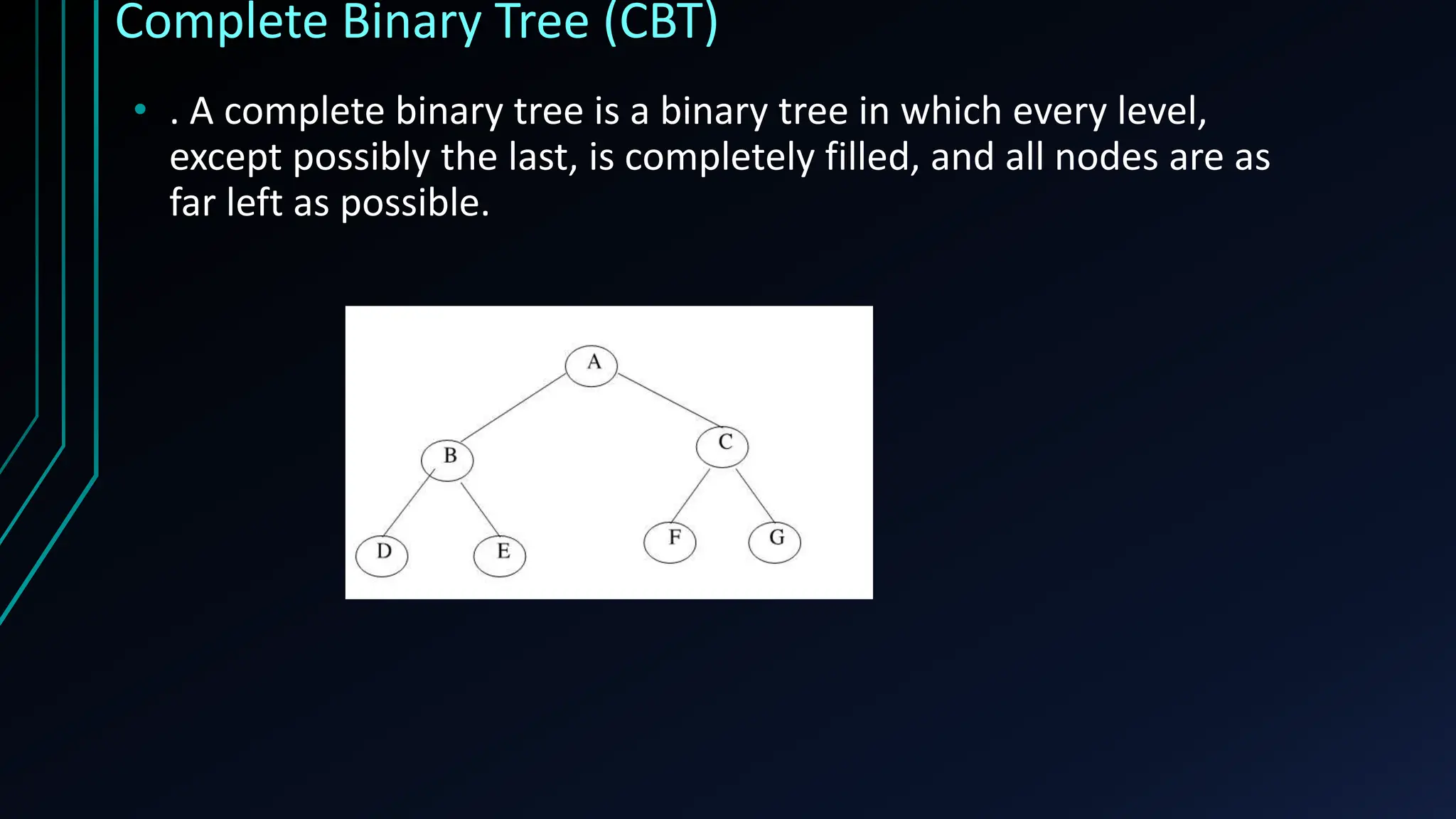
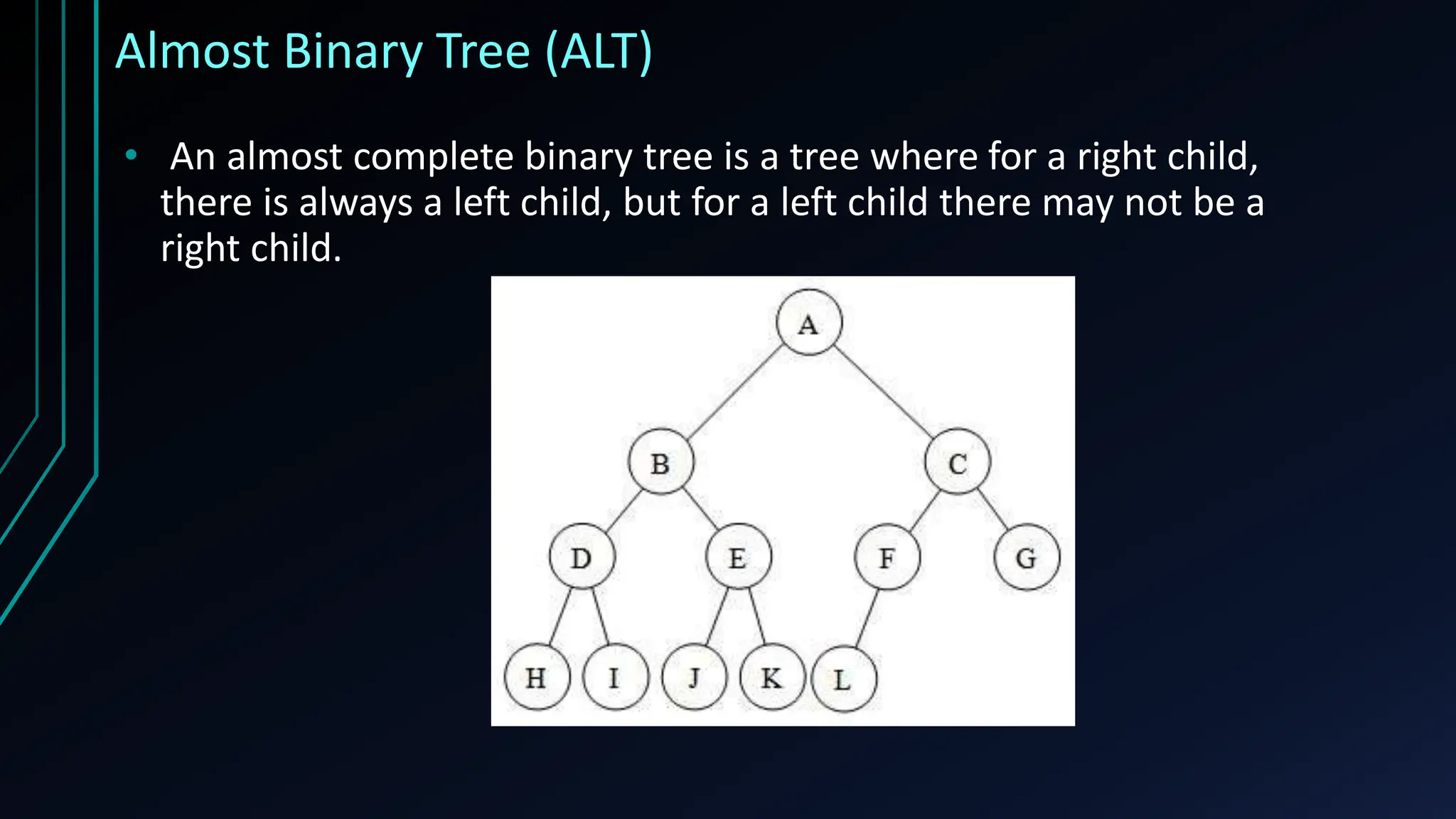
The document provides a comprehensive overview of trees in discrete mathematics, covering their definitions, basic terminology, and classifications such as m-ary, binary, and complete binary trees. It highlights key concepts like nodes, edges, depth, and height, as well as applications of trees in areas like file systems, databases, and artificial intelligence. Understanding trees is crucial for efficiently solving computational problems.