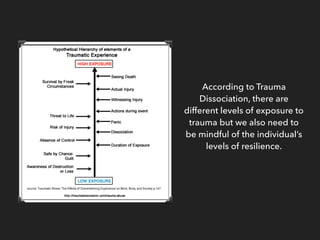
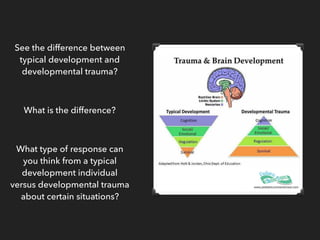
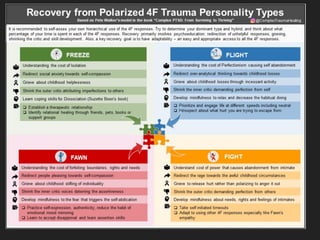
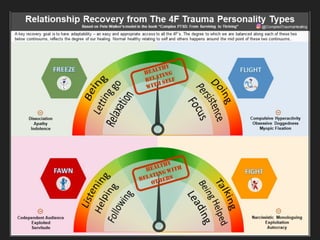
This document discusses trauma, including what causes trauma, the effects of trauma, signs of traumatic stress, and ways to cope with and heal from trauma. It defines trauma as a deeply distressing event that overwhelms one's ability to cope. It then lists and describes many different types of trauma and their potential causes. The document outlines various physical and psychological effects of trauma. It discusses triggers of traumatic stress and provides coping strategies. Finally, it discusses the journey of healing from trauma and advocacy for trauma survivors.