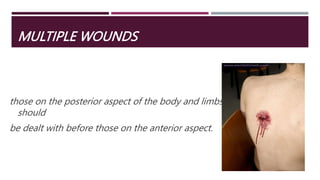
This document discusses trauma epidemiology and mechanisms of injury from various causes. It provides statistics showing that injury is a major global health problem, responsible for 16% of the disease burden worldwide. Road traffic accidents are a leading cause of death. Warfare injuries make up a significant portion of trauma and have changed over time with advances in weapons. A variety of blunt and penetrating trauma mechanisms are described, along with considerations for specific situations like explosions. Principles of management for war wounds include complete wound excision, delayed primary closure without internal fixation, use of antibiotics and tetanus prophylaxis.