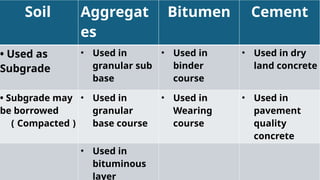
The document discusses highway materials in civil engineering, specifically focusing on desirable soil properties, index properties of soil, and methods for evaluating soil strength, including the California Bearing Ratio (CBR) test. Key factors affecting soil strength and various testing methods such as bearing, shear, and penetration tests are outlined. Additionally, the procedures for conducting the CBR test and the necessary equipment are described in detail.