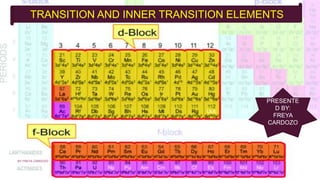
The document discusses transition elements and inner transition elements. Transition elements have an electronic configuration of (n-1)d1-10ns1-2. They are placed in periods 4 to 7 and groups 3 to 12. These constitute the 3d, 4d, 5d and 6d series. Transition elements have a partially filled d orbital in their ground state or oxidation state. Common properties of transition elements include being hard, lustrous metals with high melting points and boiling points. They often form colored compounds due to d-d electron transitions. Many transition elements act as important catalysts in chemical reactions.



















![GEOMETRY OF COMPLEX ION
When cobalt chloride (Co2⊕) is dissolved in water, it forms a pink solution of the complex
[Co(H2O)6]2⊕ which has octahedral geometry.
But when this solution is treated with concentrated hydrochloric acid, it turns deep blue.
This change is due to the formation of another complex [CoCl4]2 which has a tetrahedral structure.
BY FREYA CARDOZO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transitionandinnertransitionelements-200708043110-240210112800-3e27d667/85/transitionandinnertransitionelements-200708043110-pdf-21-320.jpg)






























![ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATION
Generally the E.C for lanthanoids is represented as [Xe] 4f0-14 5d0-1 6s2
Xe = Xenon, Z= 54
The E.C for Xe is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10
BY FREYA CARDOZO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transitionandinnertransitionelements-200708043110-240210112800-3e27d667/85/transitionandinnertransitionelements-200708043110-pdf-52-320.jpg)
![EXCEPTIONS
The electrons first fill up the 6s
4f and 5d are very close in energy
In case of lanthanum the 5d oribtal has lower energy
In case of Gd and Yb the anamolous behaviour is
observed
As half filled and fully filled electrons have extra stability
Thus general E.C for lanthanoids is [Xe] 4f0-14 5d0-1 6s2
BY FREYA CARDOZO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transitionandinnertransitionelements-200708043110-240210112800-3e27d667/85/transitionandinnertransitionelements-200708043110-pdf-53-320.jpg)


![OXIDATION STATE
G.E.C = [Xe] 4f0-14 5d0-1 6s2
thus the common O.S is +3 i.e 2 e- from 6s and the order from d/f
subshell
The 4f electrons are shielded by the inner 5s and 5p orbitals, they are
tightly bond to the nucleus. Thus they do not take part in the bonding
Some show O.S +2 and +4 this is due to f0, f7, f14 E.C
BY FREYA CARDOZO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transitionandinnertransitionelements-200708043110-240210112800-3e27d667/85/transitionandinnertransitionelements-200708043110-pdf-56-320.jpg)



![MAGNETIC MOMENT
µ=square root of n(n + 2) BM
n = no.of unpaired ELECTRONS
Calculate magnetic moment for La3+
La -57
[Xe]4f05d16s2 n=1
Magnetic moment
BY FREYA CARDOZO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transitionandinnertransitionelements-200708043110-240210112800-3e27d667/85/transitionandinnertransitionelements-200708043110-pdf-60-320.jpg)


![ACTINOIDS
Starts with Thorium Z=90 and ends with Lawrencium Z=103
They are all radioactive and man-made
High M.P, B.P, density
The electronic configuration of actinoids is
[Rn] 5f0-14 6d0-2 7s2, where Rn is the electronic
configuration of radon.
most stable oxidation state in actinoids
is +3. The highest however actinoids show a variety of O.S from +2 to +8
BY FREYA CARDOZO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transitionandinnertransitionelements-200708043110-240210112800-3e27d667/85/transitionandinnertransitionelements-200708043110-pdf-63-320.jpg)

![OXIDATION STATE
Early lanthanoids show variable O.S this is similar to transition
elements than lanthanoids
This pattern is seen mostly due to the ability of 5f orbital to
participate in bonding
A ready loss of 5f electrons by early actinoids indicates that these
electrons are much closer in energy to 7s and 6d electrons than
the 4f electrons to 6s and 5d electrons as in lanthanoids
G.E.C [Rn] 5f0-14 6d0-2 7s2
Eg. uranium has electronic configuration of [Rn]7s2 5f 36d1. The
formation of +6 oxidation state corresponds to an electronic
configuration of [Rn].
BY FREYA CARDOZO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transitionandinnertransitionelements-200708043110-240210112800-3e27d667/85/transitionandinnertransitionelements-200708043110-pdf-65-320.jpg)
























