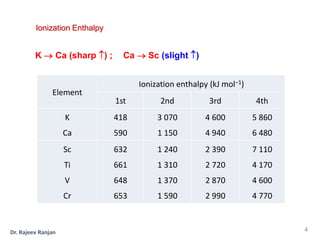
This document summarizes ionization enthalpy trends across the transition elements. It notes that:
1) The first ionization enthalpies of d-block elements are greater than s-block elements in the same period, due to their smaller size and greater effective nuclear charge.
2) There is a sharp increase in ionization enthalpy across periods but only a slight increase across each transition series, as additional 3d electrons screen the nuclear charge felt by 4s electrons.
3) Successive ionization enthalpies show a gradual increase across each transition series because the 4s and 3d energy levels are close in energy.