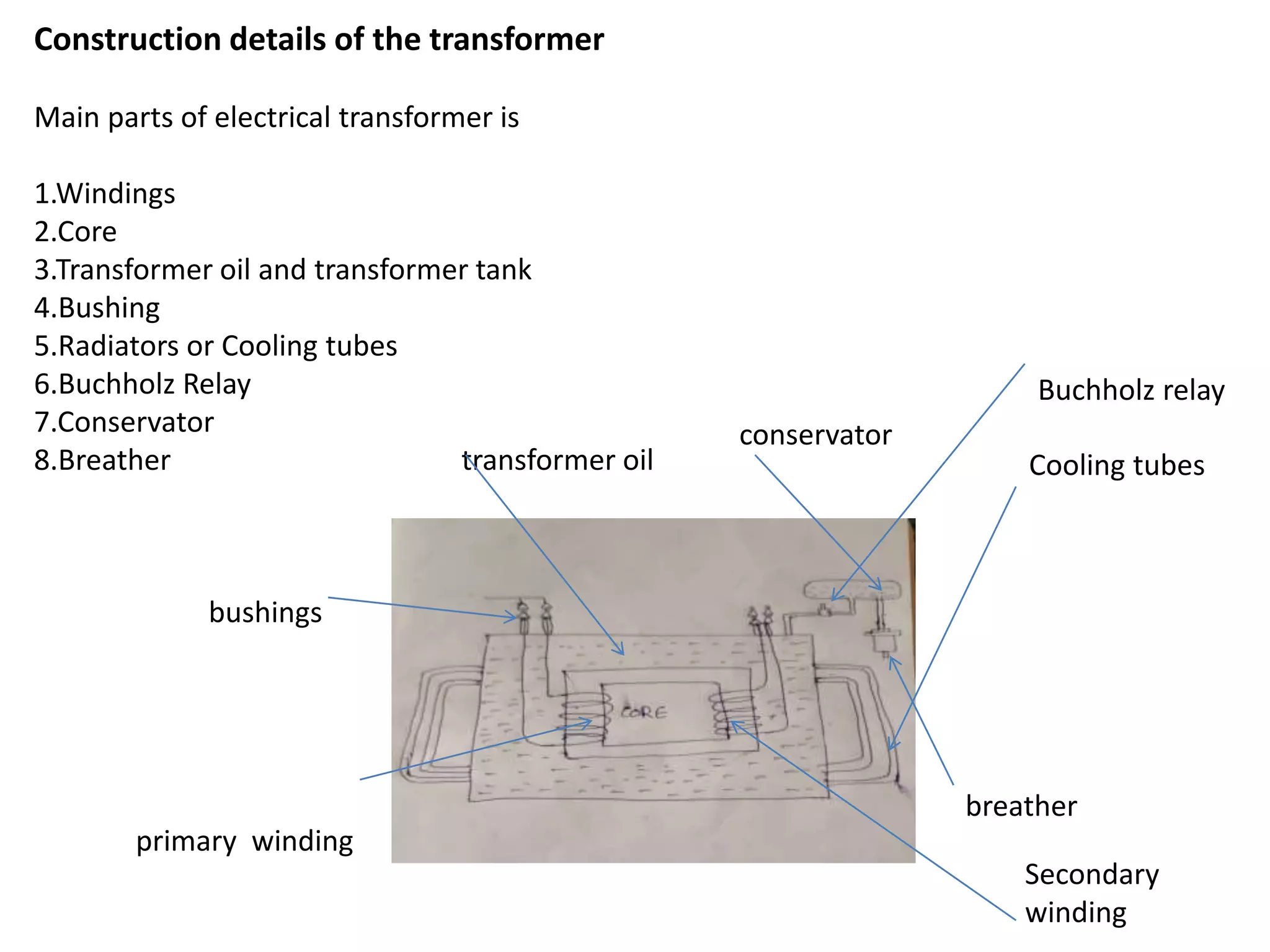
The document summarizes the main parts and construction details of a transformer. It describes the key components as the primary and secondary windings wound around the laminated silicon steel core, the transformer oil and tank that provide insulation and cooling, and protective devices like the Buchholz relay, conservator, and breather. It explains that the transformer works on the principles of electromagnetic induction and mutual induction to induce an alternating current in the secondary winding from the primary winding based on the alternating flux in the core.