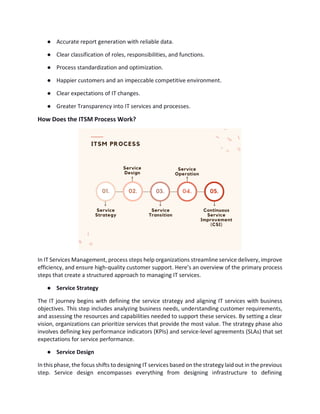
Discover essential practices to streamline workflows, enhance service delivery, and boost operational efficiency. From incident management to automation, this guide covers everything you need to elevate IT performance. For more details, please read the full document.