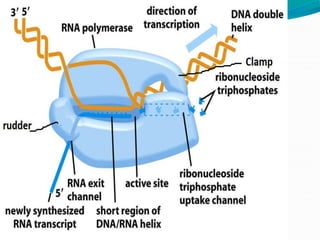
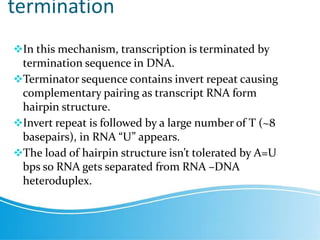
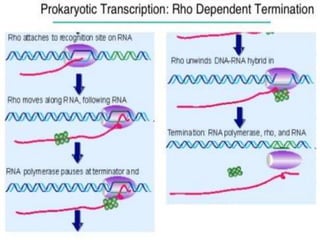
Transcription in prokaryotes involves the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template, occurring through initiation, elongation, and termination. Key components include bacterial RNA polymerase and the processes of rho-independent and rho-dependent termination. The document also highlights proofreading mechanisms and the simultaneous occurrence of transcription and translation in bacteria.