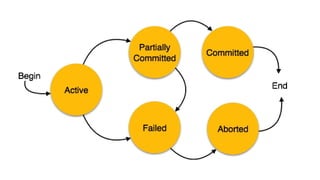
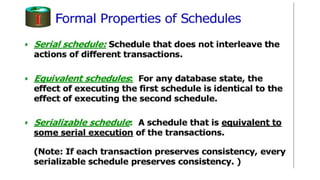
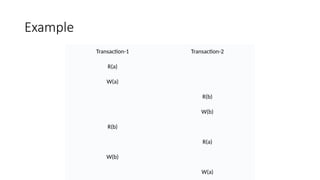
The document discusses the concepts of transaction schedules in databases, distinguishing between complete (serial) and non-serial (interleaved) schedules, and the importance of serializability for ensuring consistency. It highlights conflicts that arise from interleaved transaction executions, such as write-read, read-write, and write-write conflicts. Additionally, it elaborates on concurrency control techniques, including locking protocols, specifically two-phase locking, and timestamp ordering to manage these transactions effectively.