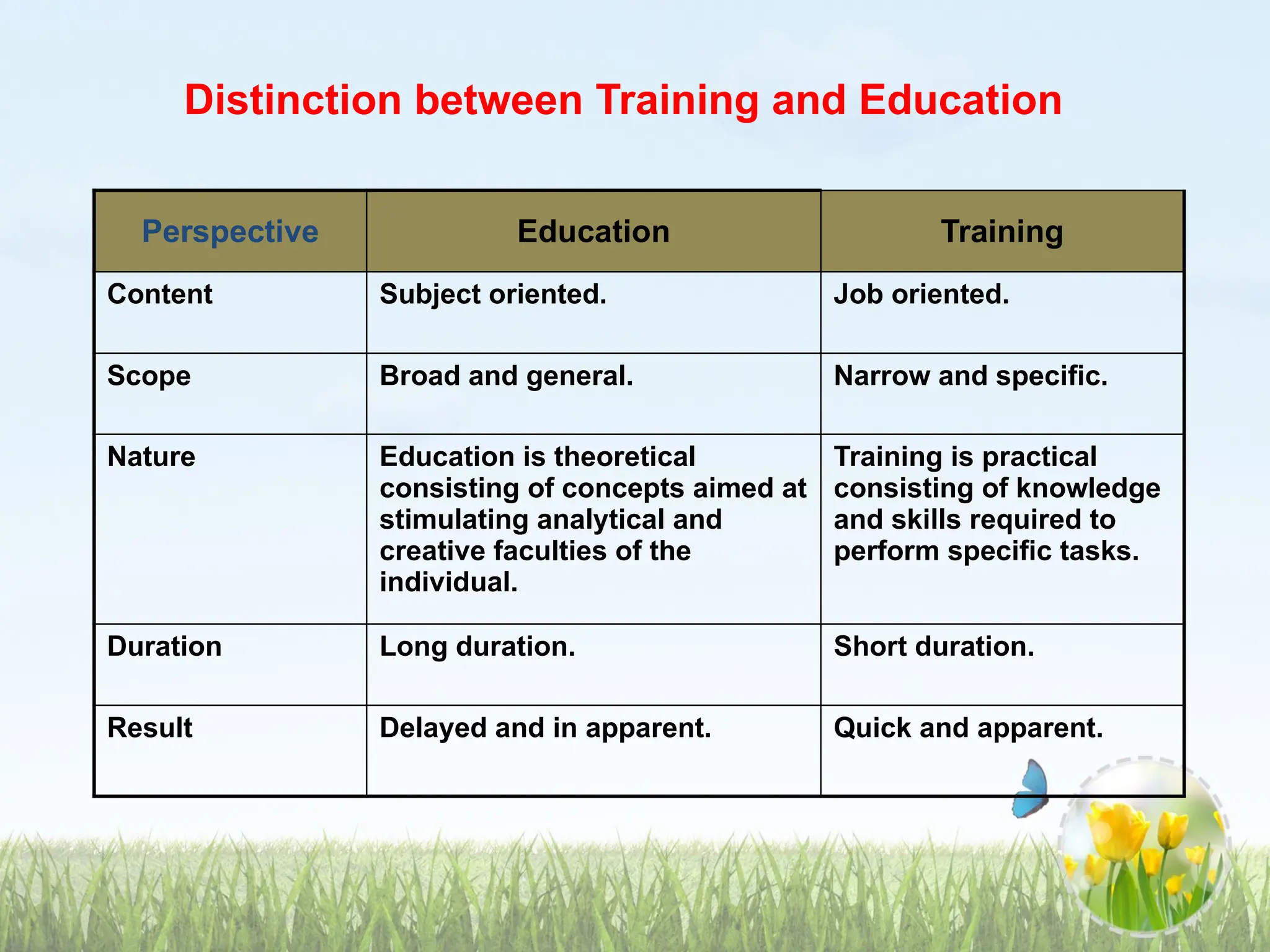
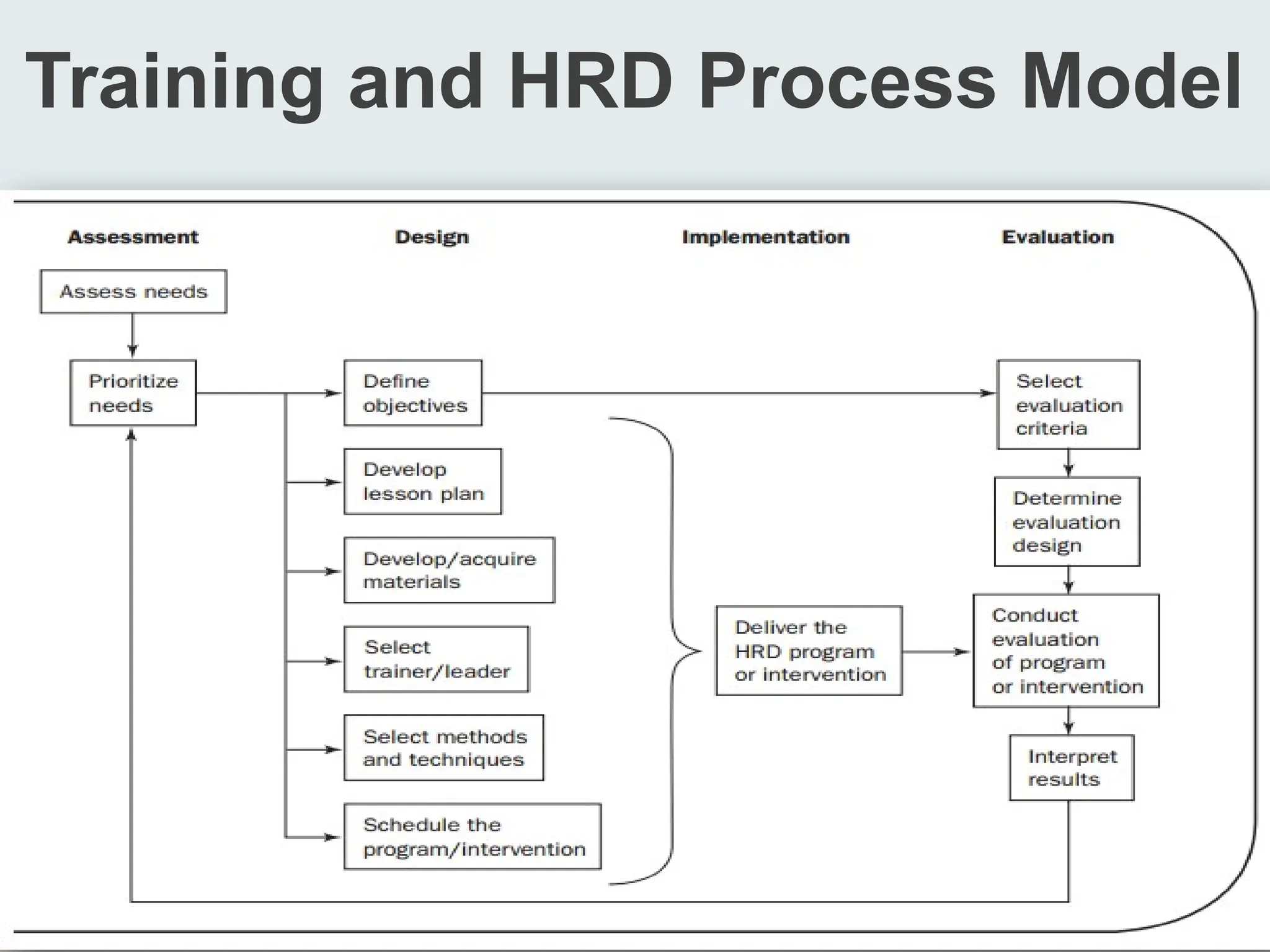
The document discusses the distinctions between training and education, highlighting that training targets job-related competencies while development aims to enhance overall individual capabilities for future roles. It emphasizes the importance of understanding adult learning principles, advocating for participatory and relevant teaching methods tailored to adult learners' experiences and needs. The document contrasts pedagogy with andragogy, stressing the necessity for a more flexible and respectful approach in adult education.