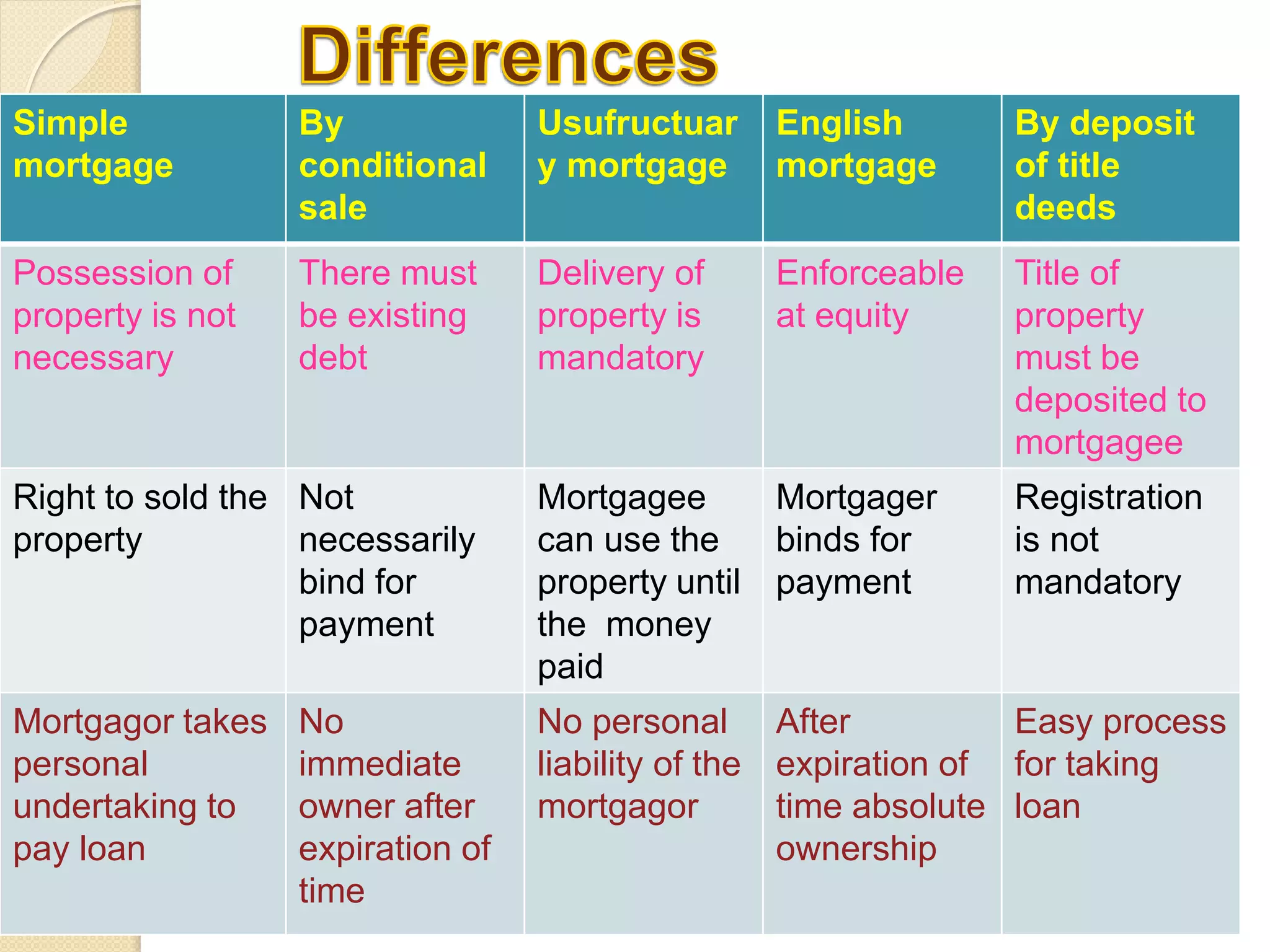
Mortgage is the transfer of an interest in specific immovable property for the purpose of securing the payment of money advance or to be advance by the way of loan, an existing or future debt or the performance of an engagement which may give rise to a pecuniary liability. Section 58 of the Transfer of Property Act defines different types of mortgages - simple mortgage, mortgage by conditional sale, usufructuary mortgage, English mortgage, mortgage by deposit of title deeds, and anomalous mortgage. The essential characteristics of each type of mortgage include the rights and obligations of the mortgagor and mortgagee with respect to possession and use of the property, personal liability for payment, and procedures for sale or return of the property