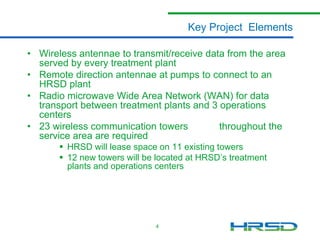
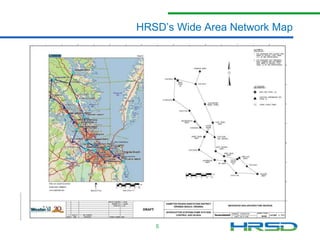
HRSD needs to upgrade its aging analog network to remotely operate and control over 120 pump stations and treatment plants across its 3,100 square mile service area. The Smart Sewer Project will install a wireless network with antennae at pump stations and treatment plants to transmit data, as well as 23 communication towers - 11 on existing towers and 12 new towers. This will allow HRSD to reduce sewer overflows and meet regulatory requirements. Entering a public-private partnership will construct the towers at a savings of $2-3 million, and colocating wireless carriers will further offset costs to ratepayers.