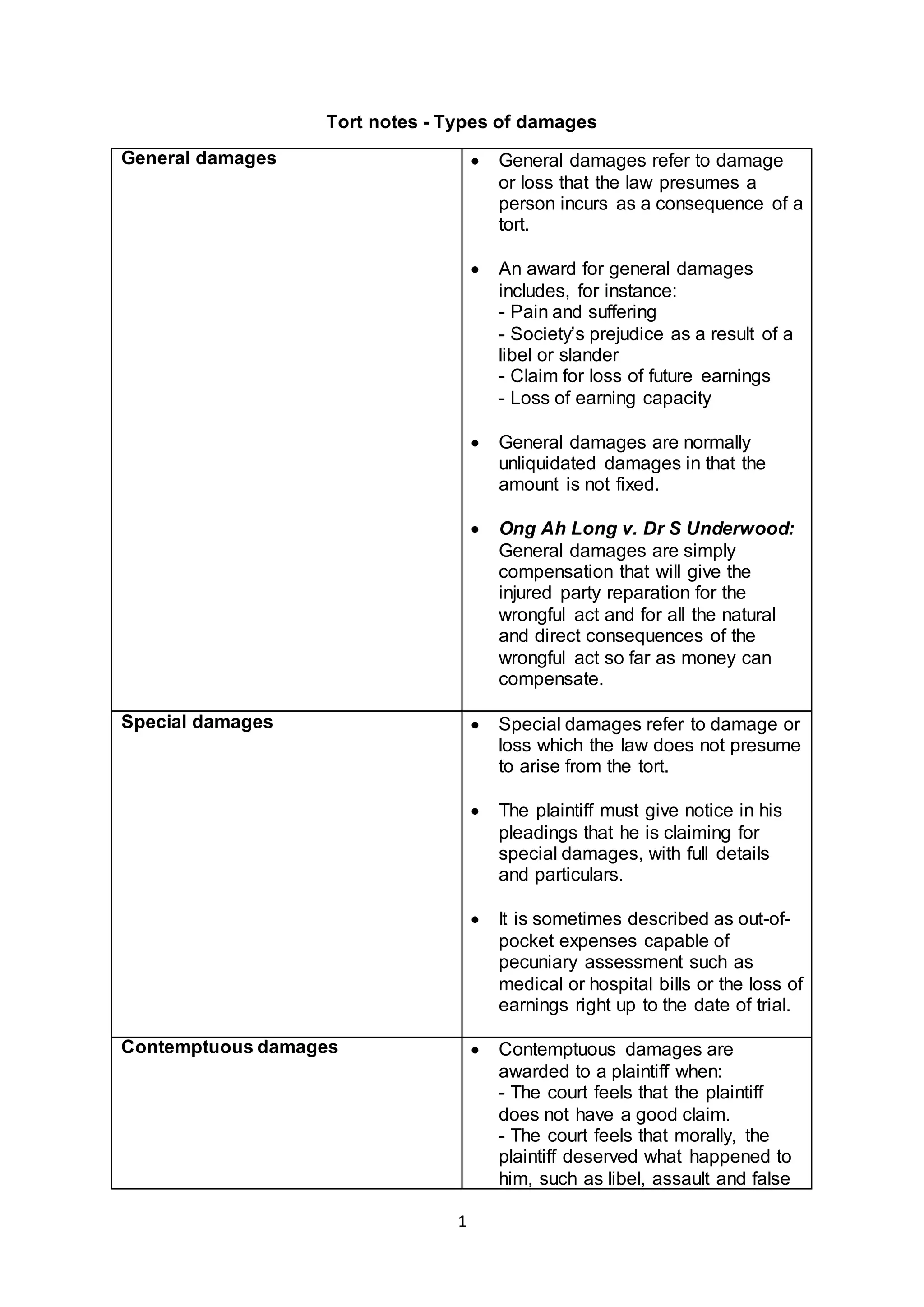
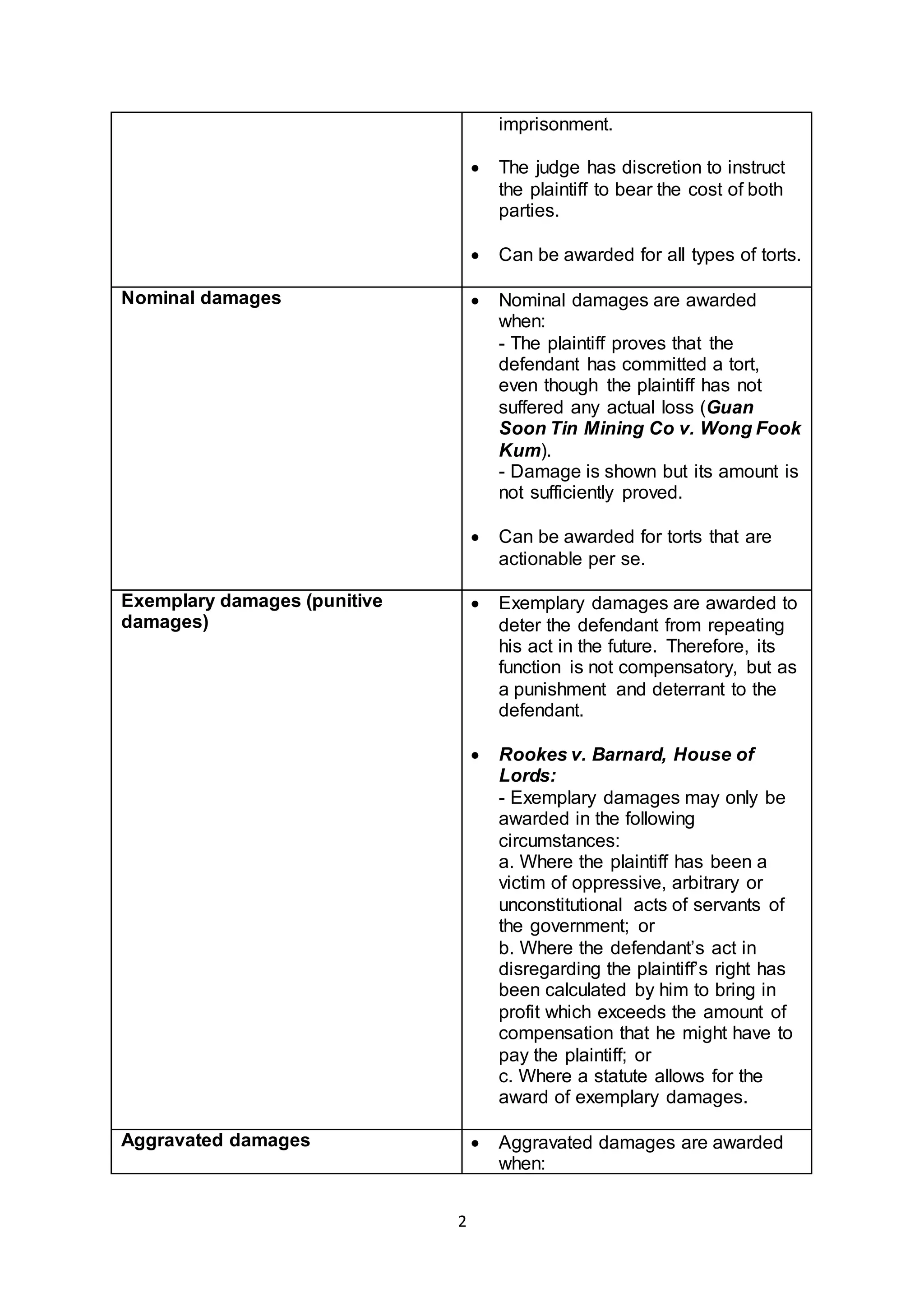
There are several types of damages that can be awarded in tort cases:
General damages are presumed to arise from the tort and include pain and suffering, loss of future earnings, and loss of earning capacity. Special damages are out-of-pocket expenses like medical bills that must be specifically pleaded. Contemptuous damages are awarded when the plaintiff does not have a good claim or deserved what happened. Nominal damages are awarded when the tort is proven but no actual loss is shown. Exemplary damages punish and deter wrongful behavior, while aggravated damages provide additional compensation beyond general damages for injuries like damage to reputation.