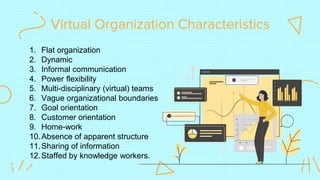
A virtual organization is a temporary or permanent collection of geographically dispersed individuals, groups, or organizations that use electronic means to collaborate to achieve common goals. Key characteristics include flat structures, informal communication, shared goals and information, and staff composed of knowledge workers. Virtual organizations can range from telecommuters to outsourcing to completely virtual. They act as boundaryless, networked organizations enabled by information and communication technologies.