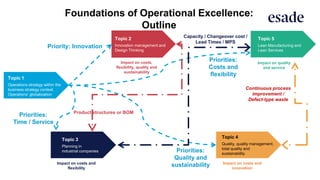
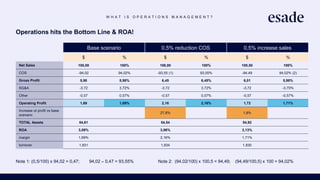
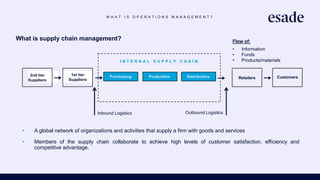
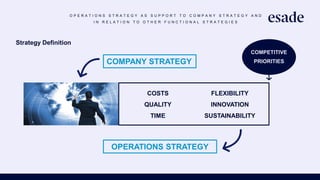
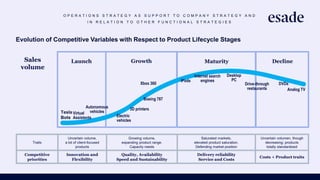
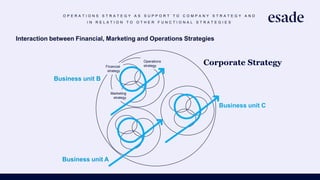
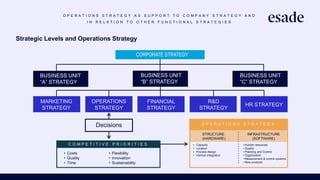
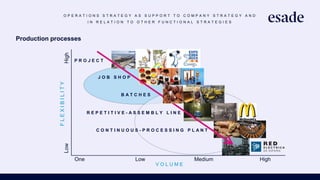
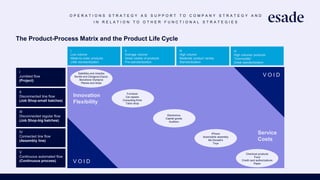
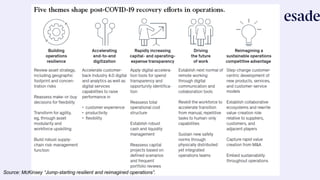
The document discusses operations strategy and its relationship to overall corporate strategy. It defines operations strategy as decisions about structural and infrastructural elements that support the company's competitive strategy. Operations strategy priorities like costs, quality, time, flexibility, and innovation help determine competitive advantage. It also discusses how operations strategy interacts with and supports marketing and financial strategies, and how the priorities evolve over a product lifecycle from launch to growth, maturity, and decline.