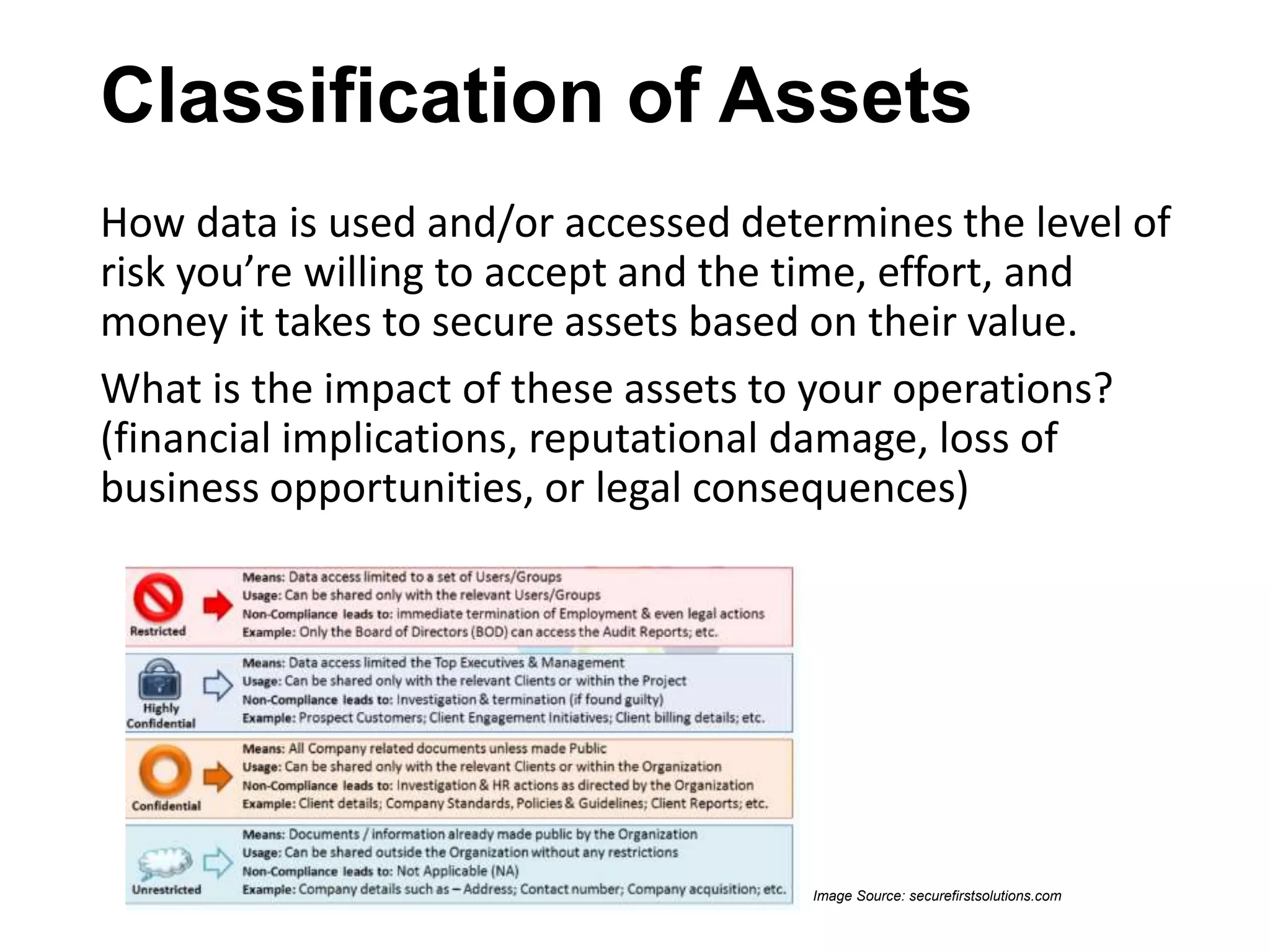
The document outlines strategies for small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) to protect against cyber threats, emphasizing the prevalence of attacks targeting these businesses. It covers common types of cyberattacks and preventative measures, including risk management, employee training, and the implementation of security technologies. The importance of vendor assessment and understanding third-party risks is highlighted, alongside real-world case studies demonstrating the consequences of ineffective cybersecurity.