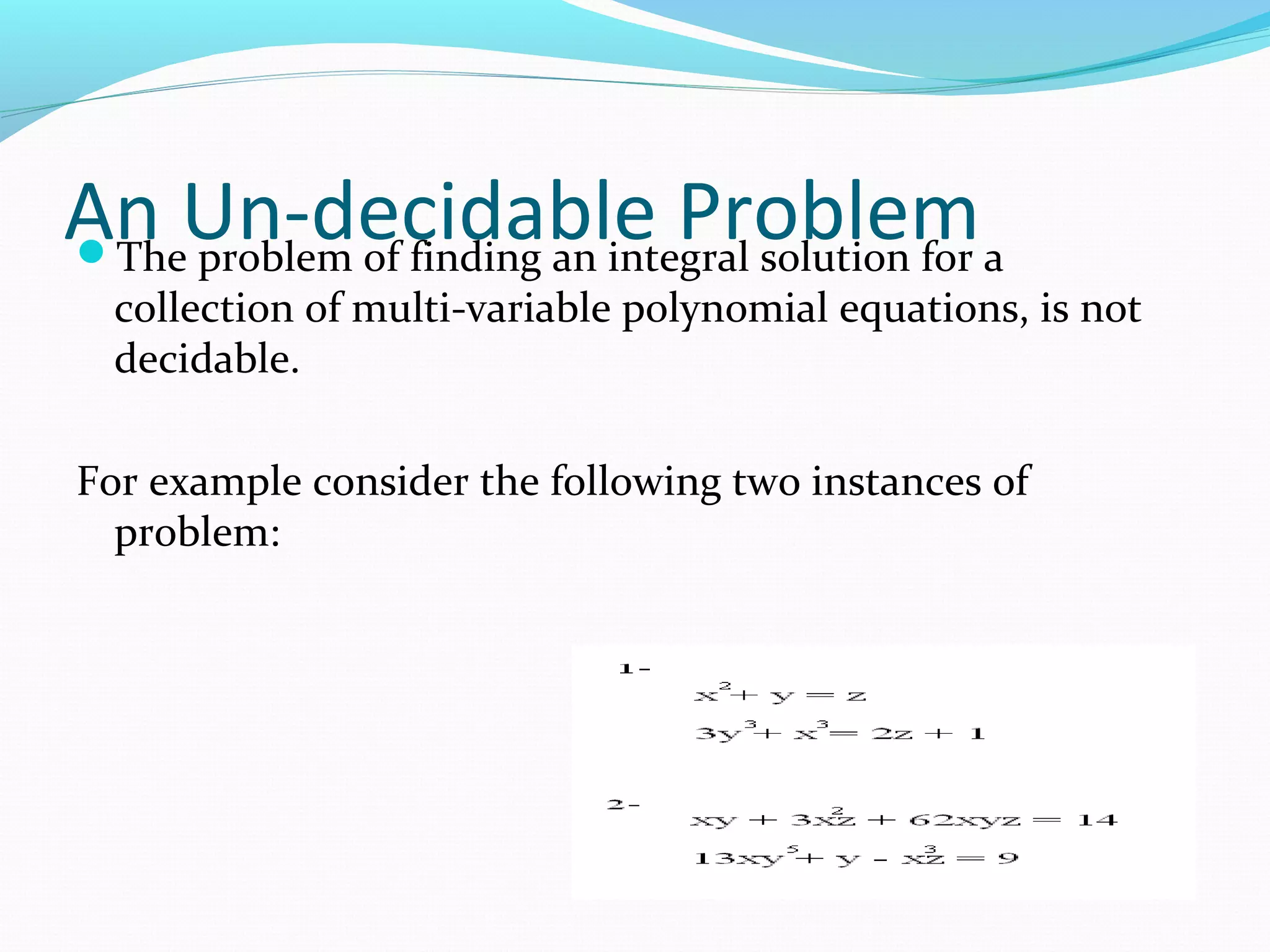
Computation involves any type of information processing that can be represented as an algorithm. An algorithm is a finite sequence of simple instructions that is guaranteed to halt in a finite amount of time. However, this definition is abstract as it does not specify the nature of the instructions or the entity executing them. Some problems cannot be solved algorithmically as there is no program that can provide answers for all possible instances of the problem within a finite time period; these are called undecidable problems. Finding integral solutions to collections of polynomial equations is an example of an undecidable problem.