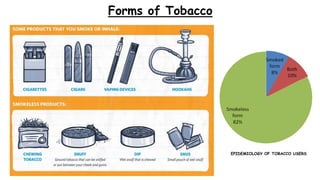
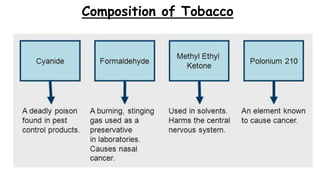
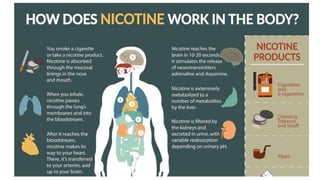
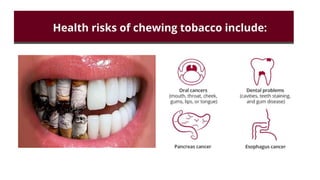
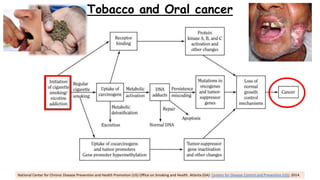
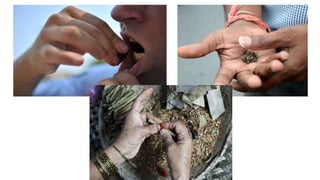
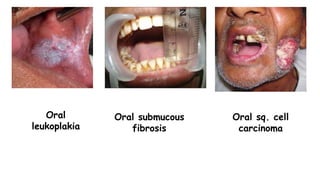
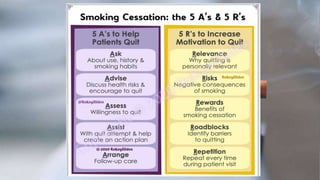
Tobacco use is the world's single greatest preventable cause of death according to the WHO. Nearly 267 million adults in India, approximately 29% of all adults, use tobacco according to a 2016-17 survey. Tobacco can be consumed in various forms like cigarettes and smokeless forms. The Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products Act of 2003 was enacted in India to discourage tobacco consumption and the National Tobacco Control Programme was launched in 2007 with the aims of creating awareness of tobacco's harms and reducing tobacco production and supply.