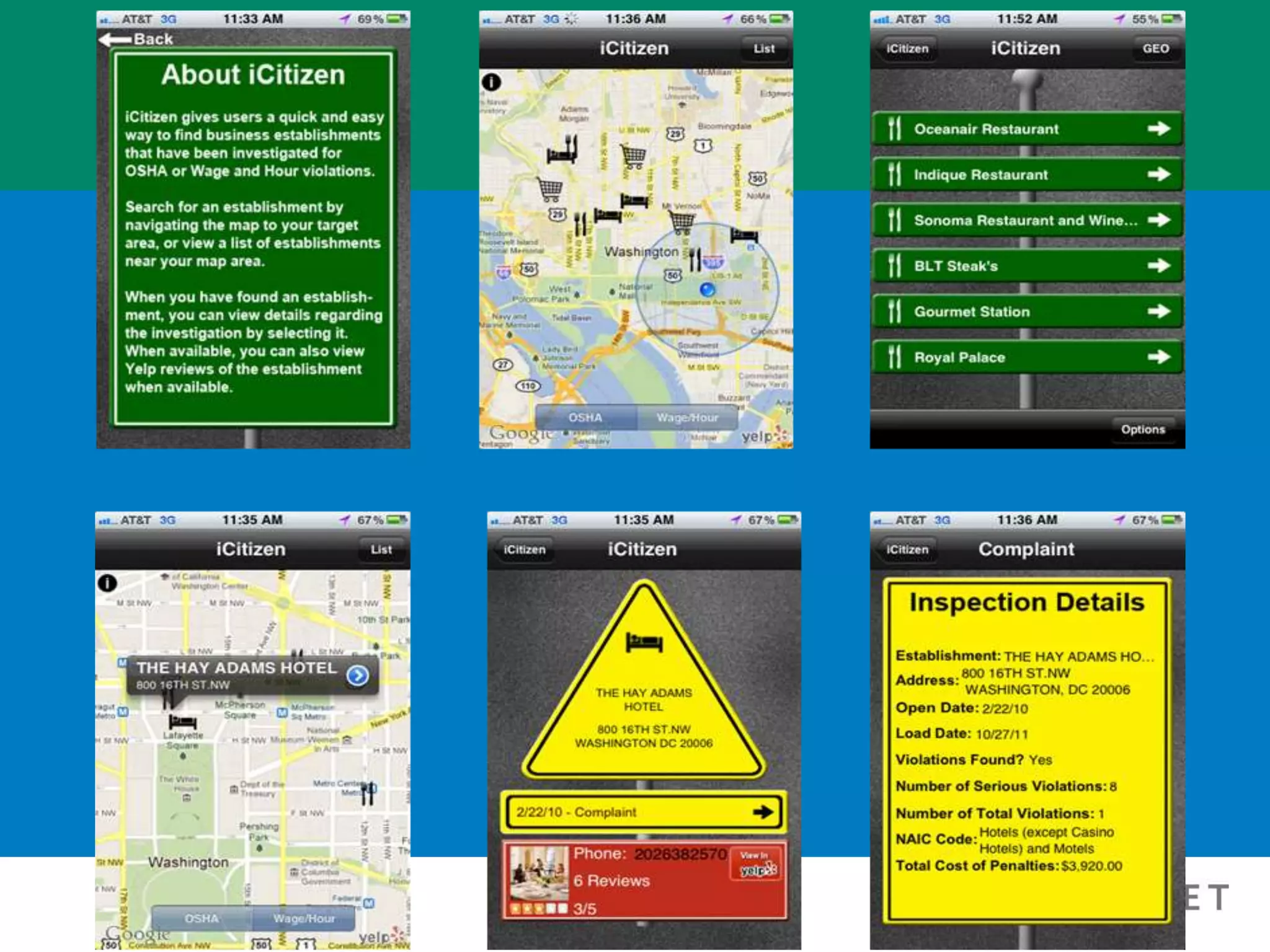
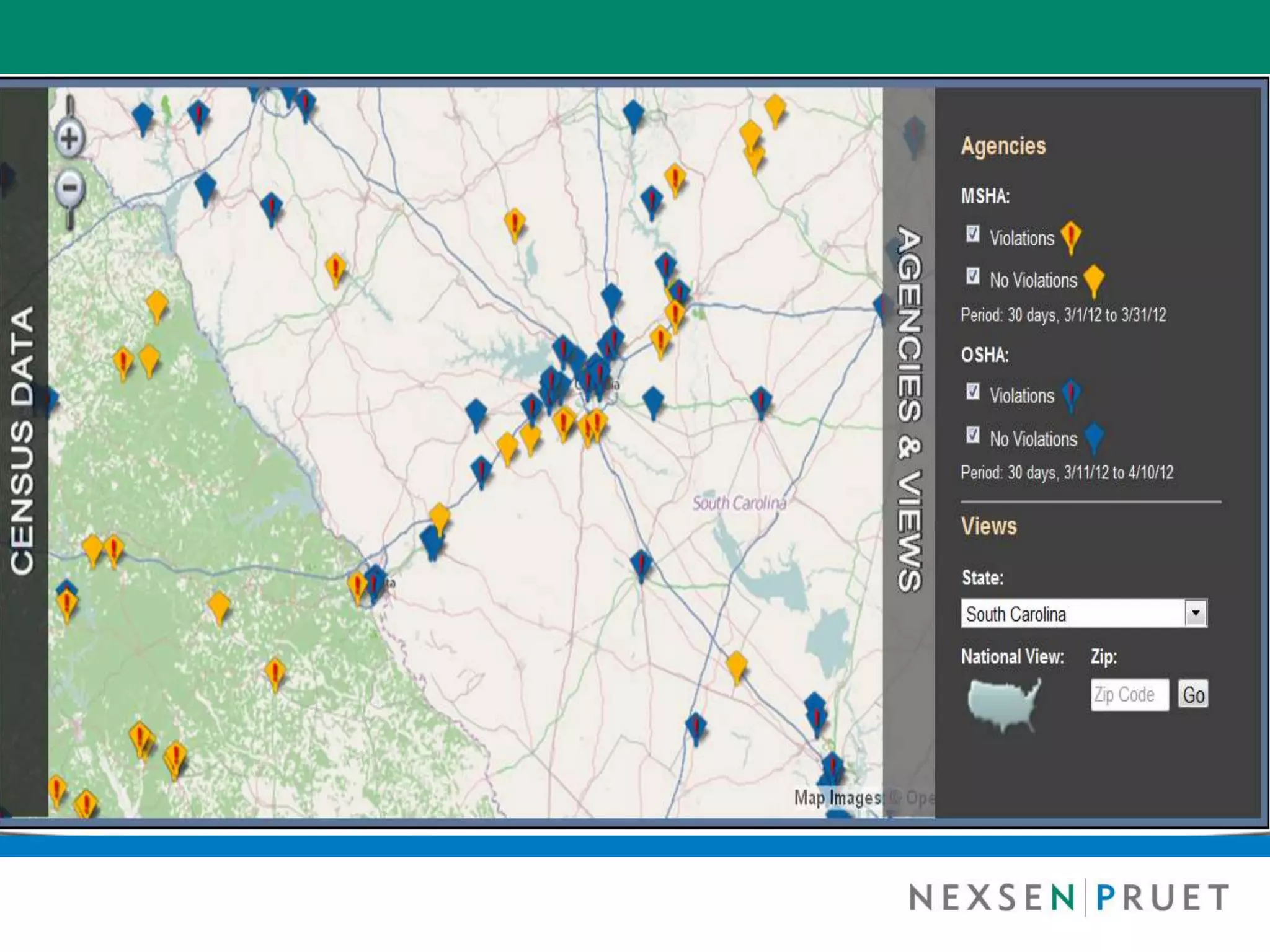
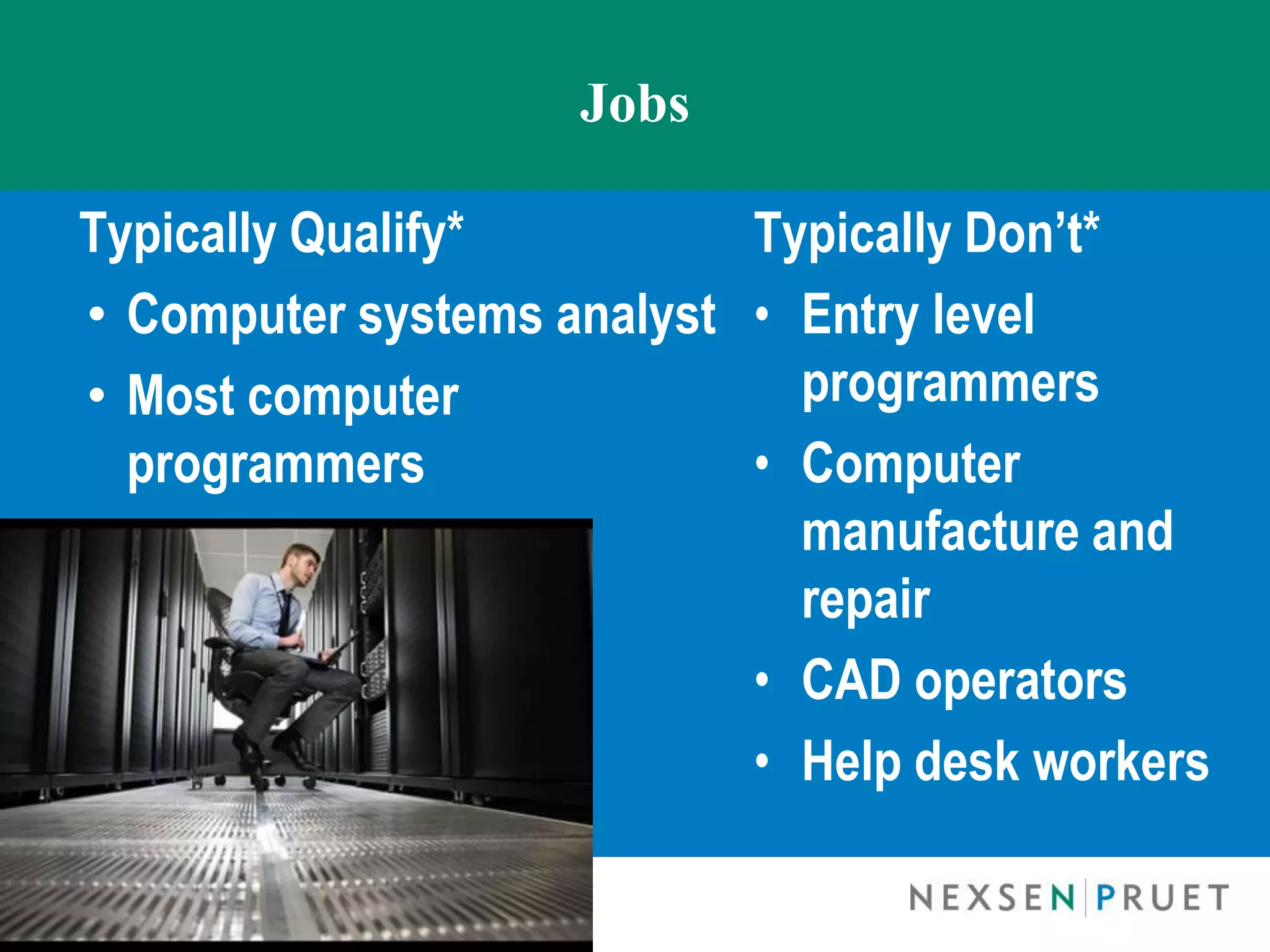
This summary discusses the key points from a presentation on exemptions under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). The presentation covered:
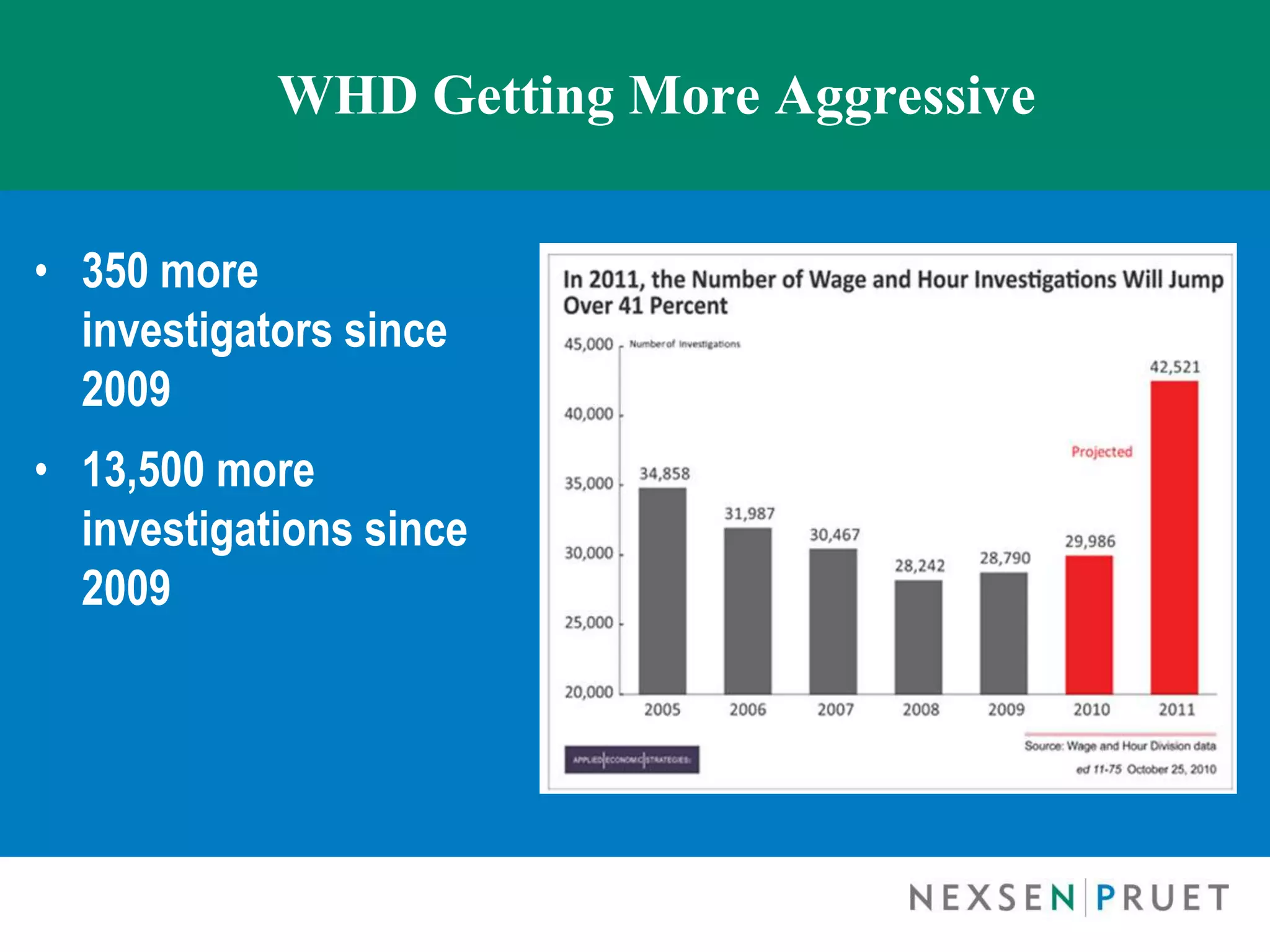
- Trends in FLSA enforcement by the Department of Labor including more investigations.
- The exemptions for executive, administrative, professional, computer, and sales employees and the salary and duties tests for each.
- Common mistakes made by employers around misclassifying employees and improper salary deductions.
- Recent court cases related to applying the exemptions.

![A Dramatic Question
“To be [exempt] or not to be [exempt], that is
the question [for HR Managers].”
[With apologies to] William Shakespeare](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/columbiashrm-flsa-tobeexemptornot-120420115718-phpapp01/75/FLSA-Exempt-or-Not-Exempt-That-is-the-Question-2-2048.jpg)