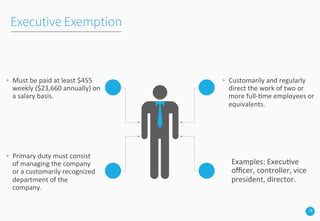
The webinar presented by Jason Zaun focuses on the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) and the distinctions between exempt and non-exempt employees, as well as their rights concerning minimum wage, overtime pay, and penalties for violations. Key topics include salary basis requirements, specific exemptions, compensable time, and common employer mistakes related to FLSA compliance. The presentation aims to educate businesses on human resources trends and best practices to meet legal standards and support workforce management.
![[Webinar] “Exempt vs. Non-Exempt”
Presented
By
Jason
Zaun
of
BeyondPay](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flsawebinar-final-151022164829-lva1-app6891/85/FLSA-Exempt-vs-Non-Exempt-1-320.jpg)