This document introduces FreeNAS 8.3, an open source network attached storage operating system based on FreeBSD. Some key points:
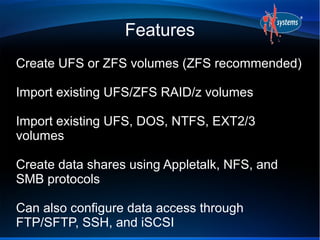
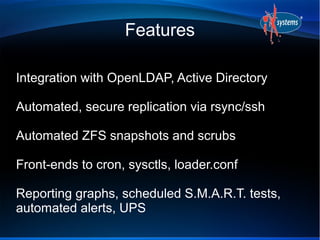
- FreeNAS uses ZFS for its filesystem and supports features like deduplication, RAIDZ3, and snapshots.
- Version 8.3 introduces ZFSv28 which adds new features like deduplication.
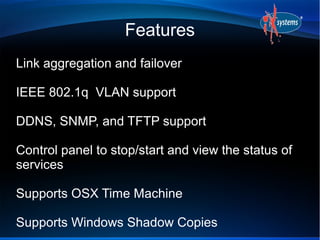
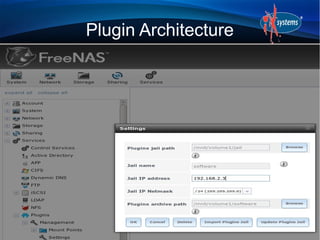
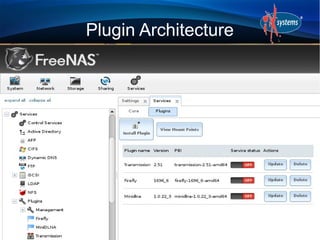
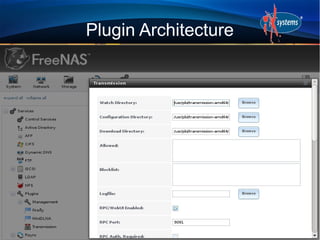
- FreeNAS can be extended through a plugin architecture, with plugins packaged using the PBI format and configurable through the GUI.
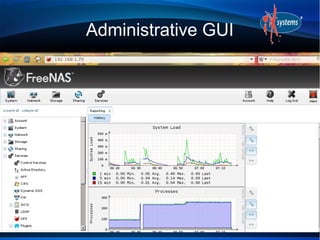
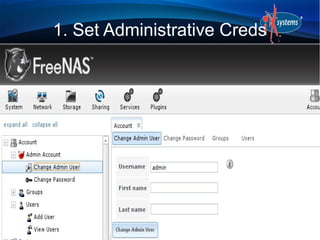
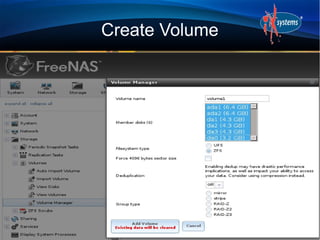
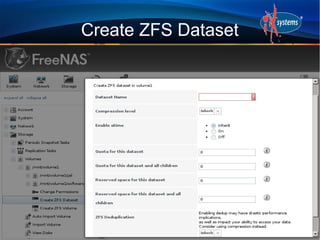
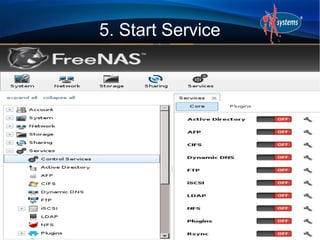
- The configuration workflow involves setting credentials, creating volumes/datasets, configuring users/groups, sharing data, and starting services.