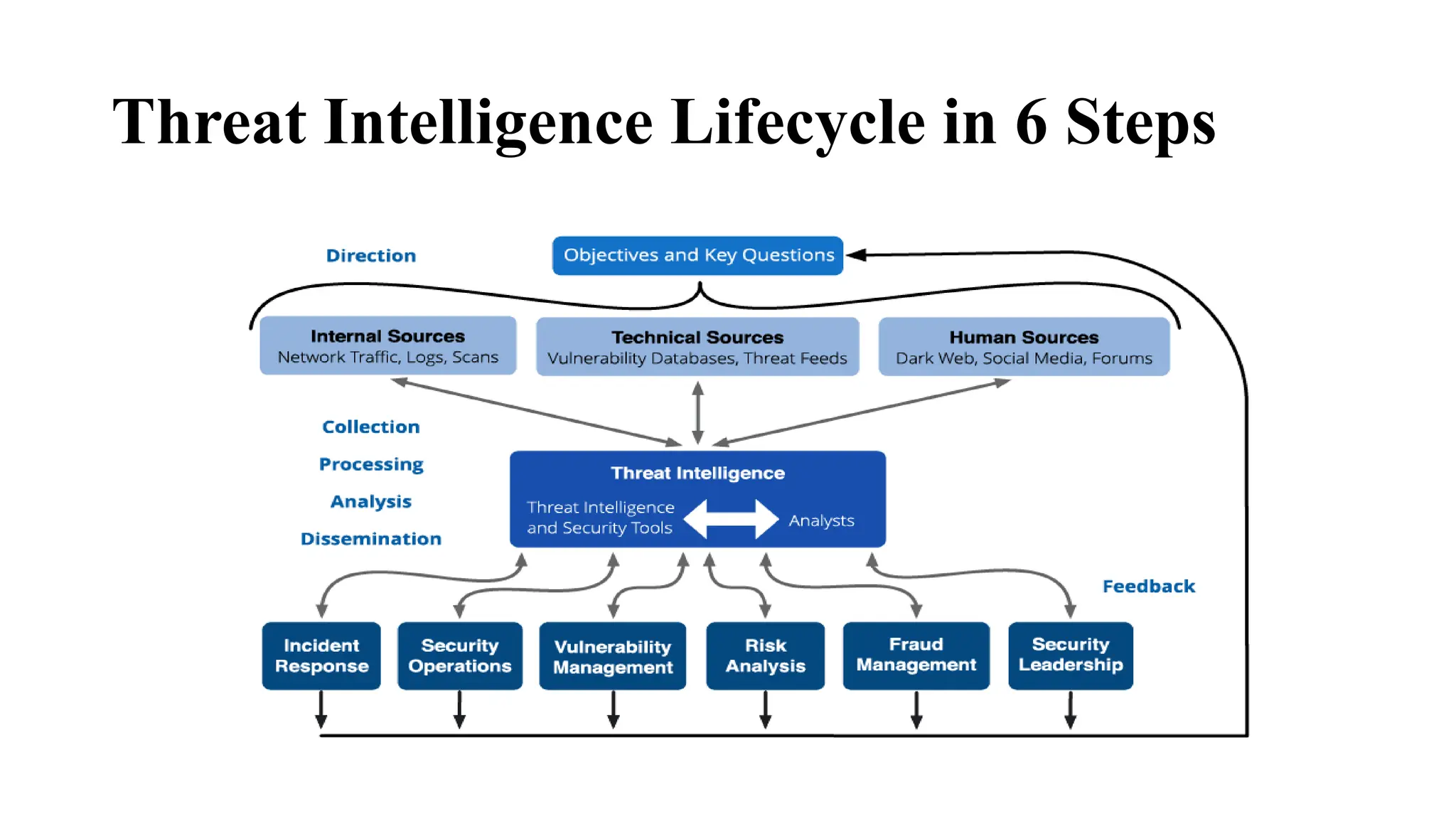
The document describes the threat intelligence lifecycle process, which consists of 6 steps: direction, collection, processing, analysis, dissemination, and feedback. It provides details on the activities involved in each step, including determining intelligence needs, gathering information from various sources, processing raw data, analyzing the data to create useful intelligence, distributing the intelligence to relevant teams, and getting feedback to continually improve the process. The lifecycle aims to help security teams better understand threats and generate actionable intelligence to strengthen defenses.