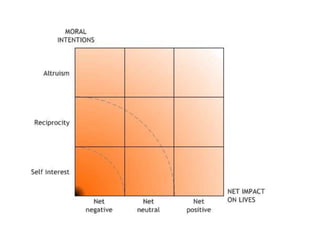
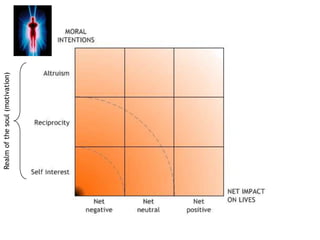
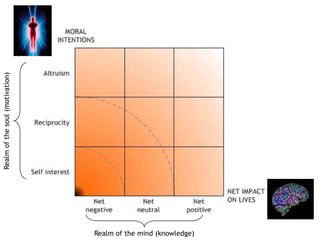
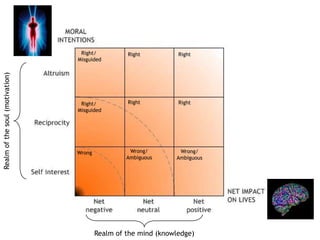
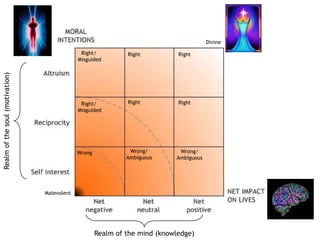
The theory of morality posits that moral judgments are formed by evaluating the motivations and impacts of behaviors through our conscience. It highlights the complexity of moral assessments due to paradoxical interactions and incomplete information that lead to subjective decision-making without absolutes. Lastly, it emphasizes the importance of awareness of consequences and interconnectedness in moral reasoning to foster a cycle of good actions.