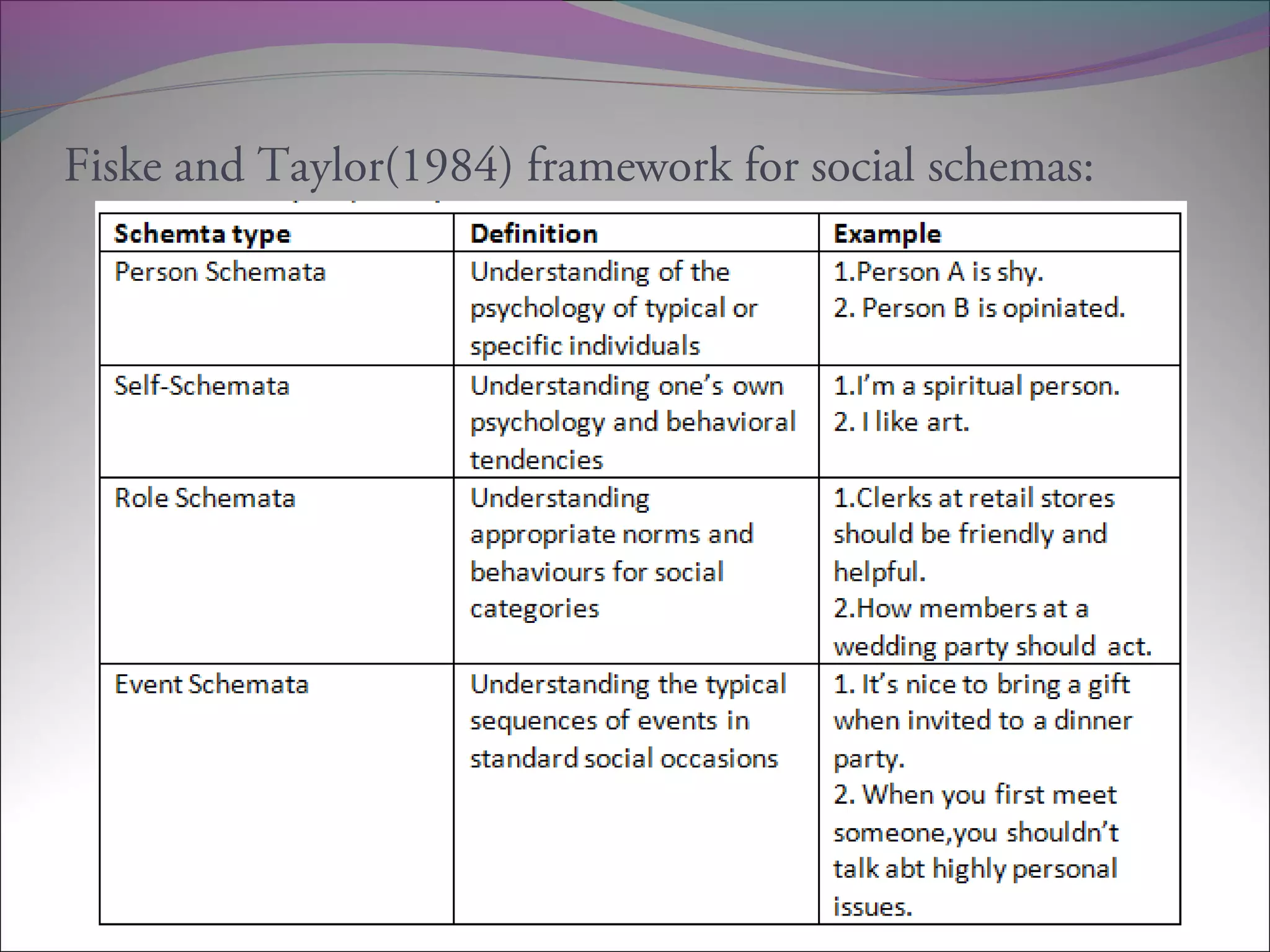
This document discusses several theories related to cognitive psychology and communication. It begins by defining schema theory, which proposes that people organize information into mental frameworks called schemas. It then discusses how schemas provide ways to make sense of information and interact with others. The document next covers attribution theory, which aims to explain the causes of behavior, and narrative theory, which relates to how storytelling shapes human thought. It concludes by summarizing Kenneth Burke's dramatism theory, which views life as a drama and analyzes human motivation and relationships using concepts like identification, the dramatistic pentad, and guilt redemption.