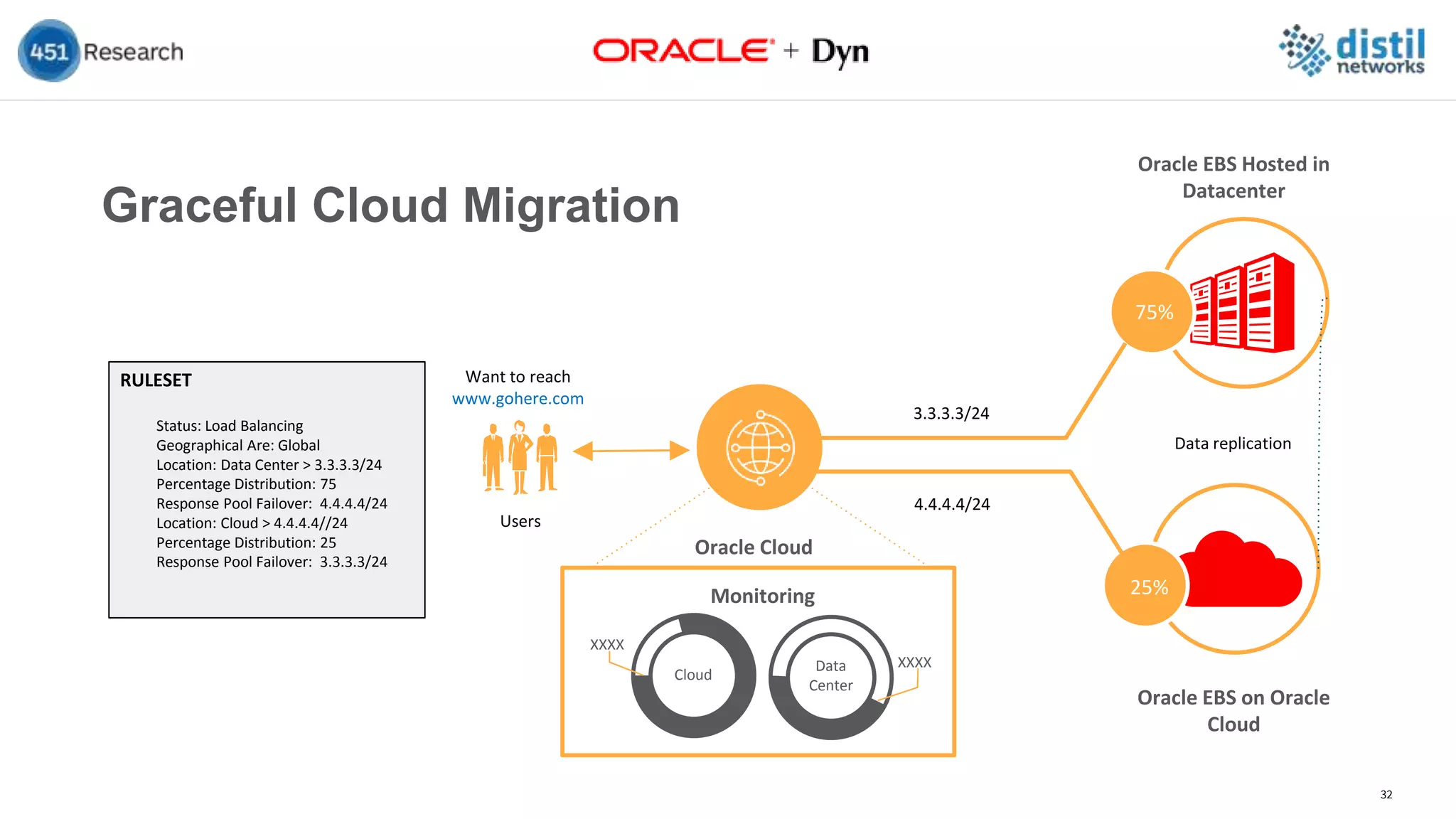
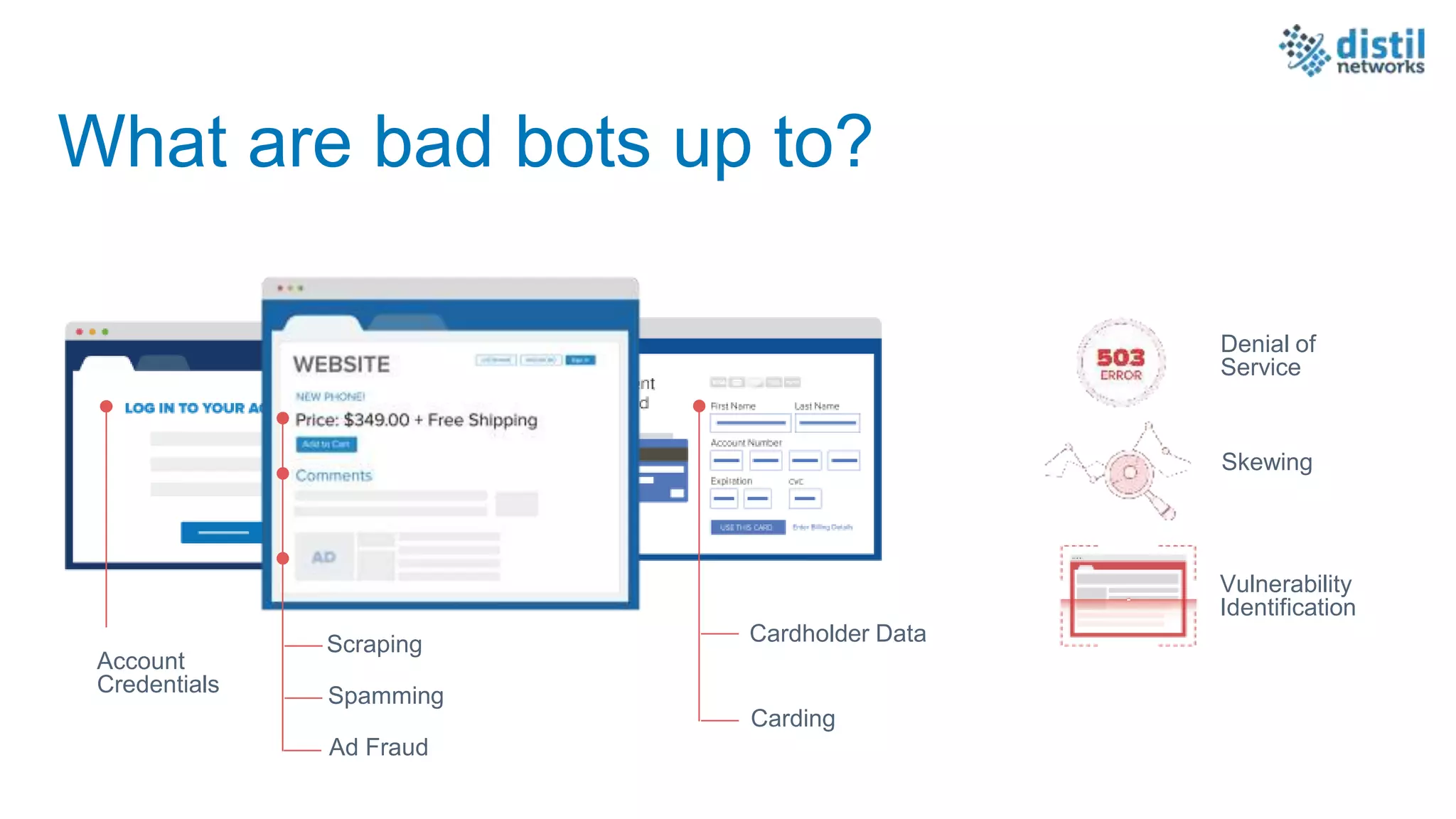
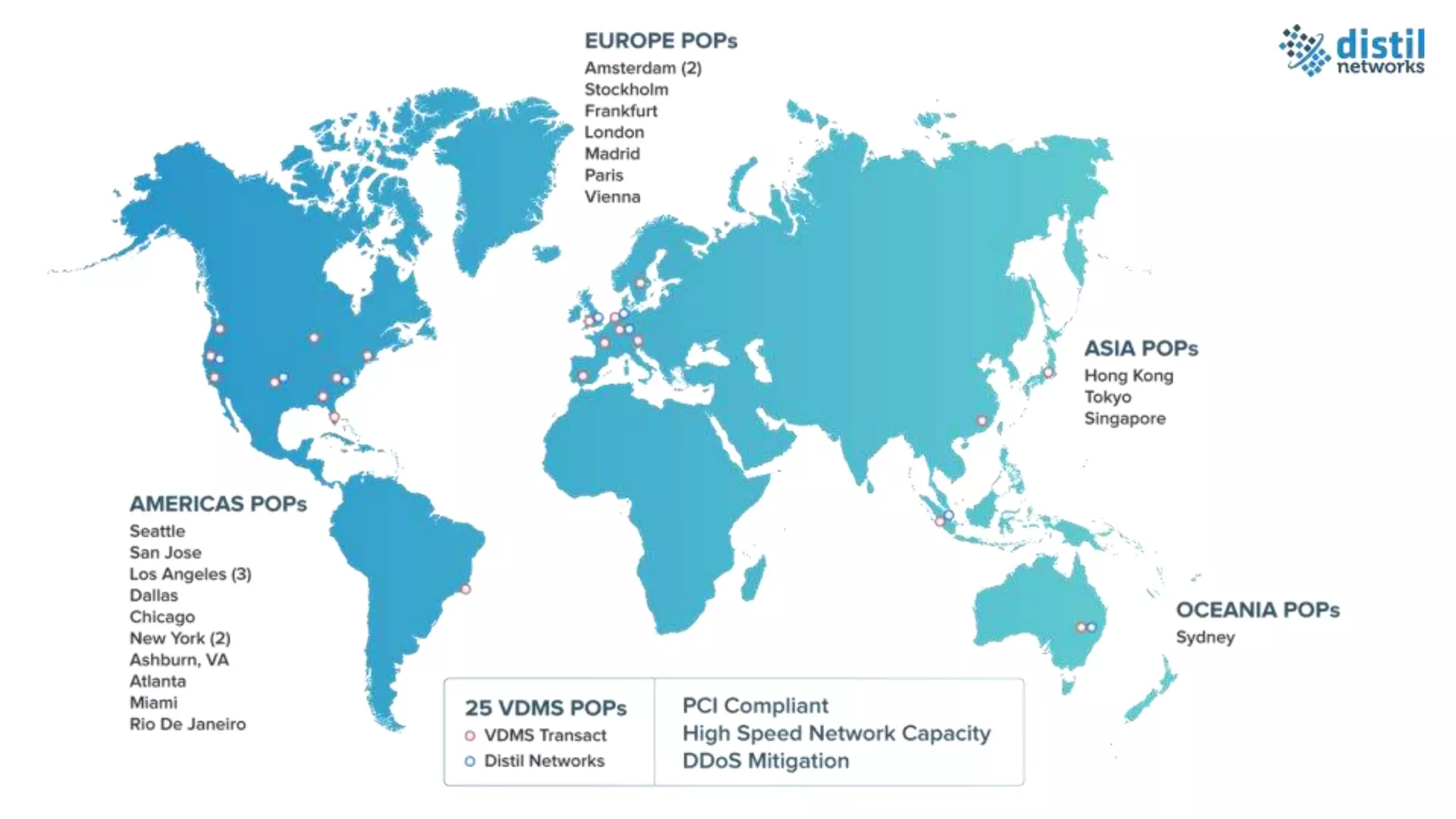
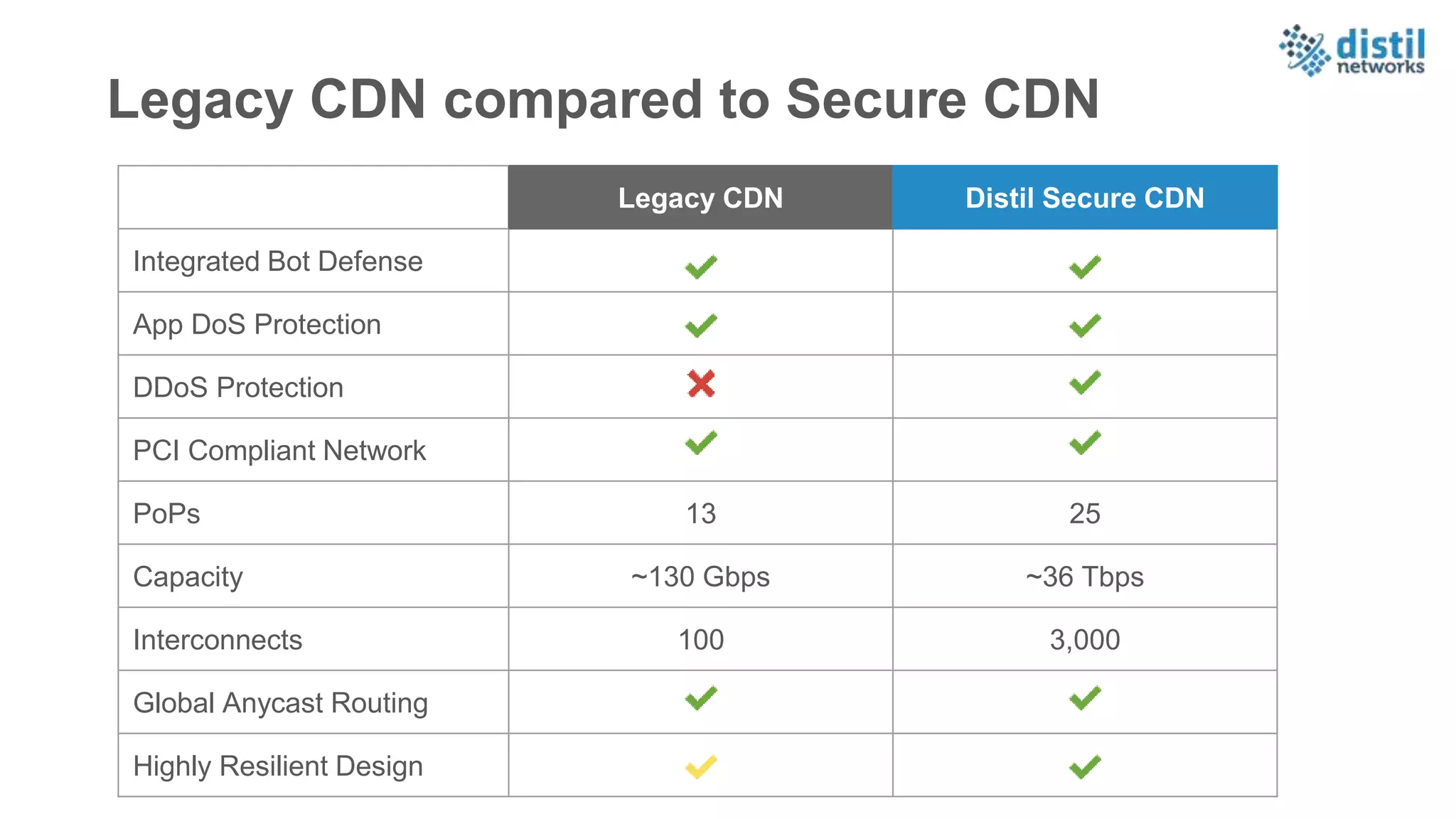
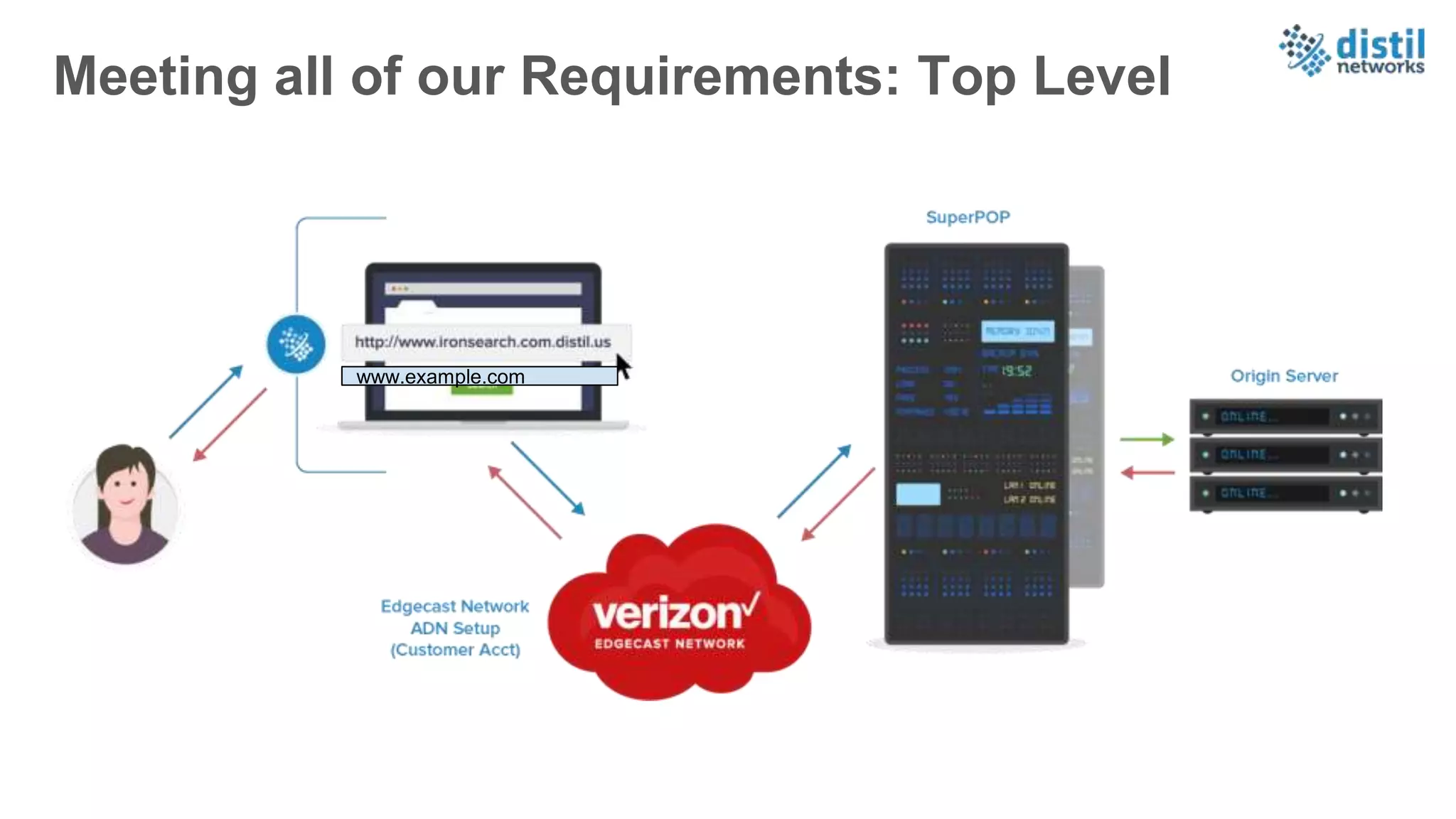
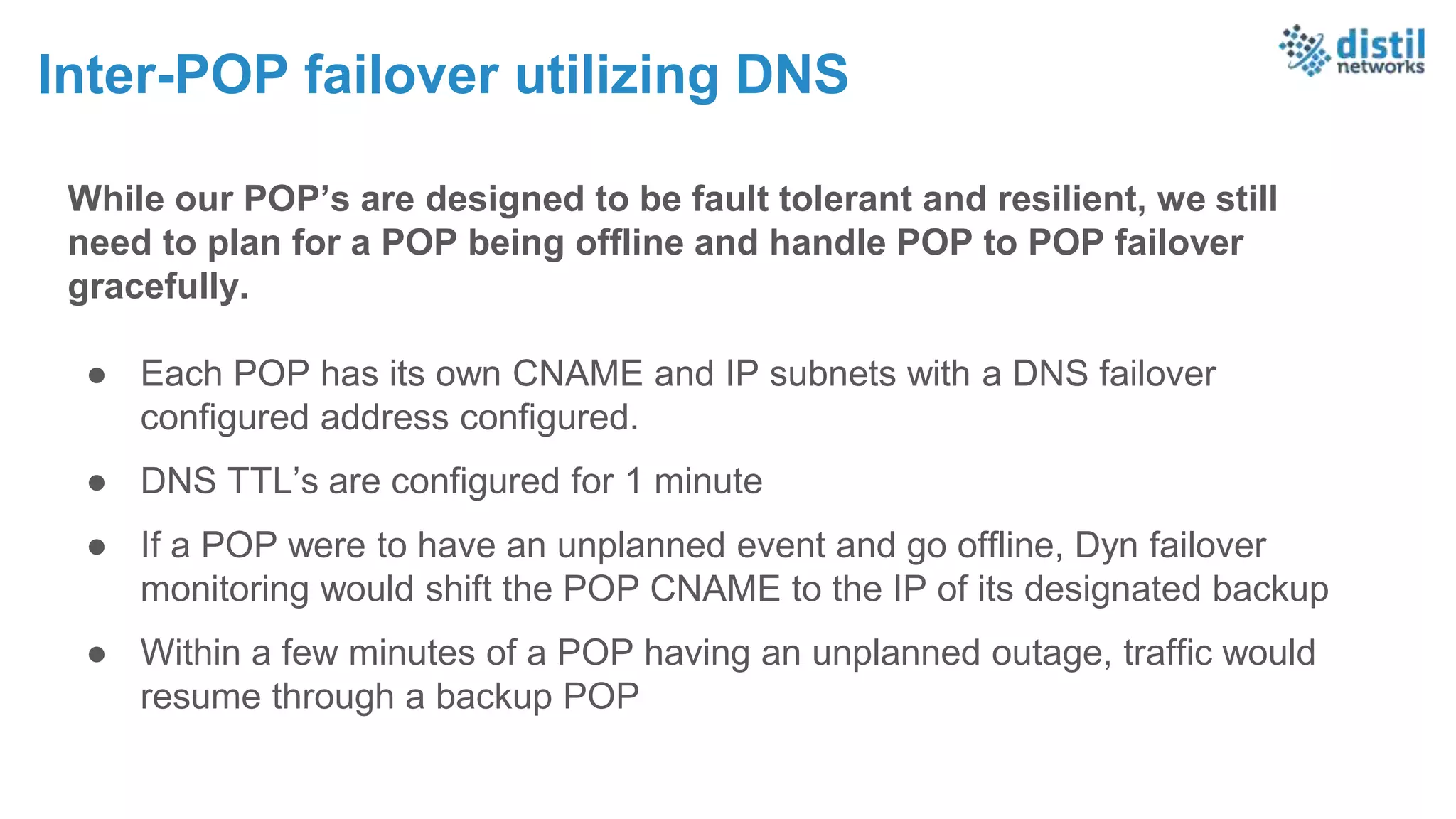
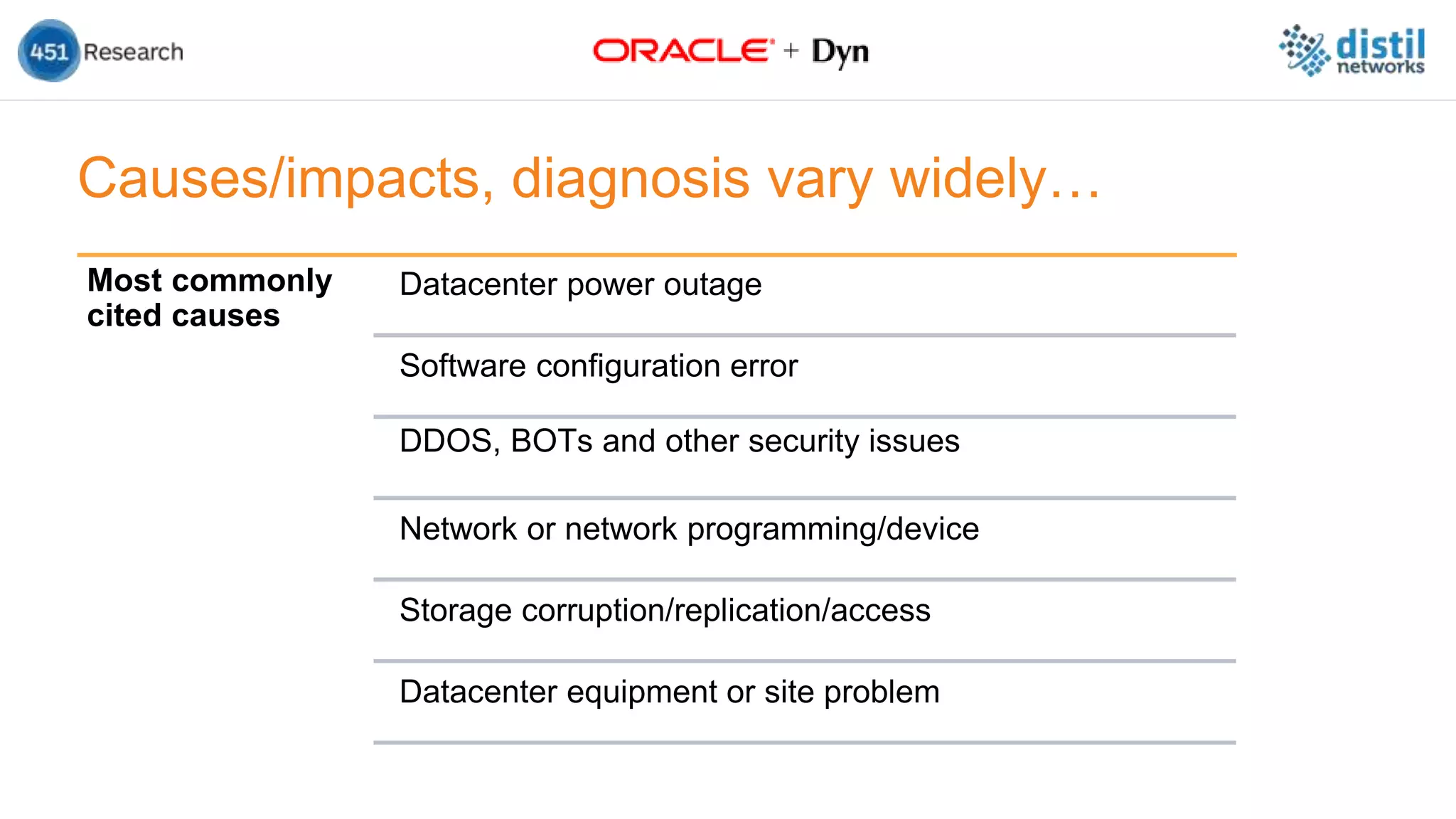
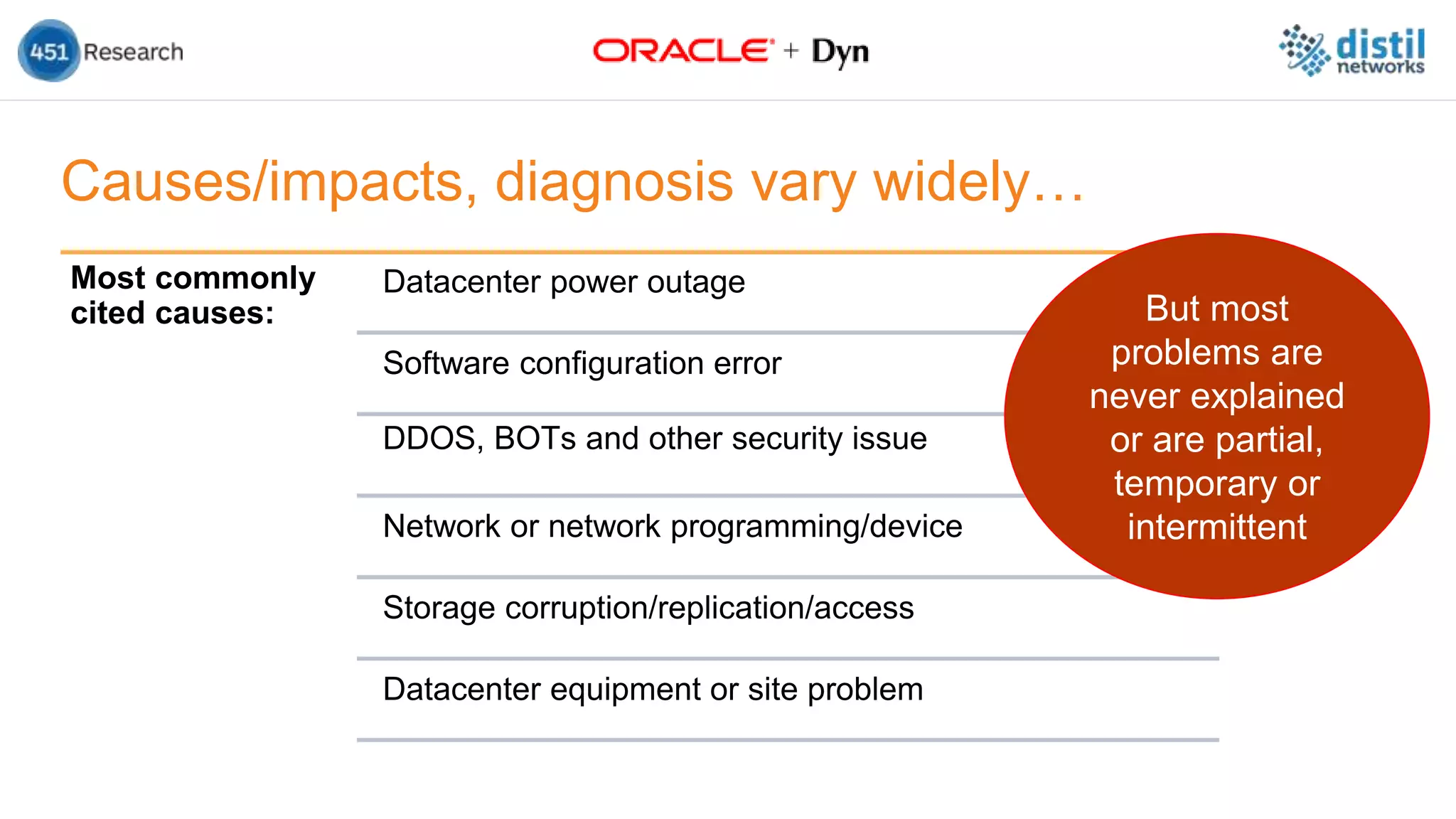
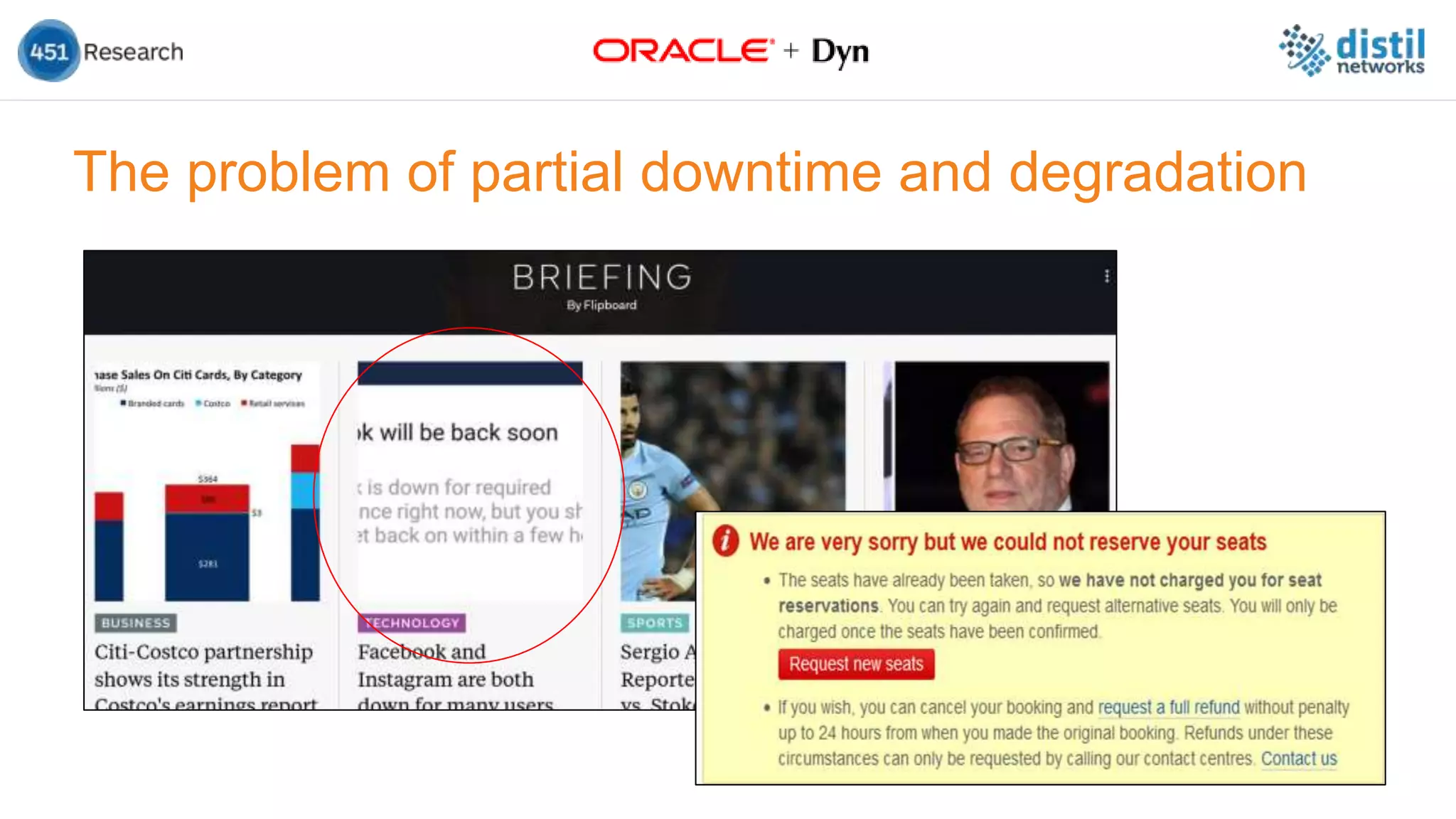
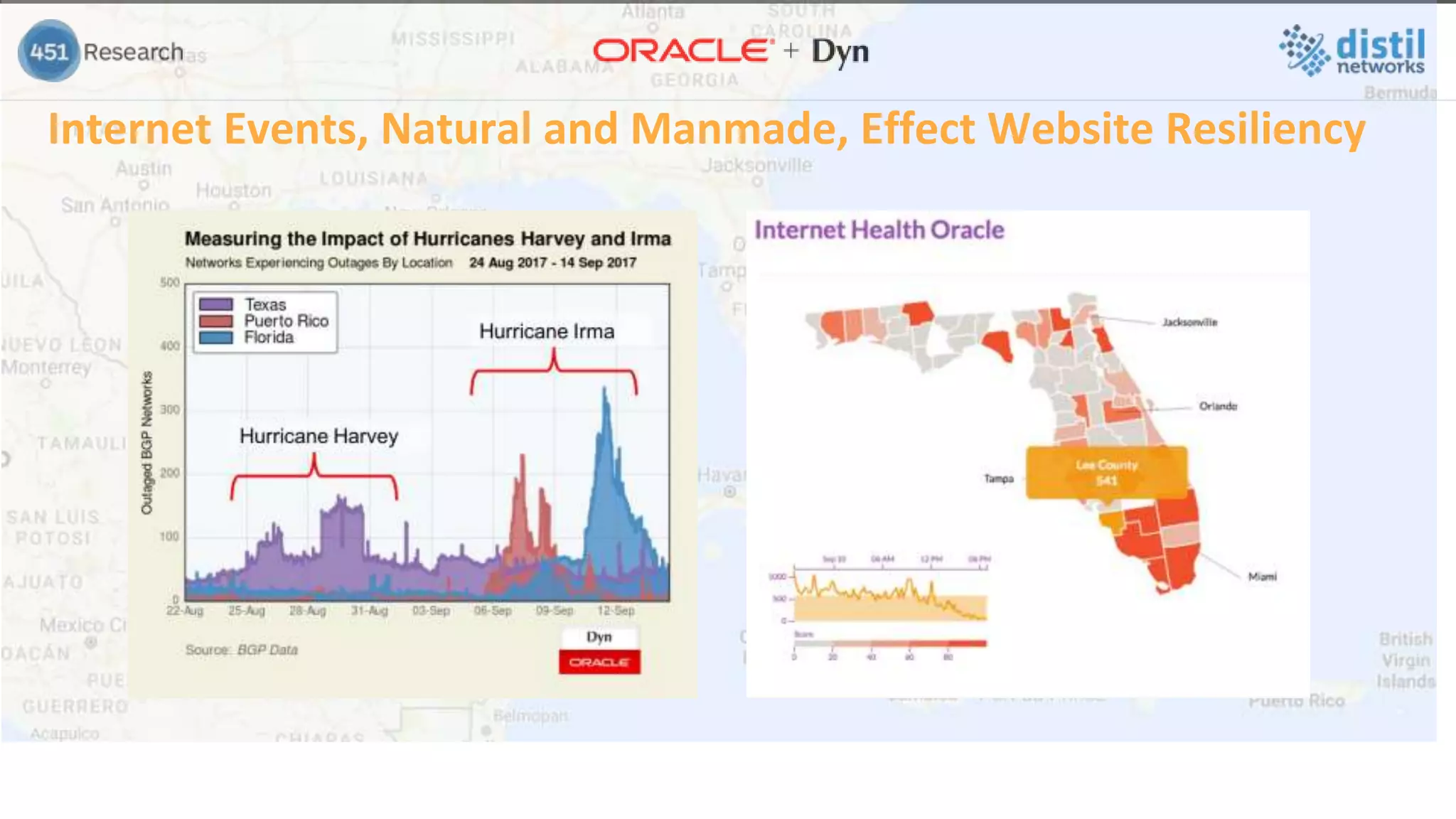
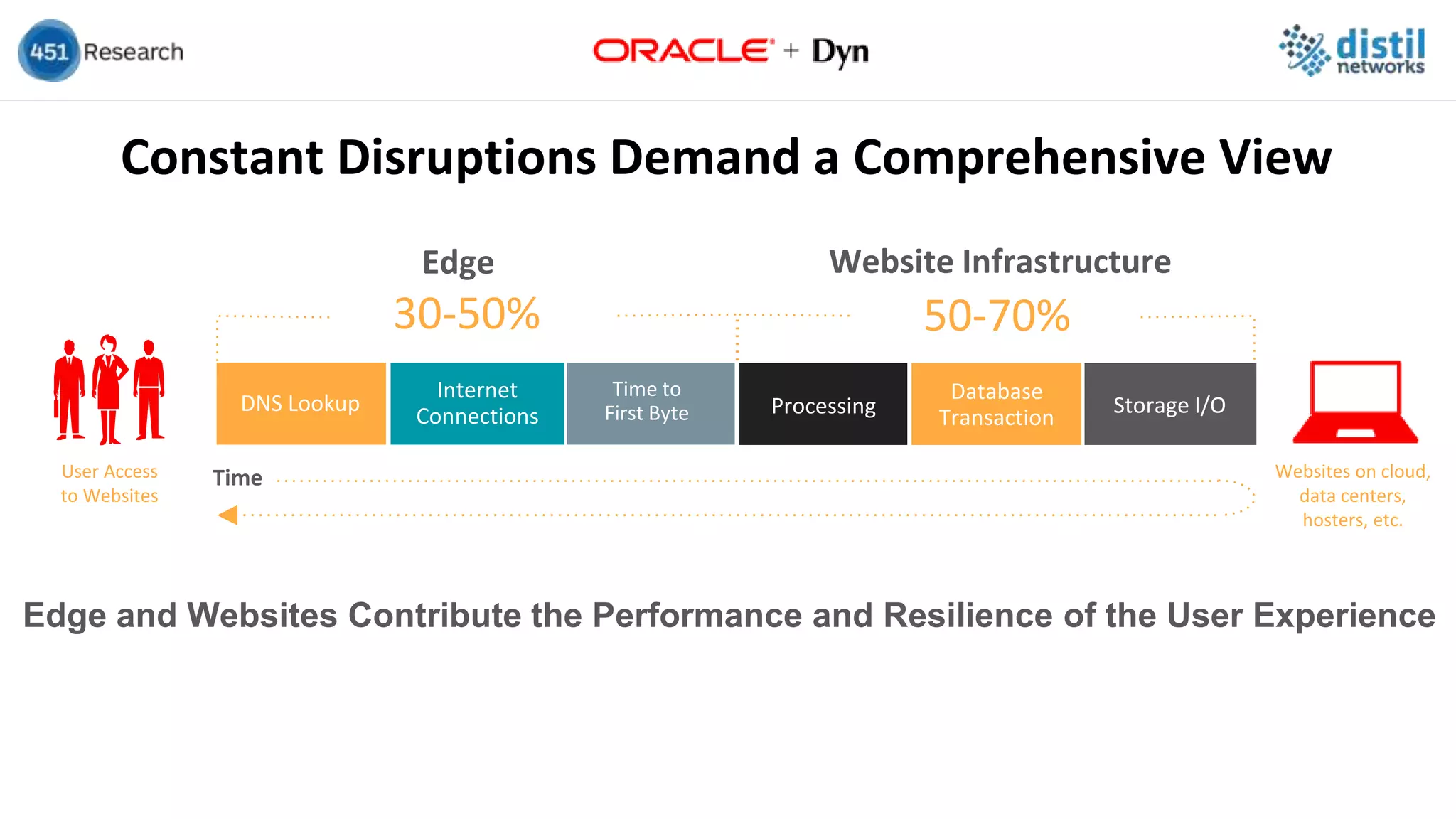
The document discusses the increasing complexity and costs associated with outages and the growing focus on achieving zero downtime through distributed resiliency strategies. Key factors include the importance of redundancy, analytics for forecasting failures, and the need for diligent IT management. It emphasizes that while distributed architectures can enhance reliability, they also introduce new challenges requiring careful planning and management.




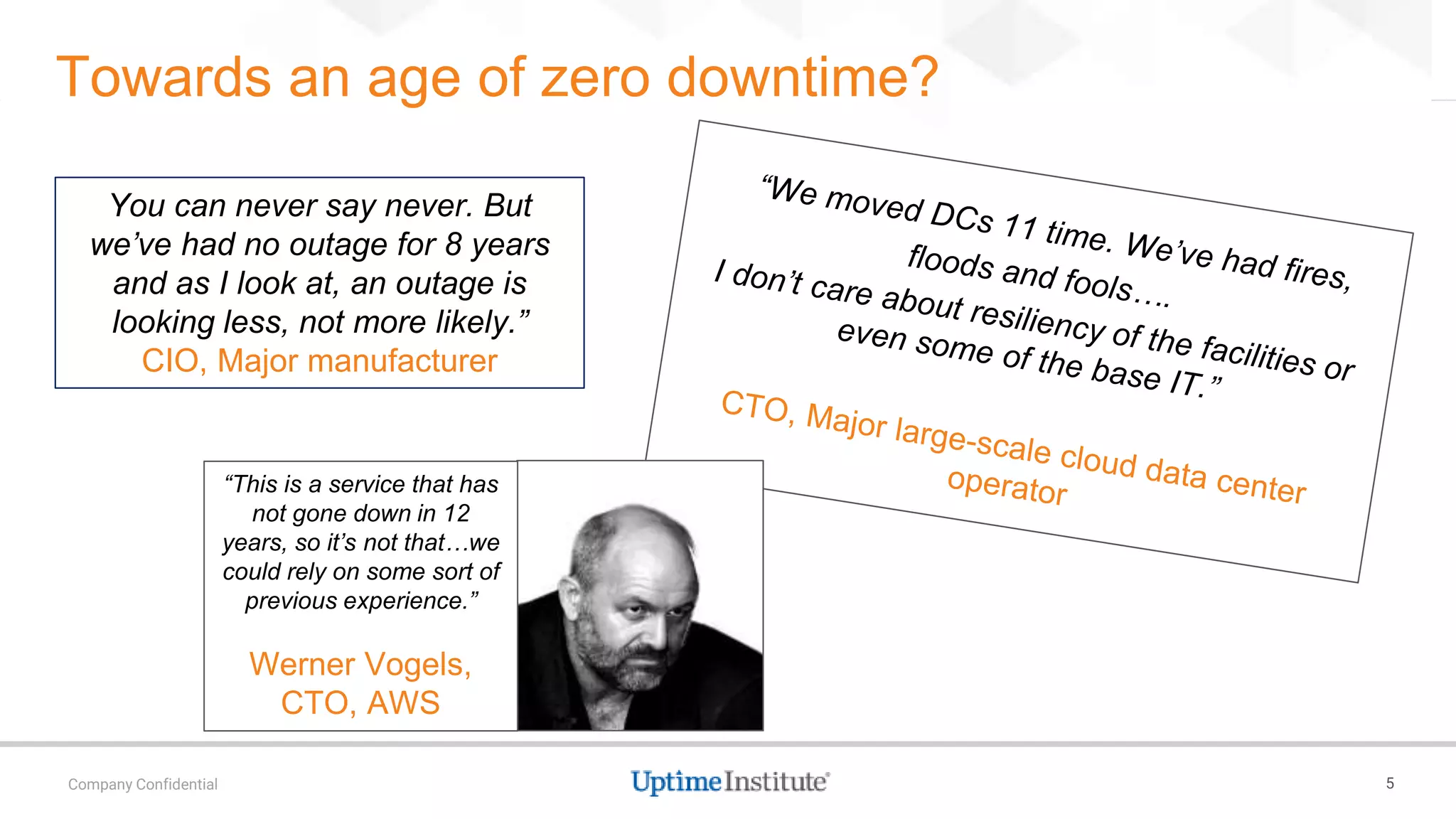







![Cloud resiliency and distributed data integrity…
[This] is possible in practice if you control the whole network,
which is rare over the wide area.”
Even then, it requires significant redundancy of network paths,
architectural planning to manage correlated failures, and very
careful operations, especially for upgrades.
Even then outages will occur……..
Professor Eric Brewer, VP Infrastructure, Google](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/451research2foracledynmaster-171108215009/75/The-Website-Resiliency-Imperative-19-2048.jpg)






![Users
[Customers,
Partners,
Employees,
Things]
IT
[DevOps,
Administrators,
Architects]
Core and Edge Create a Complete Cloud
Expectation
[High quality
experience]
Identity
Compute
Block
Storage
Database Networking
Object
Storage
Edge
Messaging
Name
Resolution
Distributed
Content
Traffic
Steering
The Next Generation Cloud
Internet
Monitoring
Availability
Performance
Security
Control
Edge
Networking
Edge
Security
Core+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/451research2foracledynmaster-171108215009/75/The-Website-Resiliency-Imperative-30-2048.jpg)