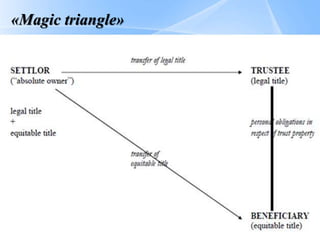
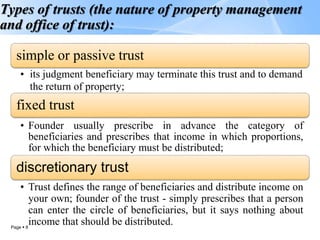
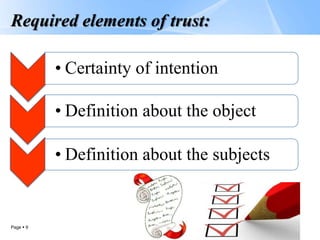
Trusts are legal arrangements where a trustee holds and manages assets for the benefit of beneficiaries. The key parties are the principal/founder who transfers assets to the trust, the trustee who manages the assets, and the beneficiary who receives benefits from the trust assets. There are different types of trusts including expressed trusts based on a declaration of trust and implied trusts established by law. Trusts can be used for various purposes such as preserving anonymity, joint property ownership, protecting beneficiaries' assets, charitable giving, pensions, and tax avoidance. Modern offshore trusts offer flexibility, tax benefits when the beneficiary resides in the trust registration country, and protections for beneficiaries' interests.