The document outlines Oracle's PaaS cloud offerings, examining the current status and future roadmap within the cloud landscape, emphasizing the need for Oracle to transition to cloud-based services. It discusses the strategic importance of cloud services for Oracle, highlighting security, scalability, and performance as critical factors for success. The document also details the competitive landscape and Oracle's approach to differentiating its services in an increasingly crowded market.



![4
Vision 2025
• 80% of production application will be in
the cloud (today 25%)
• Two Suite Providers will have 80% of the SaaS market
– “Who will be the other one?”
• 100% of Dev/Test will be in the public cloud
– 30-40% of IT spending
• Virtually all enterprise data will be stored in the clouds
– Some % in Private Clouds
• Enterprise Clouds will be the most secure IT environments
– Web scale security
– State of the art Encryption
– Latest [security] patch always applied
– Physical security at near-military level](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclearchplatform-warestaatvanpubliccloud-may2016-160518045040/75/The-True-State-of-the-Oracle-Public-Cloud-Dutch-Oracle-Architects-Platform-May-2016-4-2048.jpg)




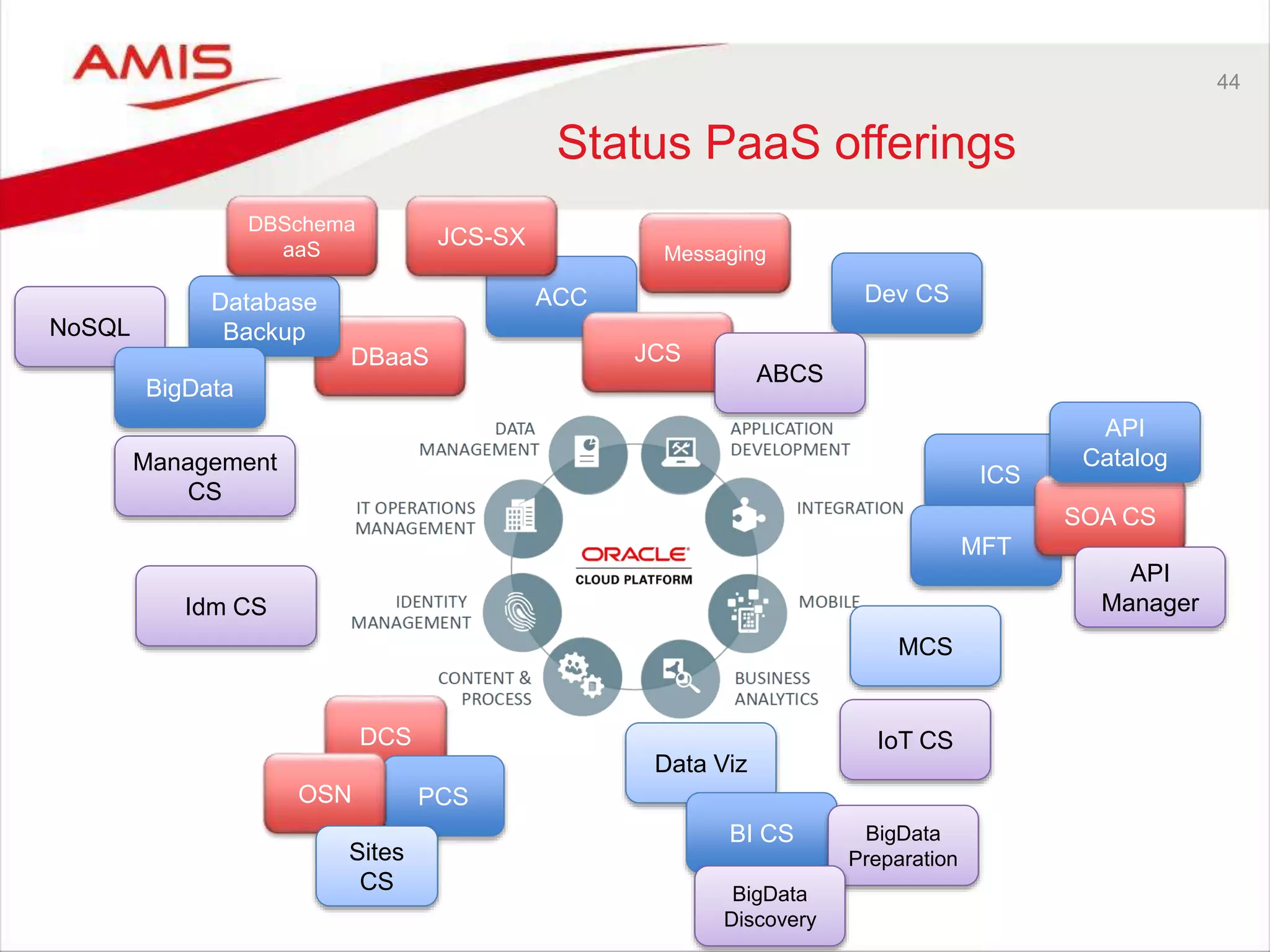
![10
[role of] PaaS Cloud](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclearchplatform-warestaatvanpubliccloud-may2016-160518045040/75/The-True-State-of-the-Oracle-Public-Cloud-Dutch-Oracle-Architects-Platform-May-2016-10-2048.jpg)
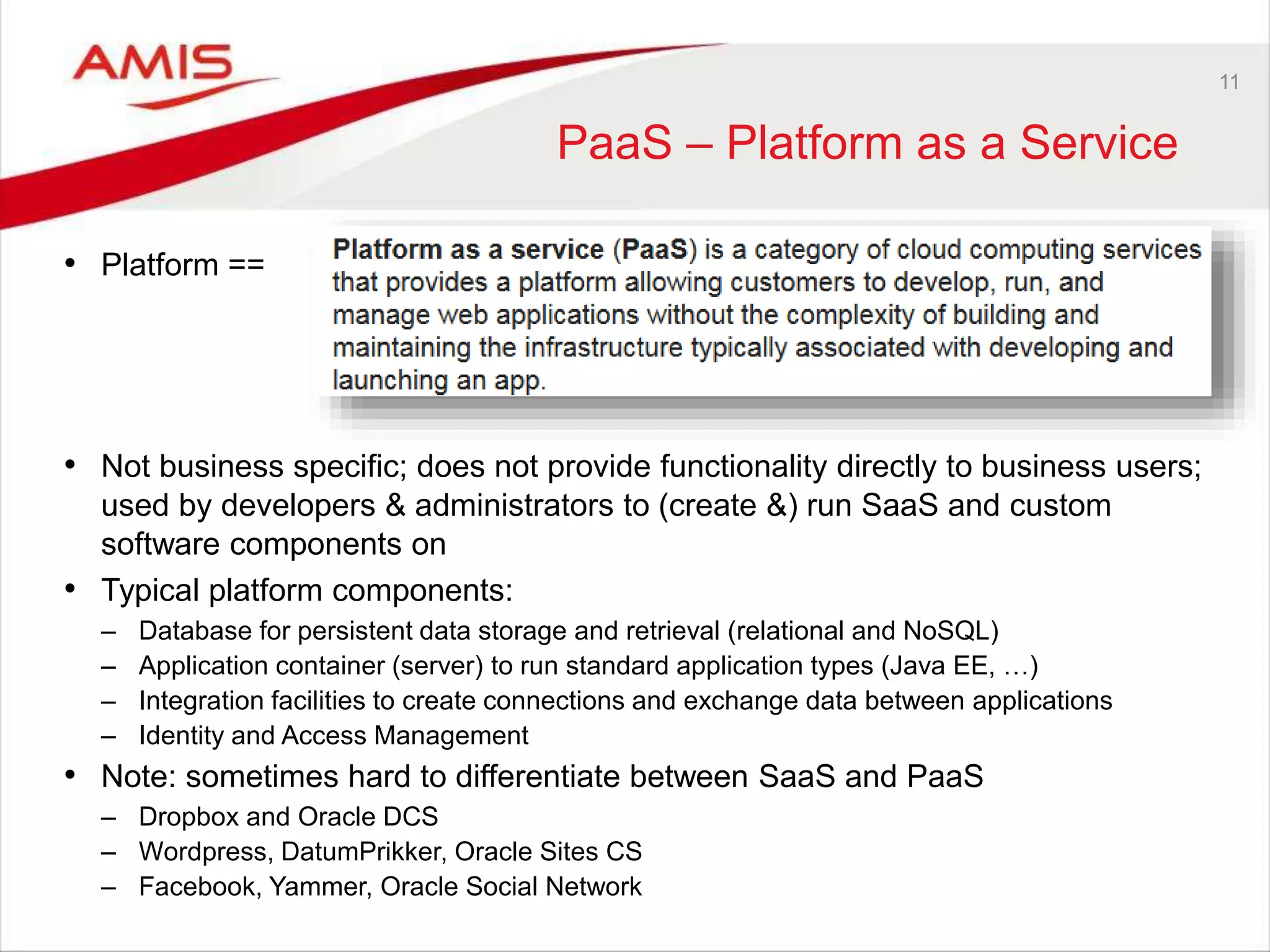

![13
What would it take to offer the Oracle
Platform successfully as PaaS?
• Criteria used for evaluating PaaS services include
– security,
– scalability,
– performance and availability,
– richness of functionality,
– adherence to standards and openness,
– ability to integrate (with),
– required and available skills,
– maturity (How proven is the technology [on the cloud]? Who is also using it?),
– ability to run existing applications
– the Total Cost of Ownership [compared to the on premises alternatives and to other
PaaS providers], including ease of administration
• Also: compare Oracle PaaS to Oracle Platform running on 3rd party IaaS
– E.g. Oracle Database on Azure and Oracle Fusion Middleware on AWS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclearchplatform-warestaatvanpubliccloud-may2016-160518045040/75/The-True-State-of-the-Oracle-Public-Cloud-Dutch-Oracle-Architects-Platform-May-2016-13-2048.jpg)




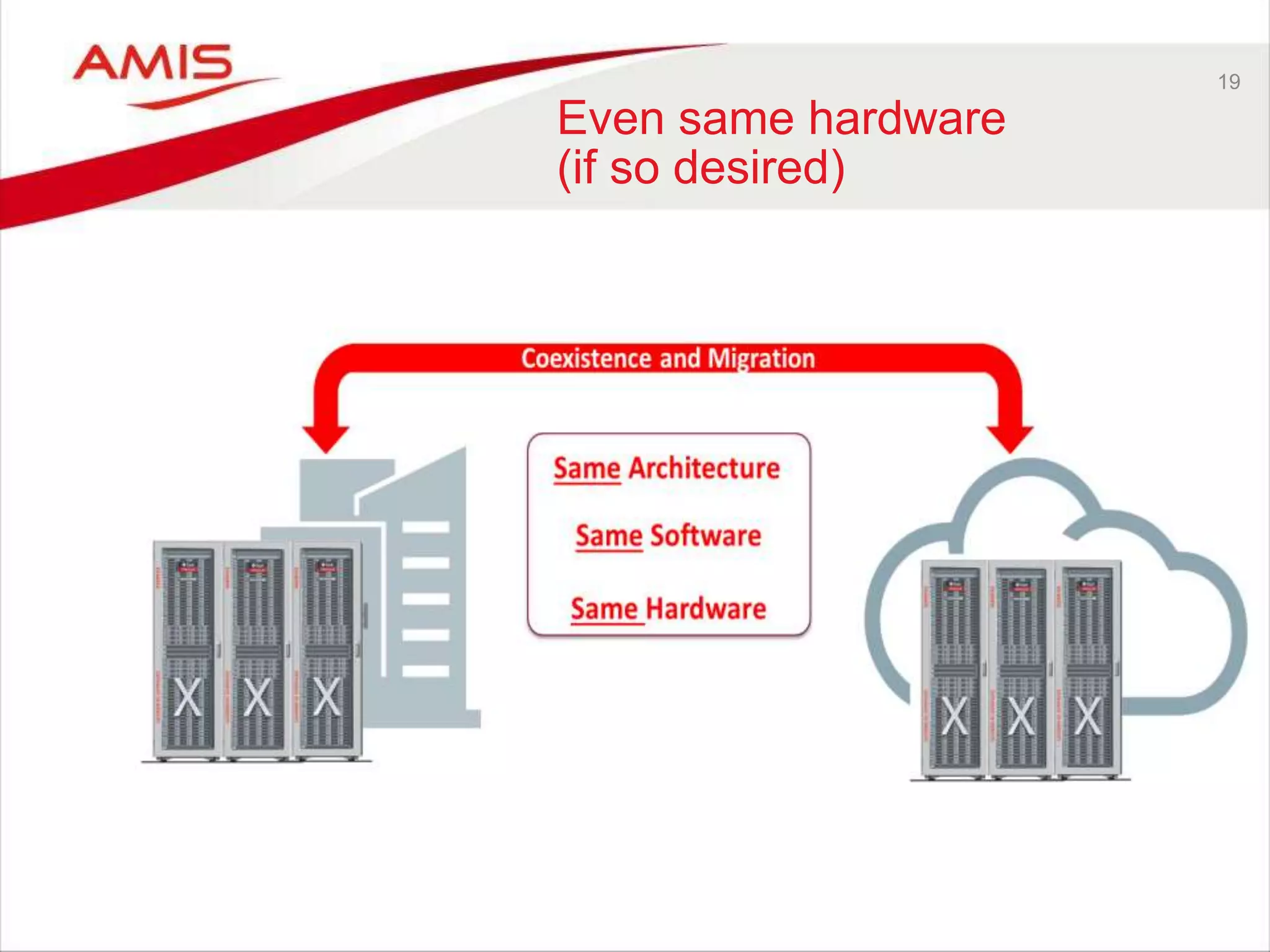

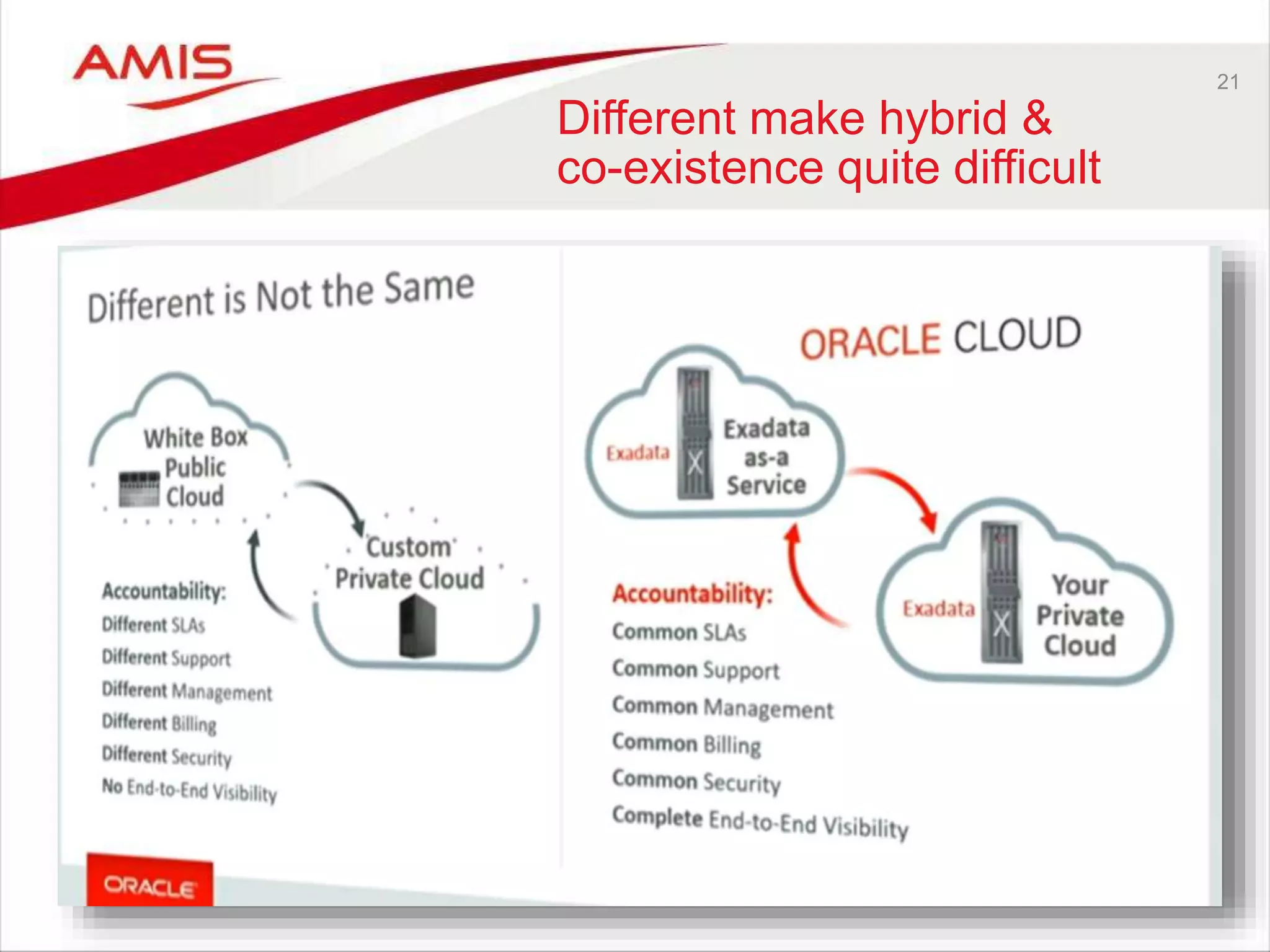
![22
Some observations around
cloud == on premises
• Release cycles for Public PaaS and on premises are not synchronized
– For example: WLS (12.2.1 and 12.2.2)
• Configuration is not the same on premises as in the cloud
– Though similar, the deployment process is not exactly the same; some new ‘cloud
skills’ are required
• Some Oracle PaaS Services are not available as on premises product
– Note: Oracle [Public] Cloud Machine
• Some Cloud Vendors provide local development environments that
emulate the cloud run time
• ≈ != =](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclearchplatform-warestaatvanpubliccloud-may2016-160518045040/75/The-True-State-of-the-Oracle-Public-Cloud-Dutch-Oracle-Architects-Platform-May-2016-22-2048.jpg)

![24
Internal challenges Oracle
needs to address
• Continuous Availability
– Uptime, fail-over, SLAs, zero-down-time patching and application deployment, …
• Density and enough IaaS capacity
– Get more PaaS out of IaaS
• Automated IT Operations
– Ease and speed of provisioning [and patching, upgrading, scaling, …]
• Pricing models
– what do you charge for, how [and when] do you compensate Sales staff
– BYO, elastic scale, what can you charge Support fees for?
• Billing
• Properly integrate all services
– Common user experience, one implementation of each function, SSO, single agent,
shared architecture vision
• Communication with users of cloud service
– Pro-active, consistent, clear
• DevOps](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclearchplatform-warestaatvanpubliccloud-may2016-160518045040/75/The-True-State-of-the-Oracle-Public-Cloud-Dutch-Oracle-Architects-Platform-May-2016-24-2048.jpg)

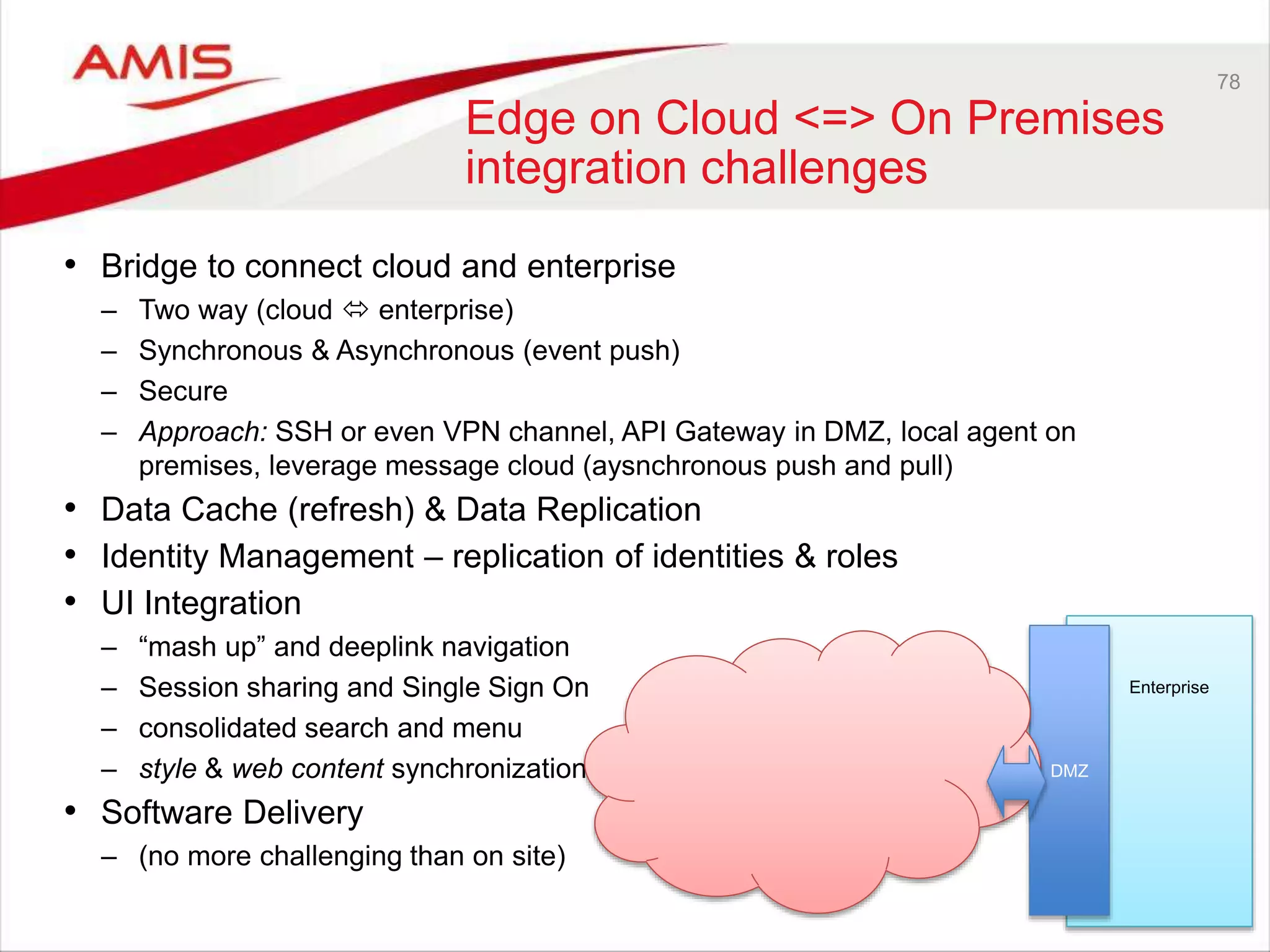
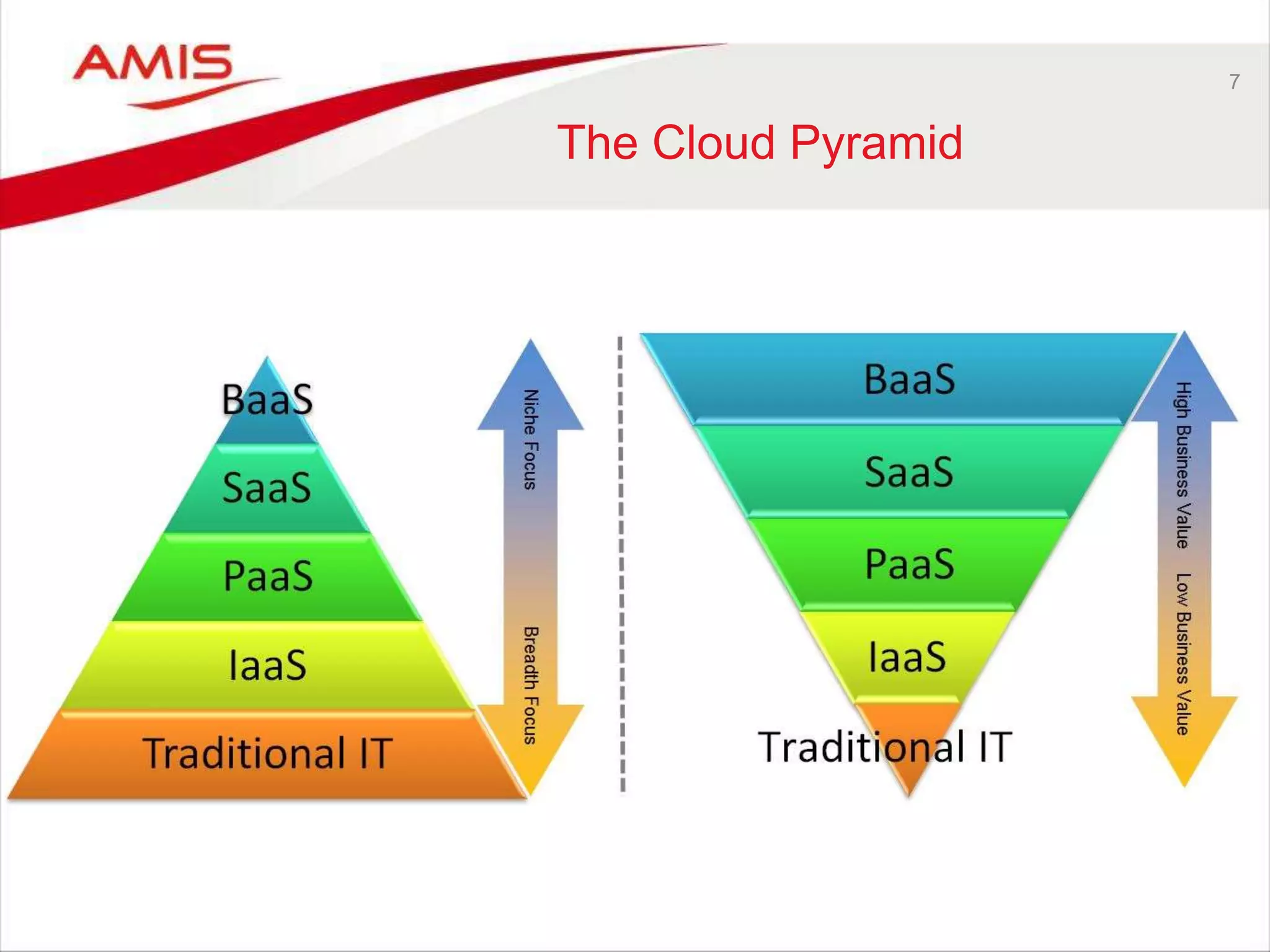
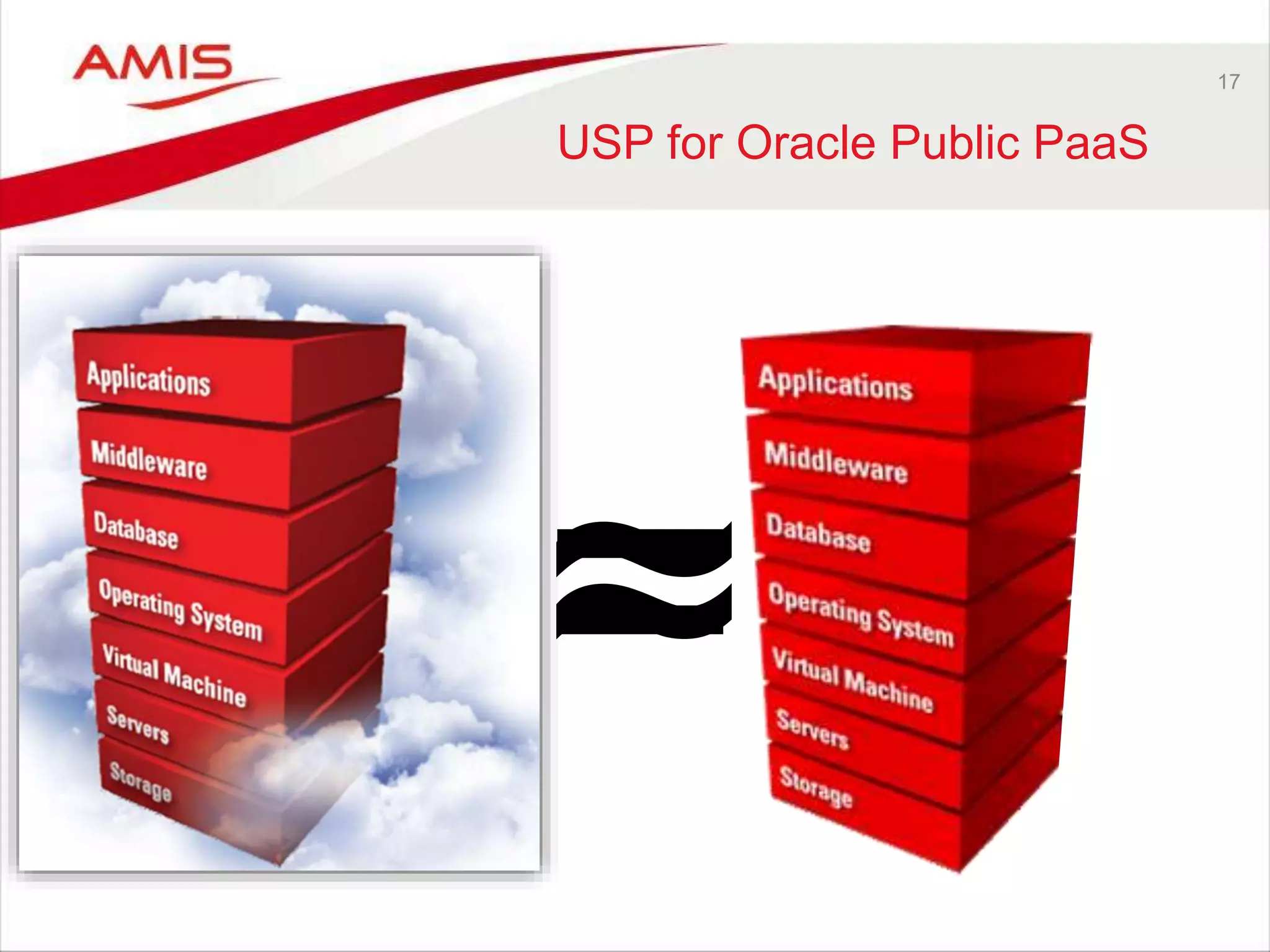
![26
IaaS
• To run a Platform you need Infrastructure: Compute, Storage, Network
• If you want to be a PaaS provider – you need IaaS
– Your own or someone else’s
• Criteria to select an IaaS provider
– Price, Scale/Elasticity, Security, Image
• Oracle cannot afford to depend on third party IaaS
– Besides: it want to offer a complete cloud portfolio
• It needs to set up IaaS
– And offer it as Public IaaS to not drive customers away
• However: it cannot differentiate on IaaS
– Or even make money with IaaS [for now]
• Oracle offers the exact same stack in the cloud
as is available to customers on premises
– That means it implements its IaaS with Exalogic & Exadata,
Oracle Enterprise Linux and OVM.
– Perhaps at some point M7 powered SuperCluster as well?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclearchplatform-warestaatvanpubliccloud-may2016-160518045040/75/The-True-State-of-the-Oracle-Public-Cloud-Dutch-Oracle-Architects-Platform-May-2016-26-2048.jpg)


![30
As an aside: on premises is alive
and kicking too [and benefits]
• Oracle Hardware and Software powers
the cloud
and is being optimized for that purpose
– You benefit on premises
with your private cloud
• Multitenancy support
– Density – usage of physical resources
(consolidation)
– Isolation
– Ease of admin (provisioning, patch, backup,…), Single Pane of Glass
• Availability (KSplice Hot Patching, DB RAC, WLS Continuous Availability,
Stretch Active-Active)
• Portability (PDB, Partition, Docker support)
• Dynamic Scalability (In Memory, M7, Database Sharding)
• Performance (reduced latency) DirectConnect, In Memory
• User Experience – Alta, Oracle JET](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclearchplatform-warestaatvanpubliccloud-may2016-160518045040/75/The-True-State-of-the-Oracle-Public-Cloud-Dutch-Oracle-Architects-Platform-May-2016-30-2048.jpg)








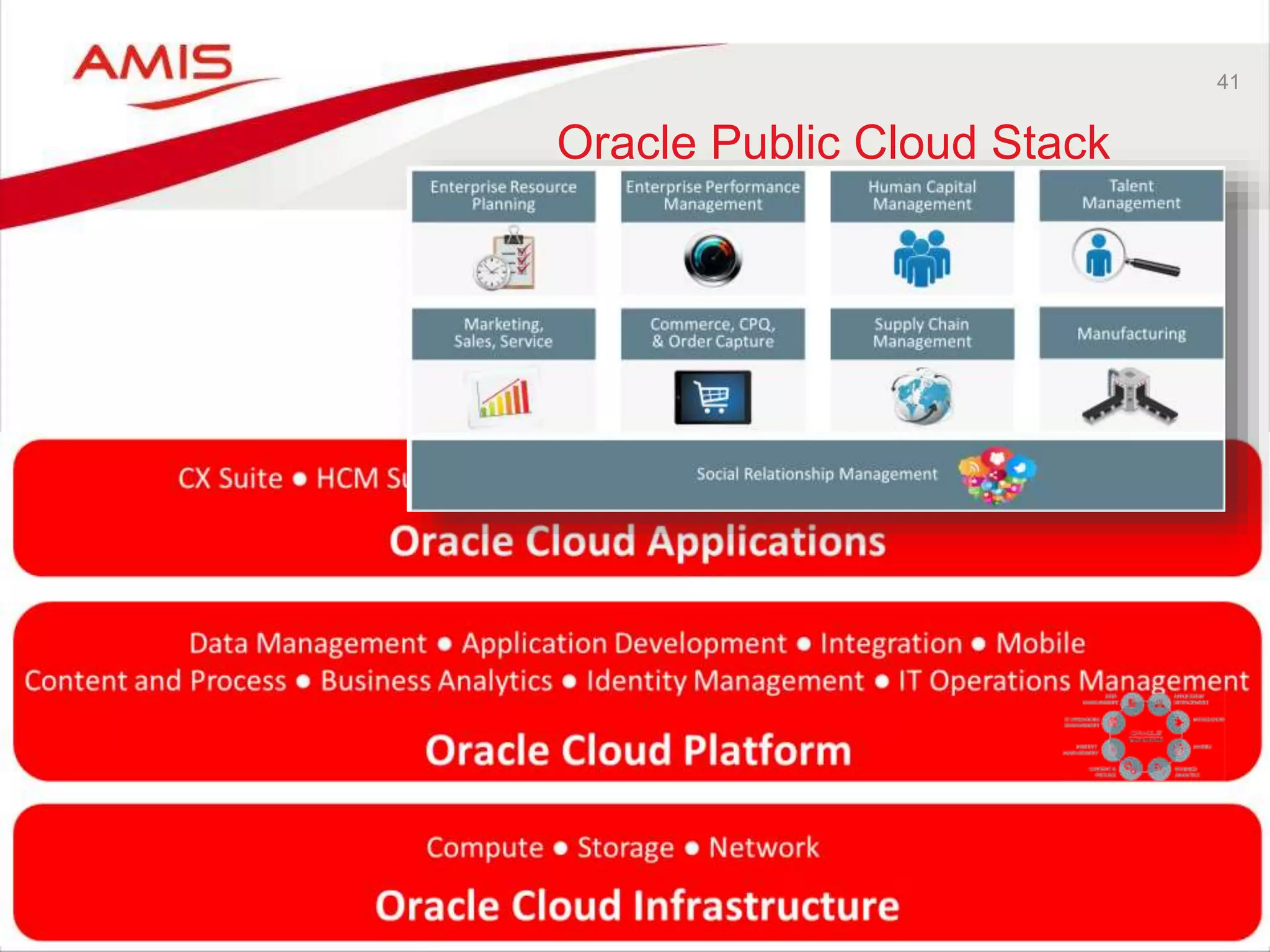

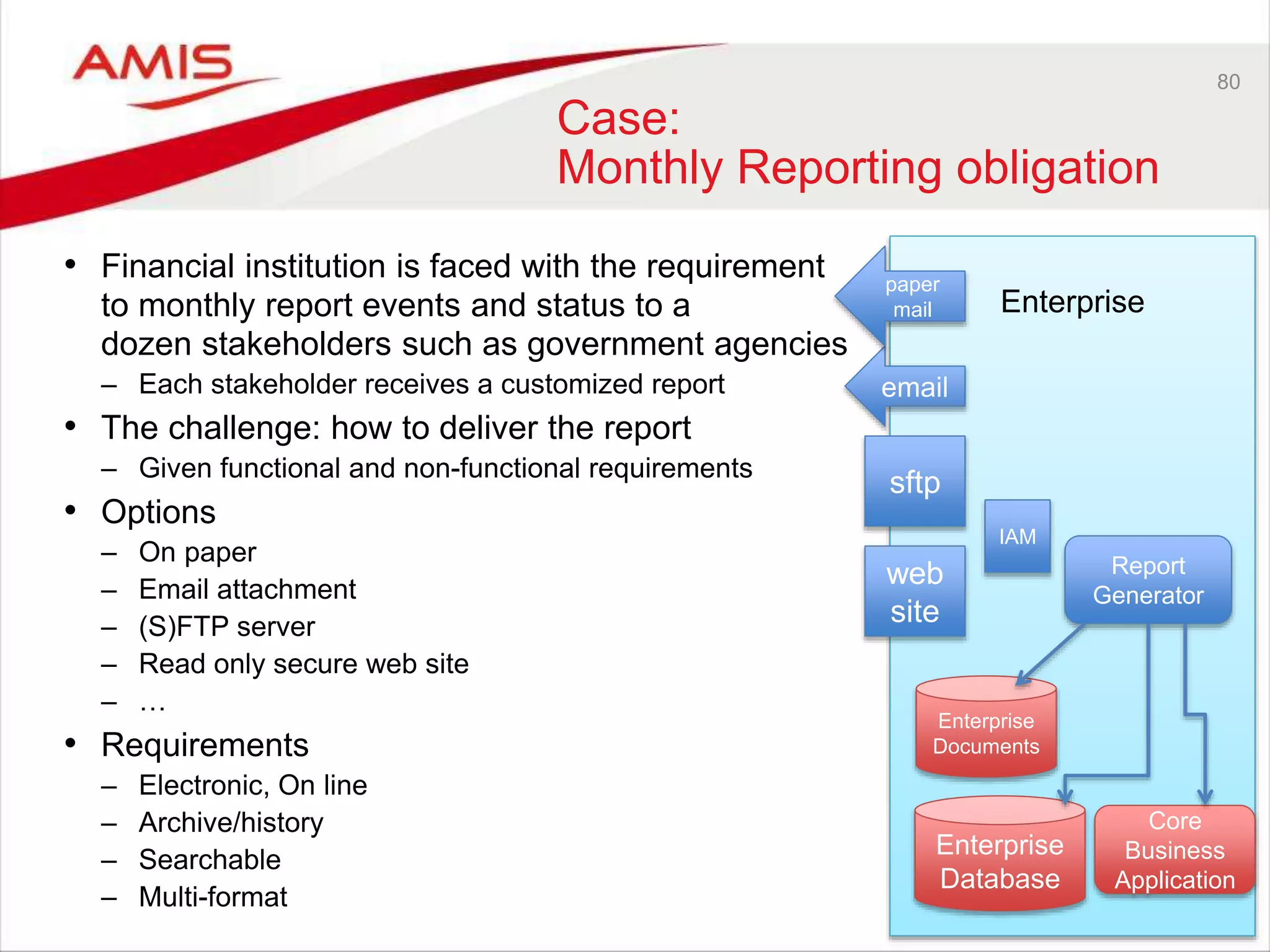
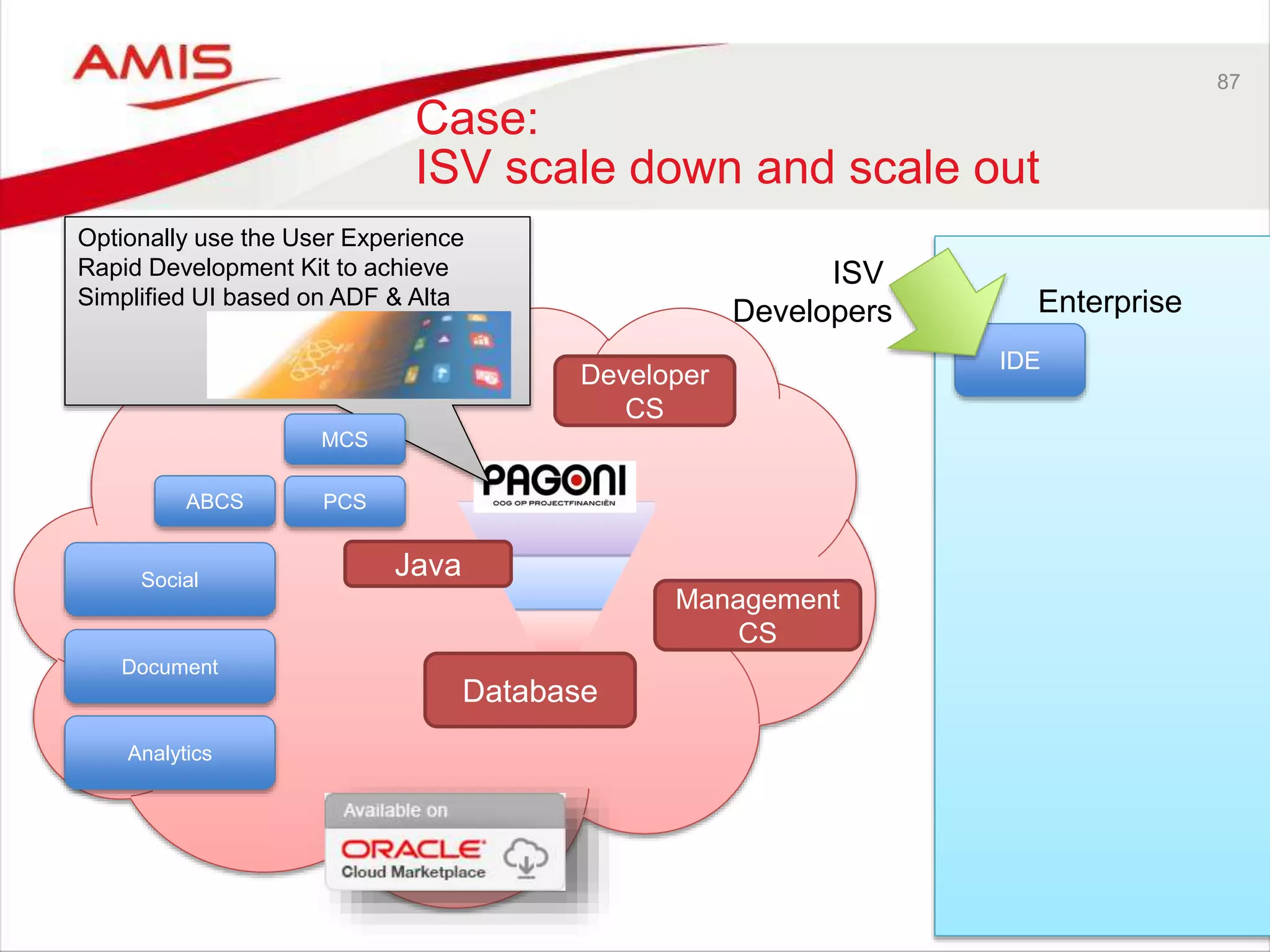
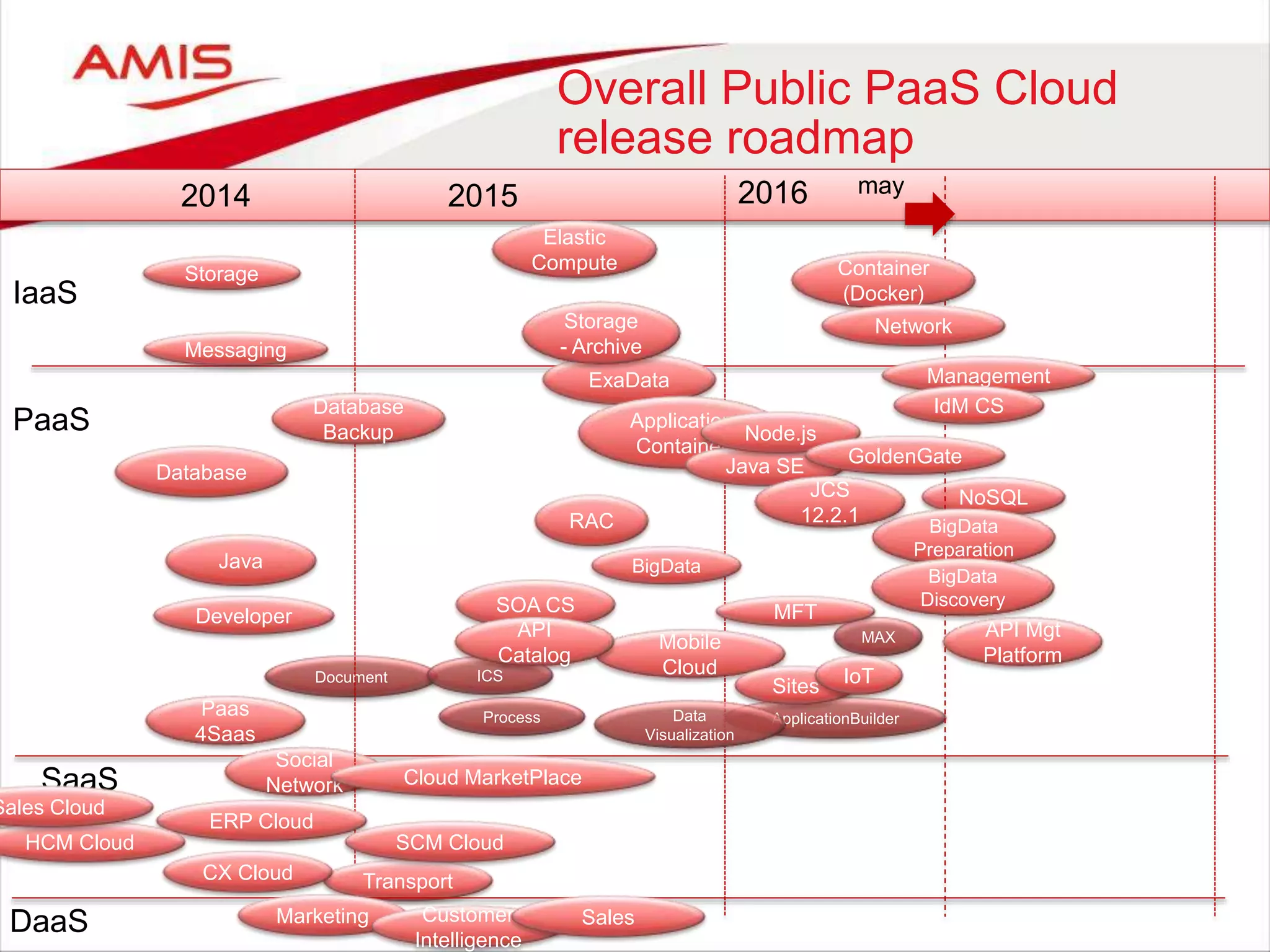
![43
Two categories of PaaS
Services are defined
• On Premises product offered from the cloud [as is]
– Easy provisioning (click-click install on secure compute and storage);
– IaaS is managed; Platform components are managed by customer
– Largely the same experience for administrators and entirely the same experience for
developers
– Lift and Shift of workloads is possible
– Examples: DBaaS, SOA CS, JCS, Data Visualization, API Catalog, MFT, BigData
• Cloud only product – developed for and offered from the cloud
– (sometimes based on a pre-existing on premises product; that association is bound
to fade over time – ICS OSB, PCS BPM, DCS WC Content))
– Examples: MCS, ICS, PCS, DCS, IoT CS, ABCS, BICS, Sites CS, BigData
Preparation, Developer CS, OSN, Messaging, Management CS, Idm CS
• Third category: On Premises Platform Product provisioned on JCS and
DBaaS
– You install and manage yourself
– Example: BPM Suite, WebCenter Portal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclearchplatform-warestaatvanpubliccloud-may2016-160518045040/75/The-True-State-of-the-Oracle-Public-Cloud-Dutch-Oracle-Architects-Platform-May-2016-43-2048.jpg)









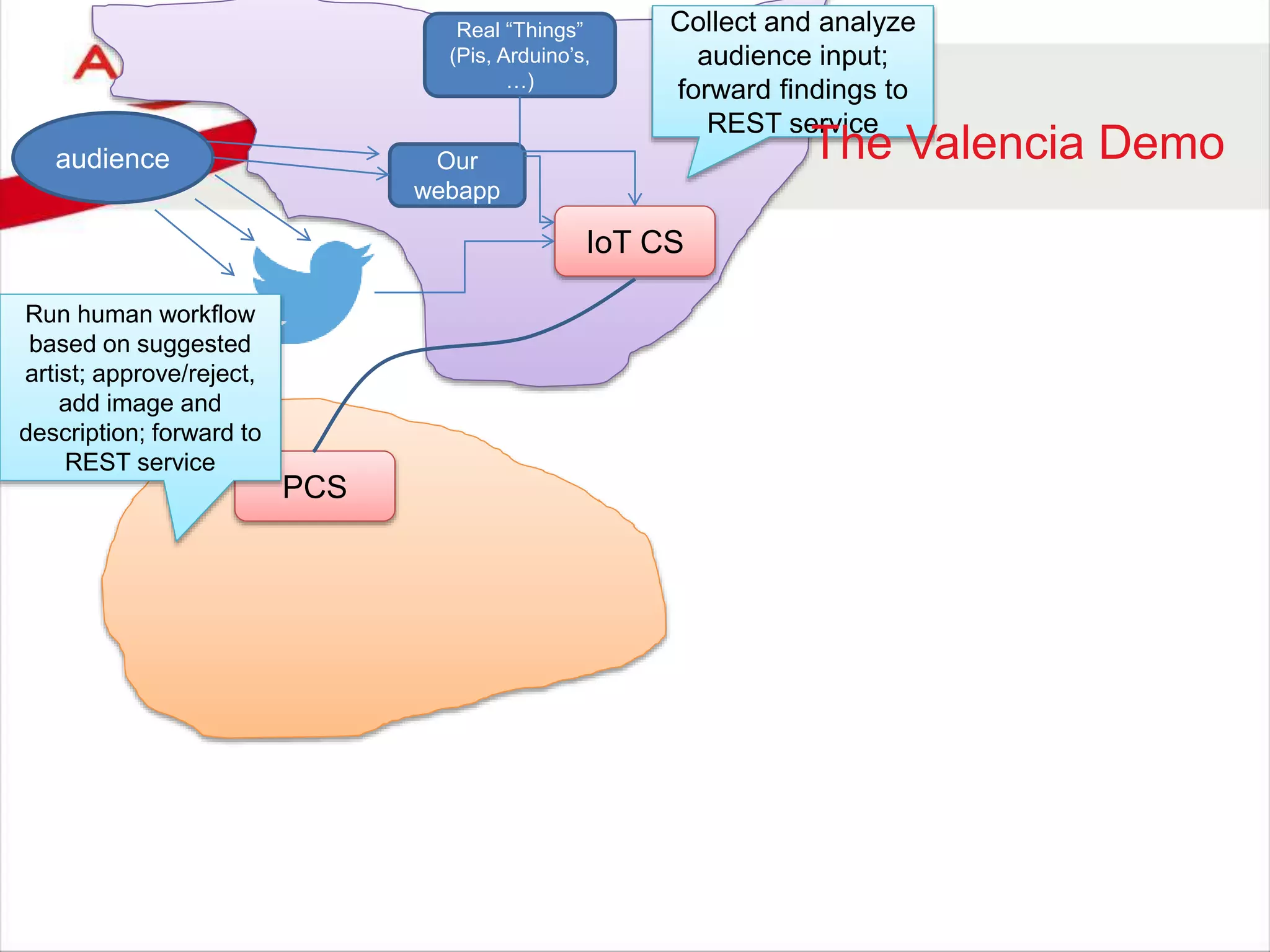
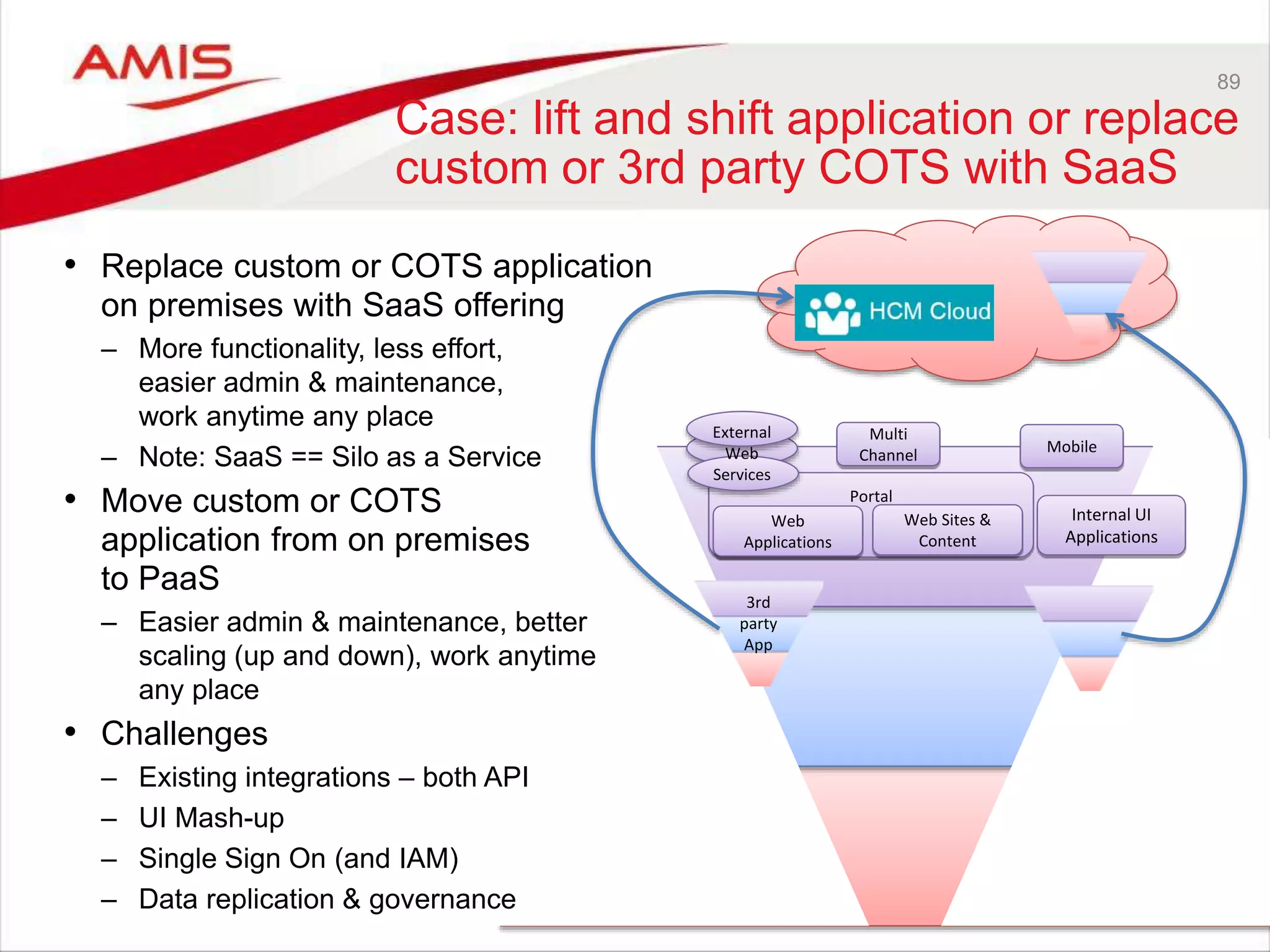
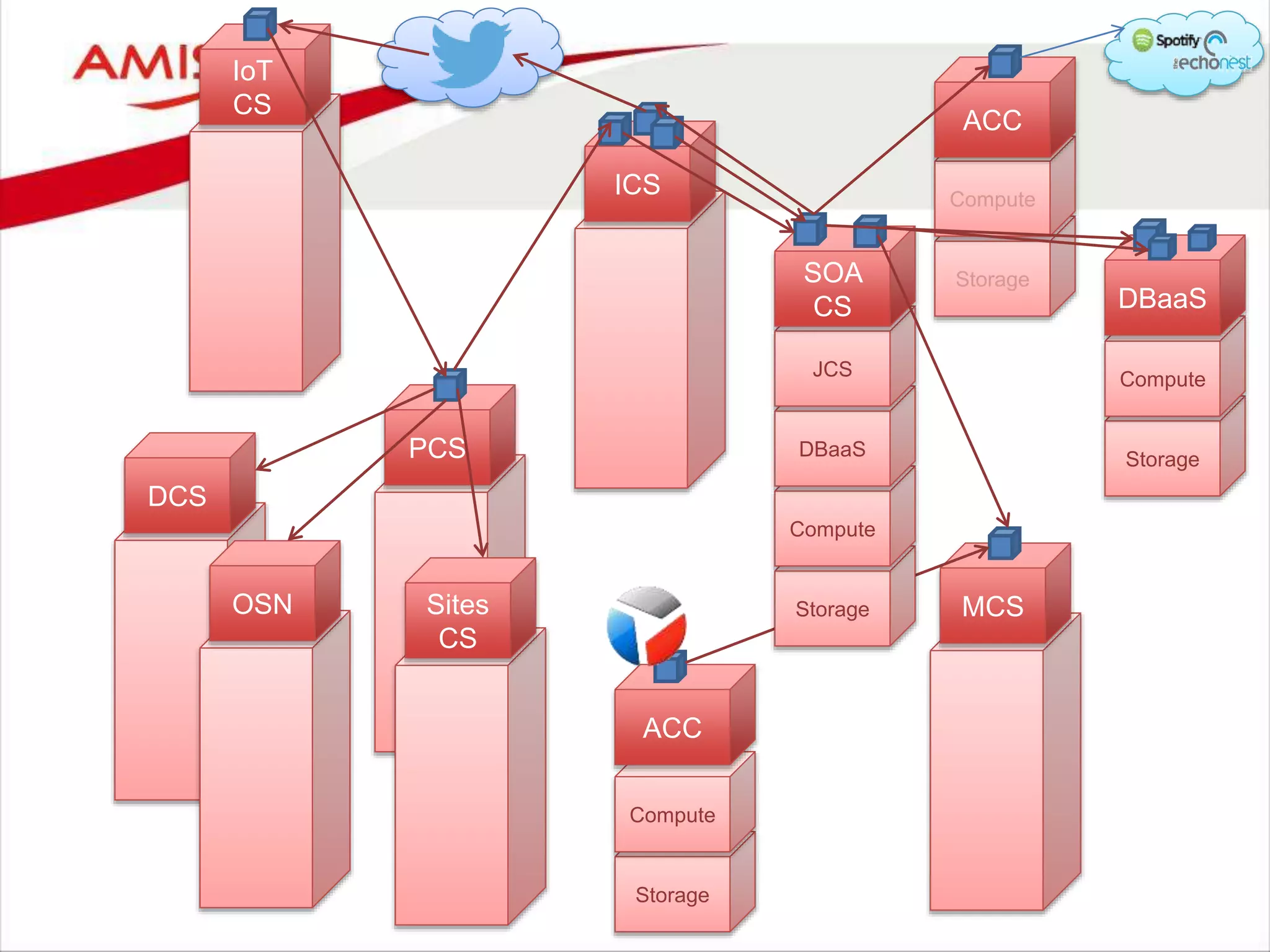
![audience
IoT CS
PCS
DCS
ICS SOA CS
DBaaS
Our
webapp
Storage
CS
OSN?
Real “Things”
(Pis, Arduino’s,
…)
Collect and analyze
audience input;
forward findings to
REST service
Run human workflow
based on suggested
artist; approve/reject,
add image and
description; forward to
REST service
Expose REST API [for PC
to invoke] to register a
proposed artist and a
supporting image; recor
artist details persistently
[with some enrichment]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclearchplatform-warestaatvanpubliccloud-may2016-160518045040/75/The-True-State-of-the-Oracle-Public-Cloud-Dutch-Oracle-Architects-Platform-May-2016-59-2048.jpg)
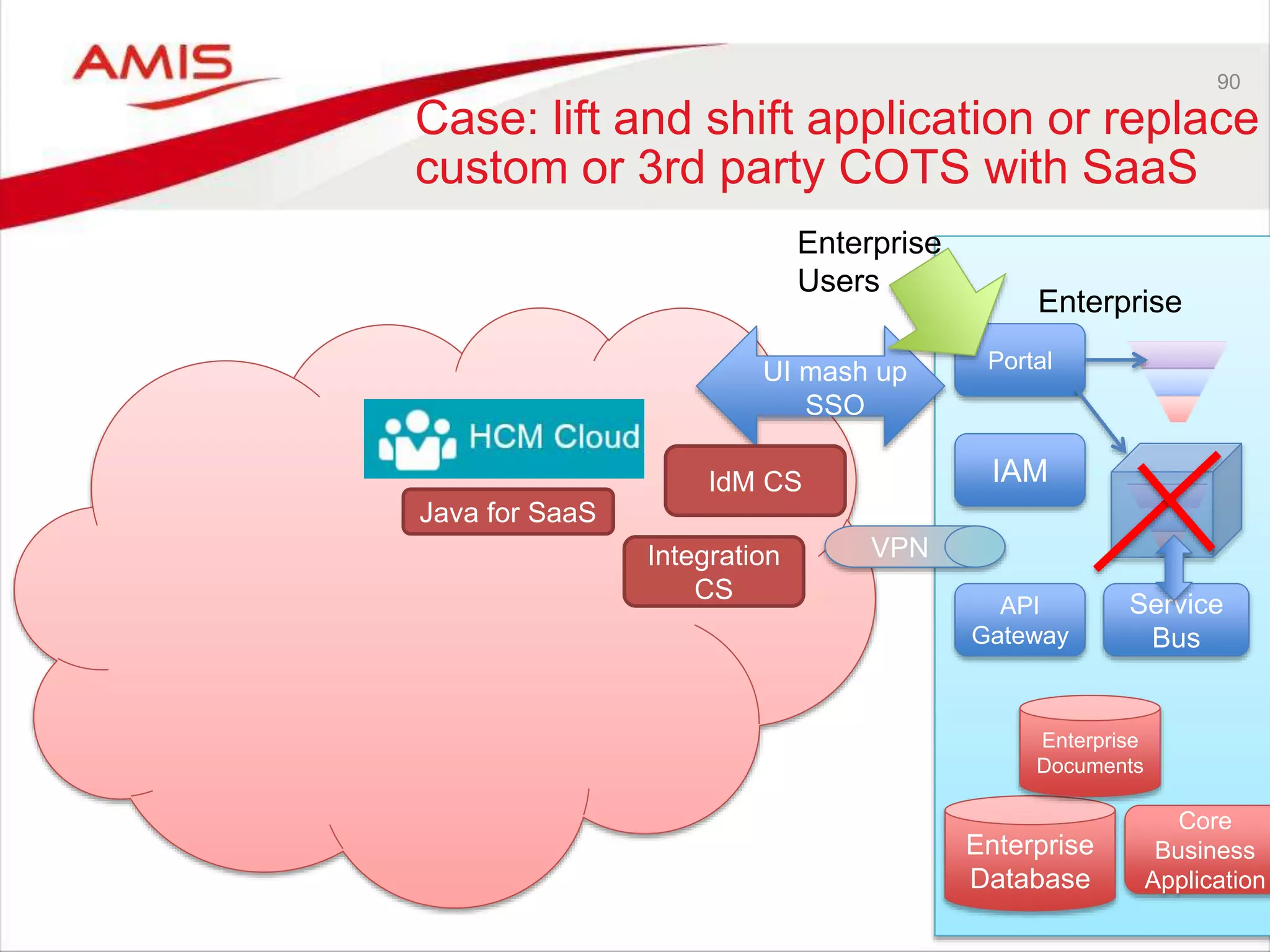
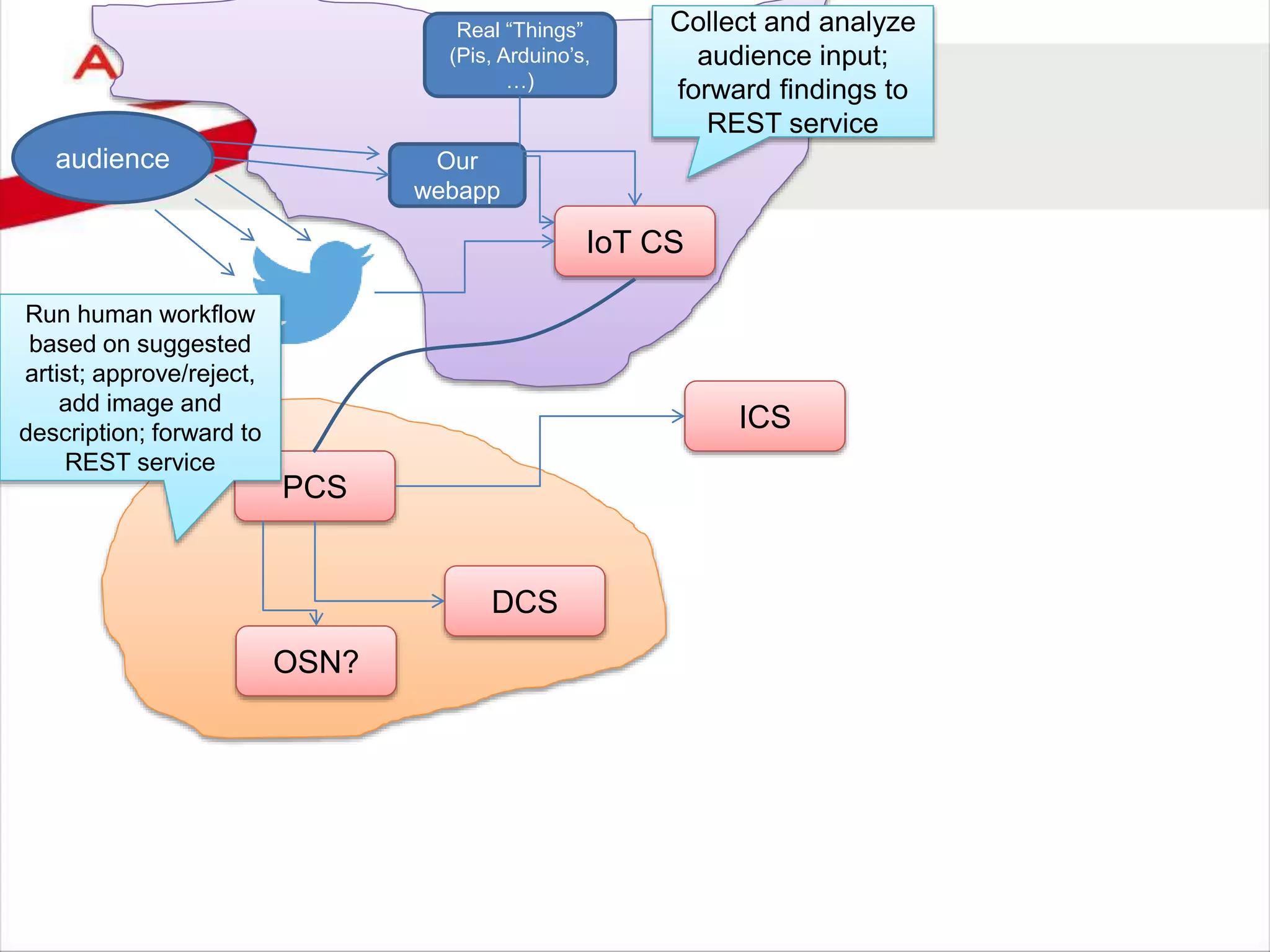
![audience
IoT CS
PCS
DCS
ICS SOA CS
DBaaS
Our
webapp
MCS
Storage
CS
OSN?
Real “Things”
(Pis, Arduino’s,
…)
Collect and analyze
audience input;
forward findings to
REST service
Run human workflow
based on suggested
artist; approve/reject,
add image and
description; forward to
REST service
Publish REST APIs that
expose data on proposed
artists including the selected
image
(could be from MCS, ICS, JCS,
ABCS or SOA CS)
Expose REST API [for PC
to invoke] to register a
proposed artist and a
supporting image; recor
artist details persistently
[with some enrichment]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclearchplatform-warestaatvanpubliccloud-may2016-160518045040/75/The-True-State-of-the-Oracle-Public-Cloud-Dutch-Oracle-Architects-Platform-May-2016-60-2048.jpg)
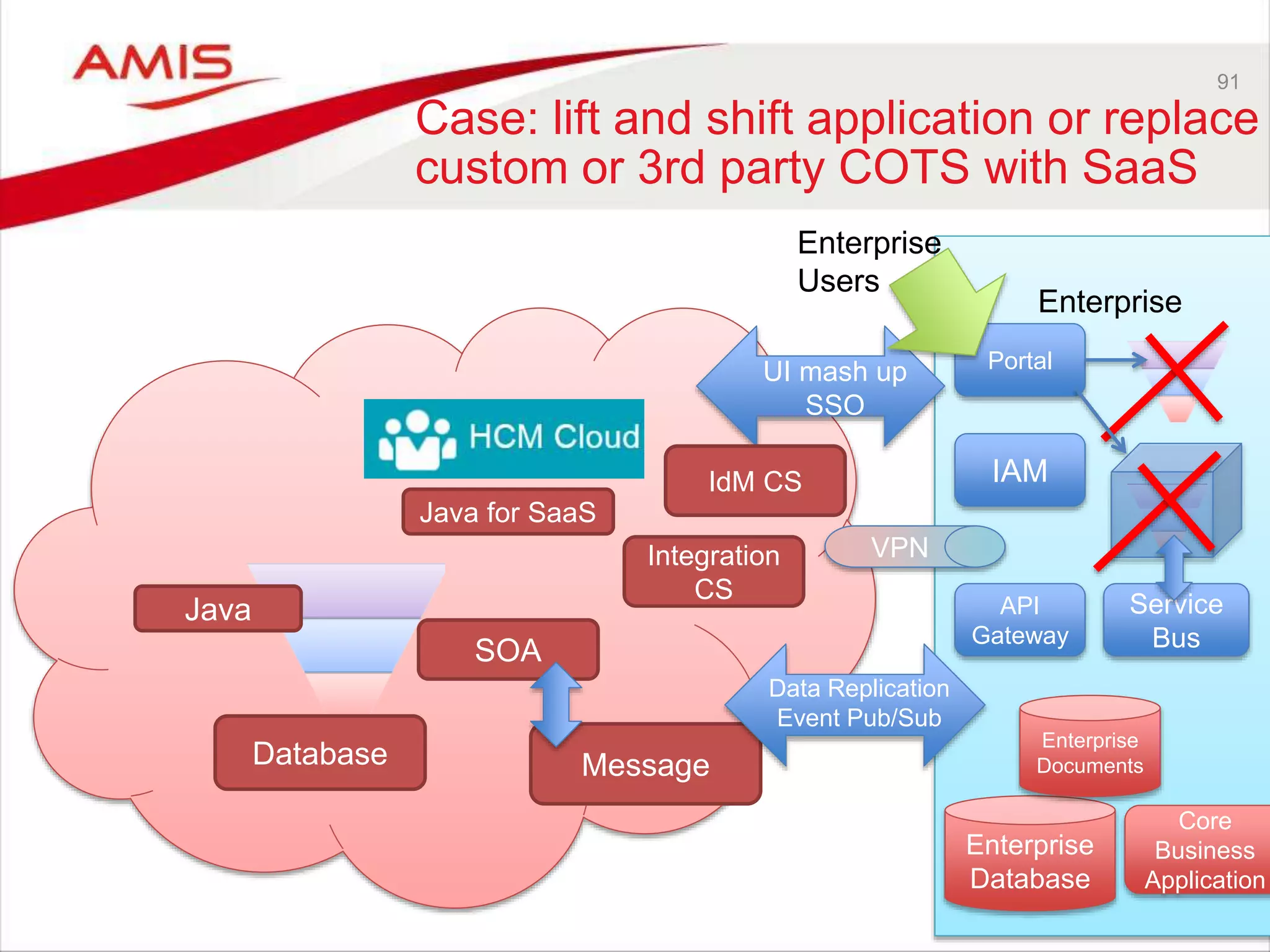
![audience
Some script
(SoapUI,
Postman)
IoT CS
PCS
DCS
ICS SOA CS
DBaaS
Our
webapp
MCS
JET on
AppContainer CS (or
JCS)
ABCS
Storage
CS
OSN?
Real “Things”
(Pis, Arduino’s,
…)
Collect and analyze
audience input;
forward findings to
REST service
Run human workflow
based on suggested
artist; approve/reject,
add image and
description; forward to
REST service
Expose User Interface that
contains the proposed artist
with some enrichment,
based on REST APIs
(exposed from MCS, ICS, JCS,
ABCS or SOA CS)
Publish REST APIs that
expose data on proposed
artists including the selected
image
(could be from MCS, ICS, JCS,
ABCS or SOA CS)
Expose REST API [for PC
to invoke] to register a
proposed artist and a
supporting image; recor
artist details persistently
[with some enrichment]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclearchplatform-warestaatvanpubliccloud-may2016-160518045040/75/The-True-State-of-the-Oracle-Public-Cloud-Dutch-Oracle-Architects-Platform-May-2016-61-2048.jpg)





![71
Cloud adoption in
bottom-up steps
IaaS/PaaS
Self study
PoC
Training
Load Test
Func Test
Peak, Failover
Peripheral Applications
Backup
BI
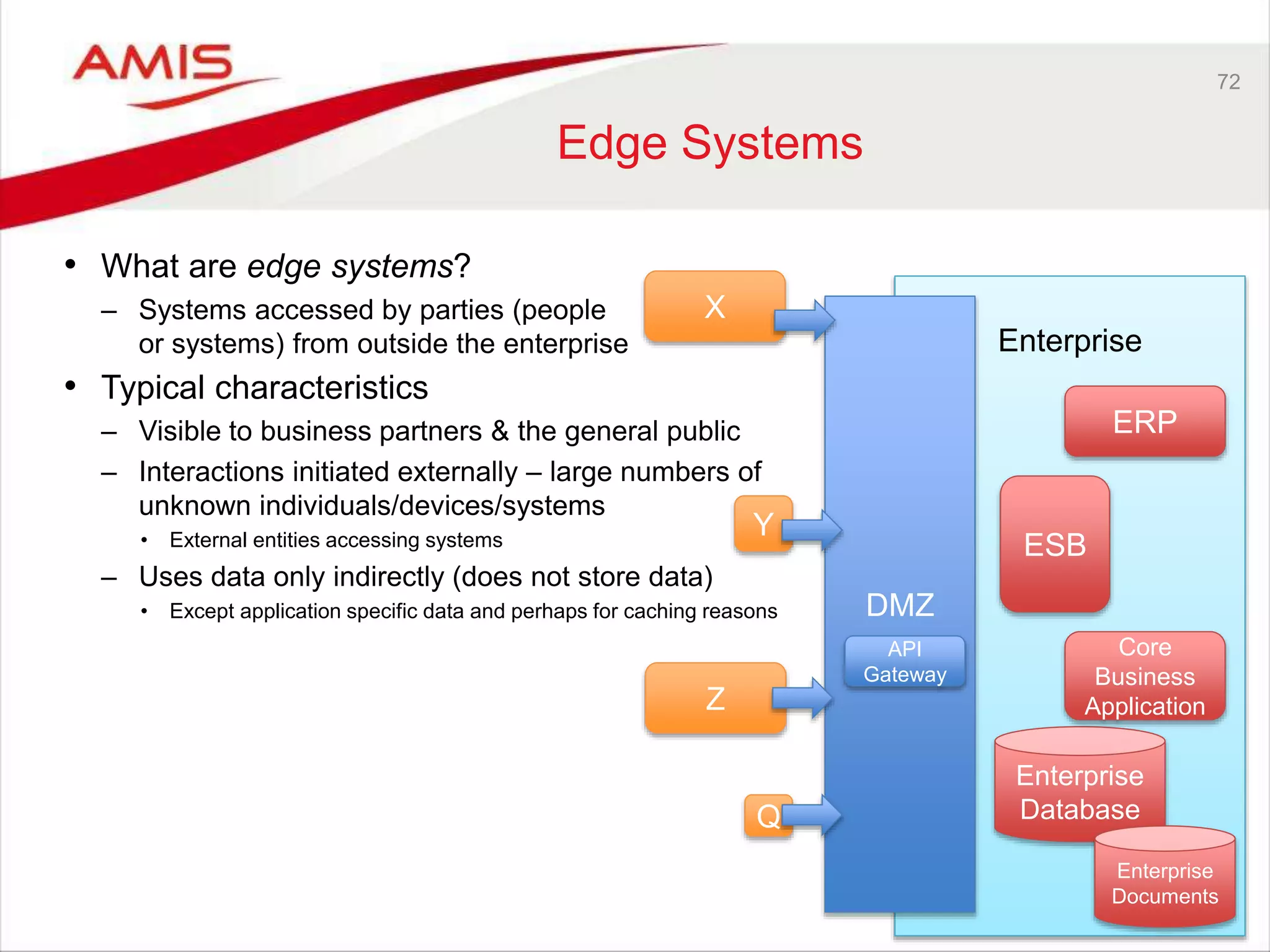
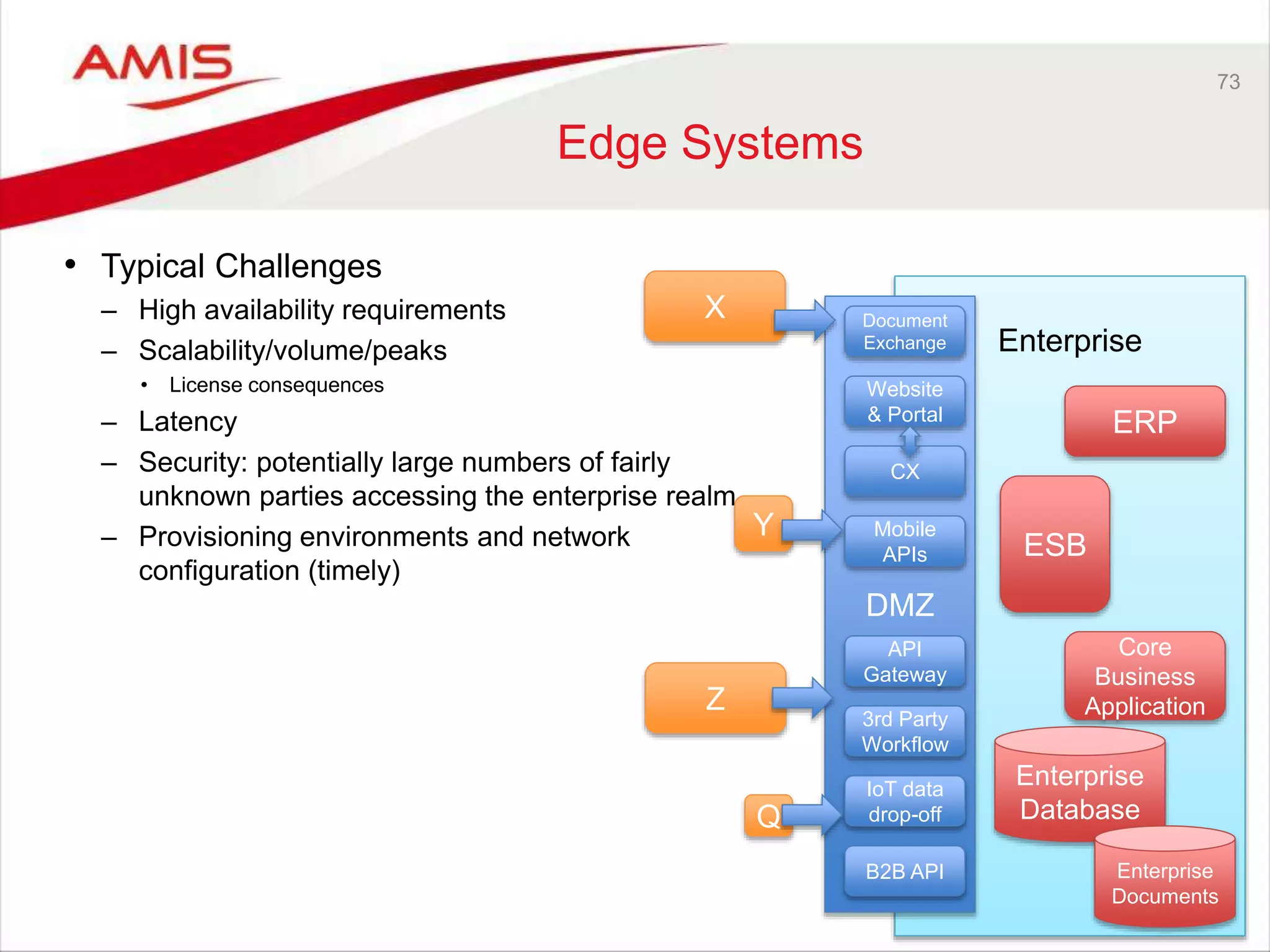
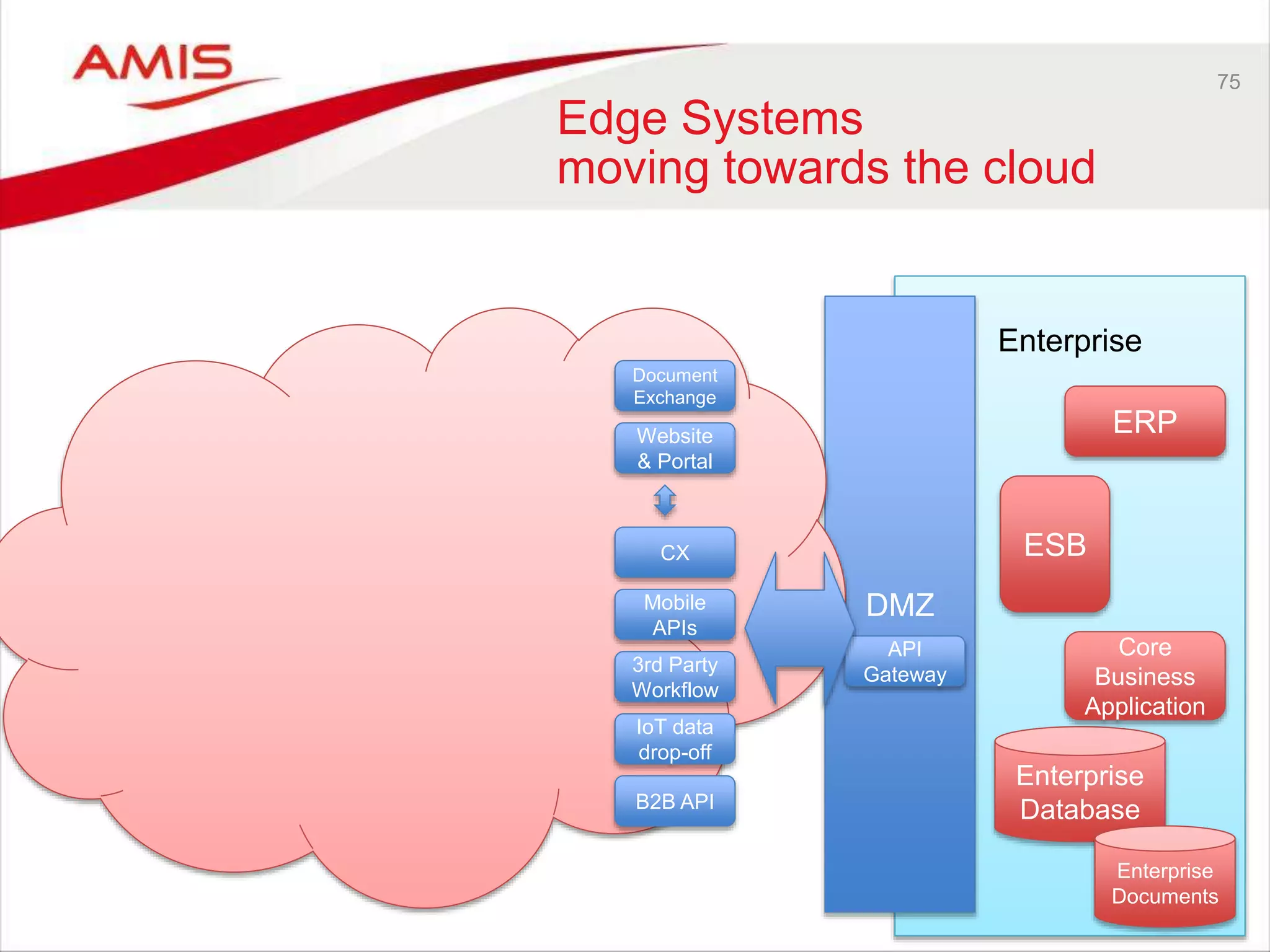
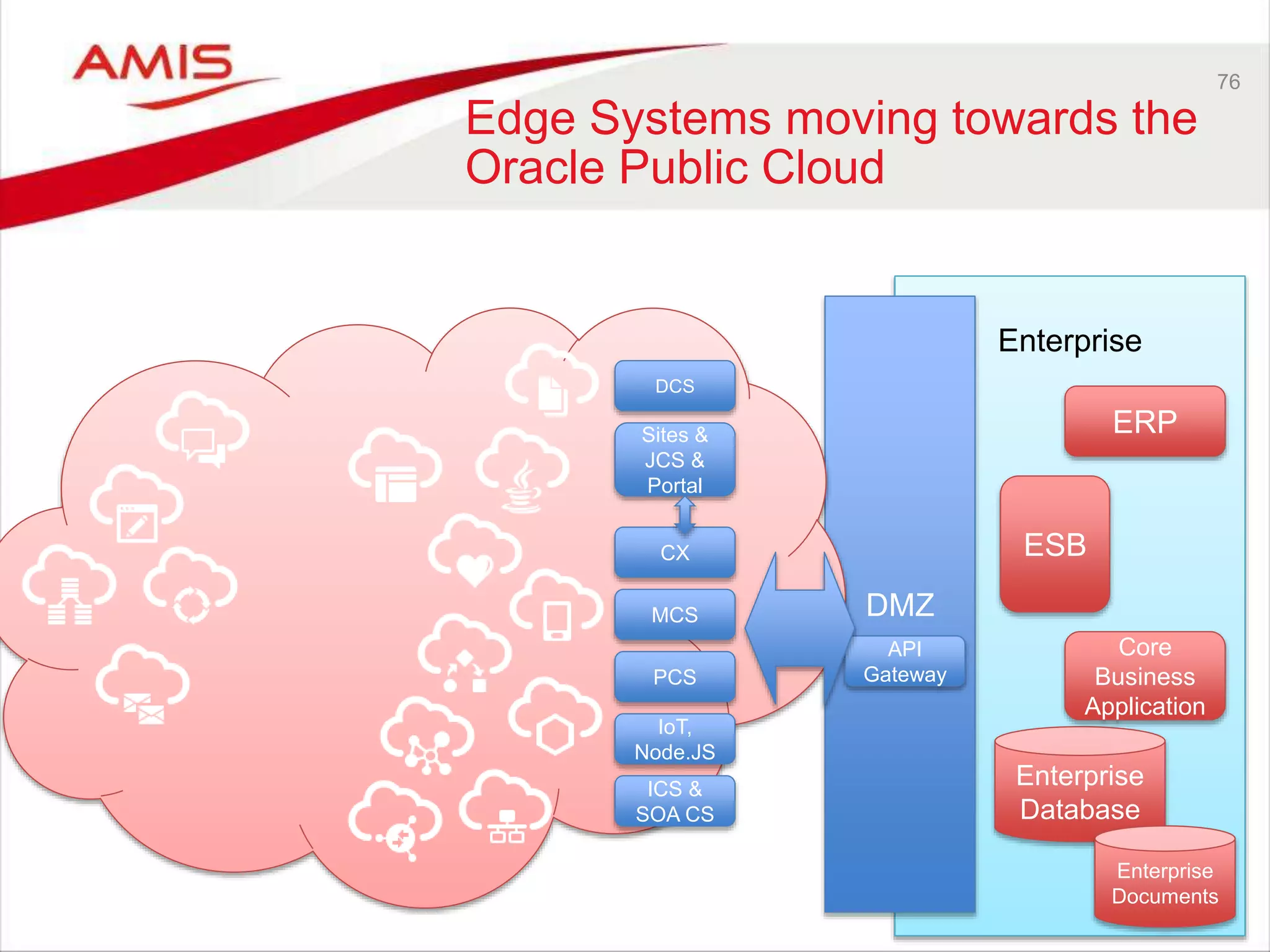
Edge Systems
Core Systems & Secure Data
[Distributed] Development
BPO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclearchplatform-warestaatvanpubliccloud-may2016-160518045040/75/The-True-State-of-the-Oracle-Public-Cloud-Dutch-Oracle-Architects-Platform-May-2016-71-2048.jpg)