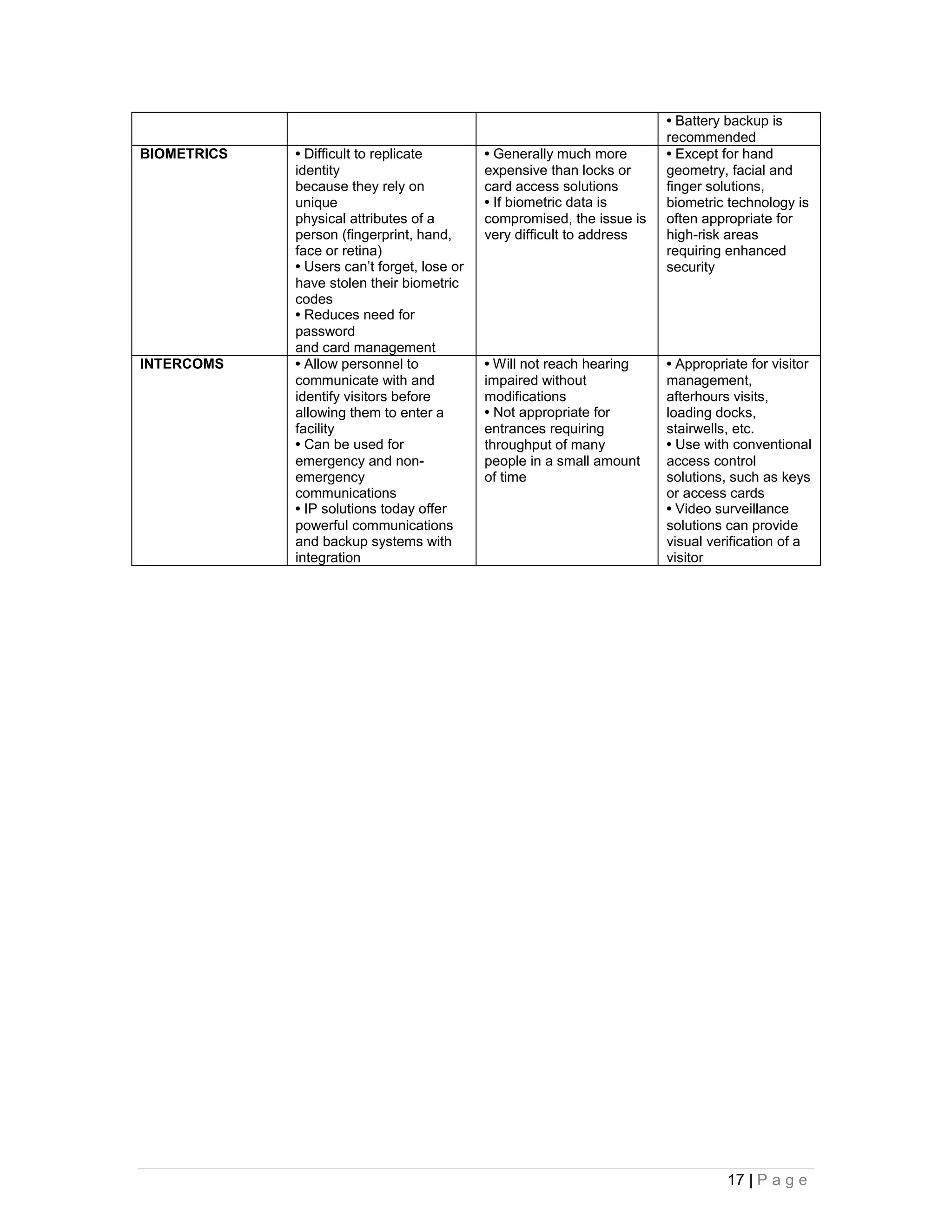
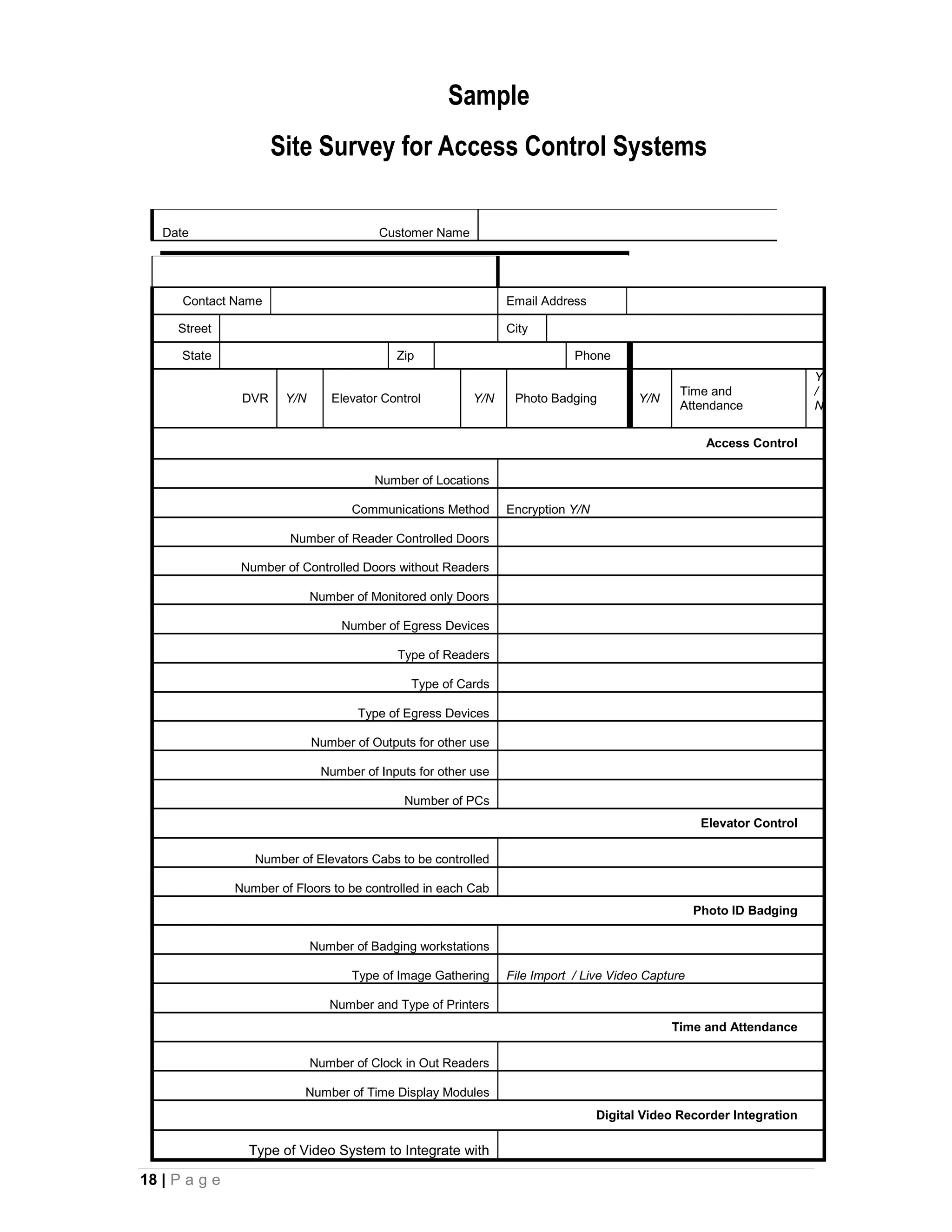
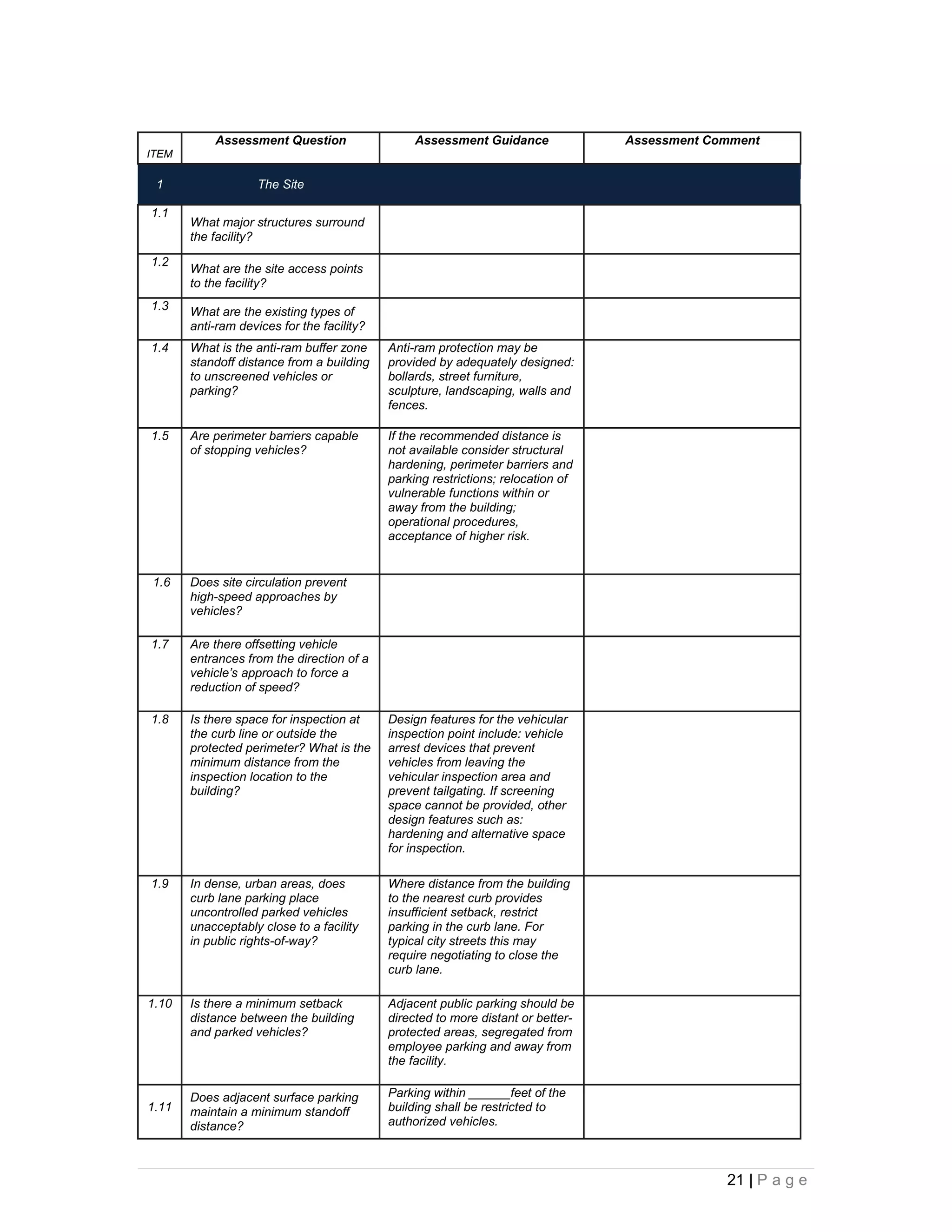
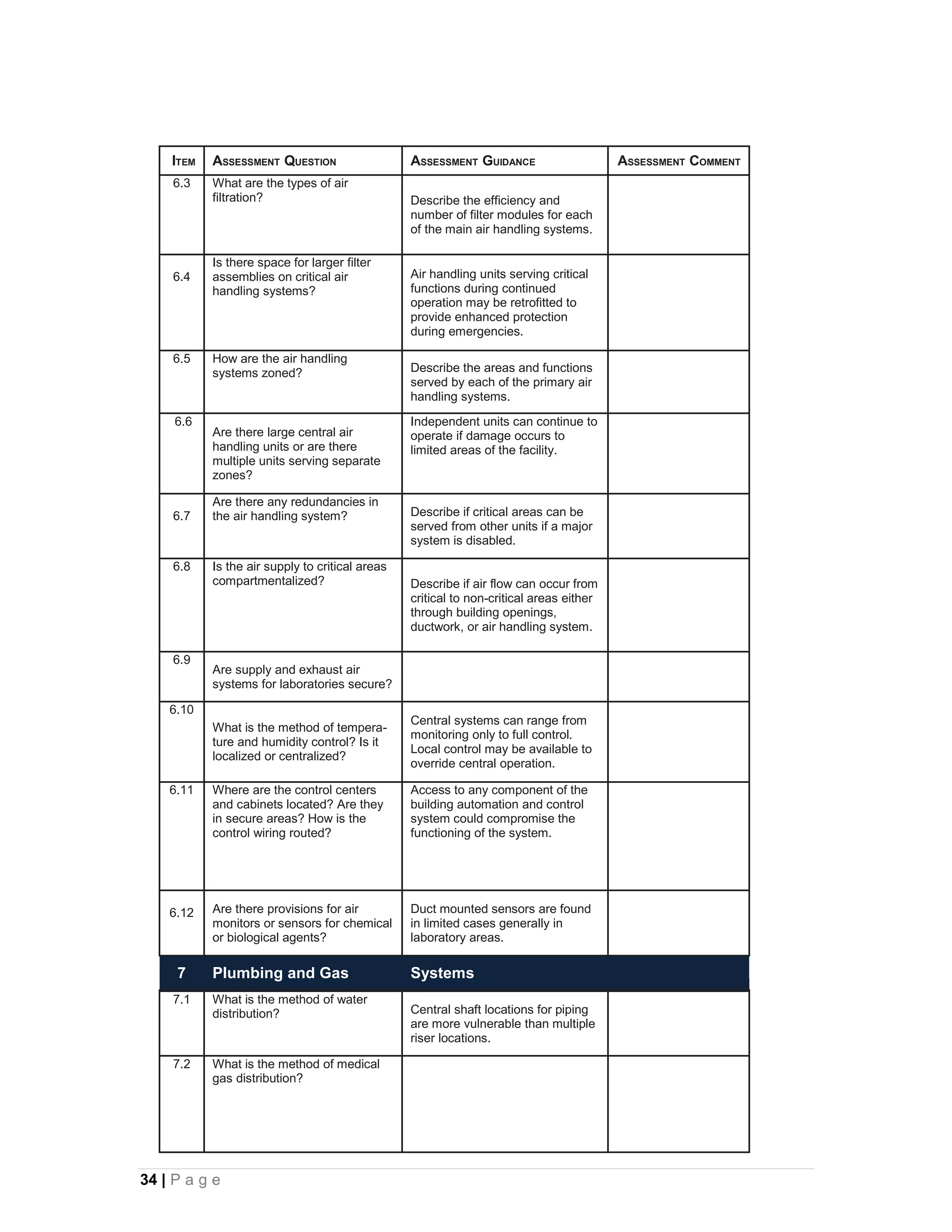
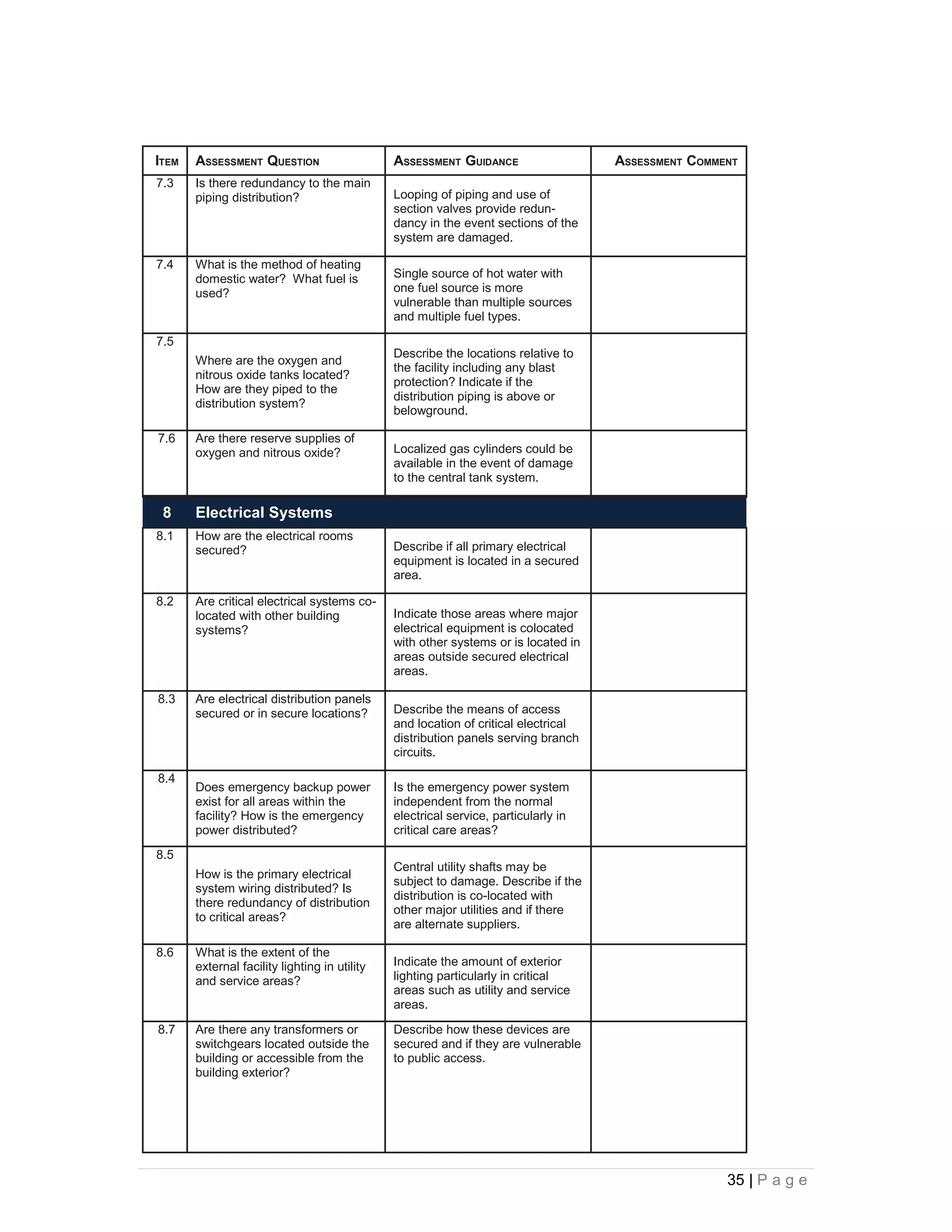
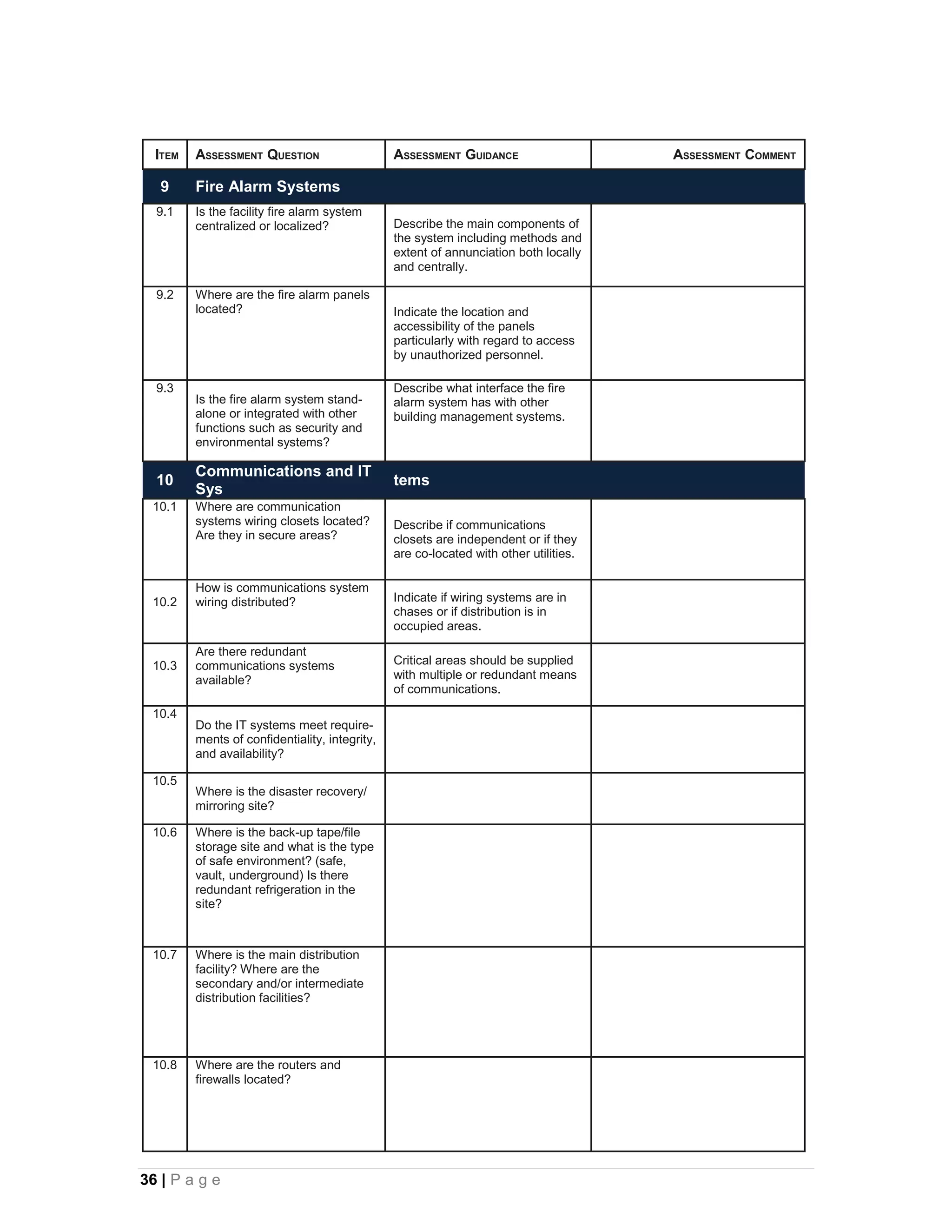
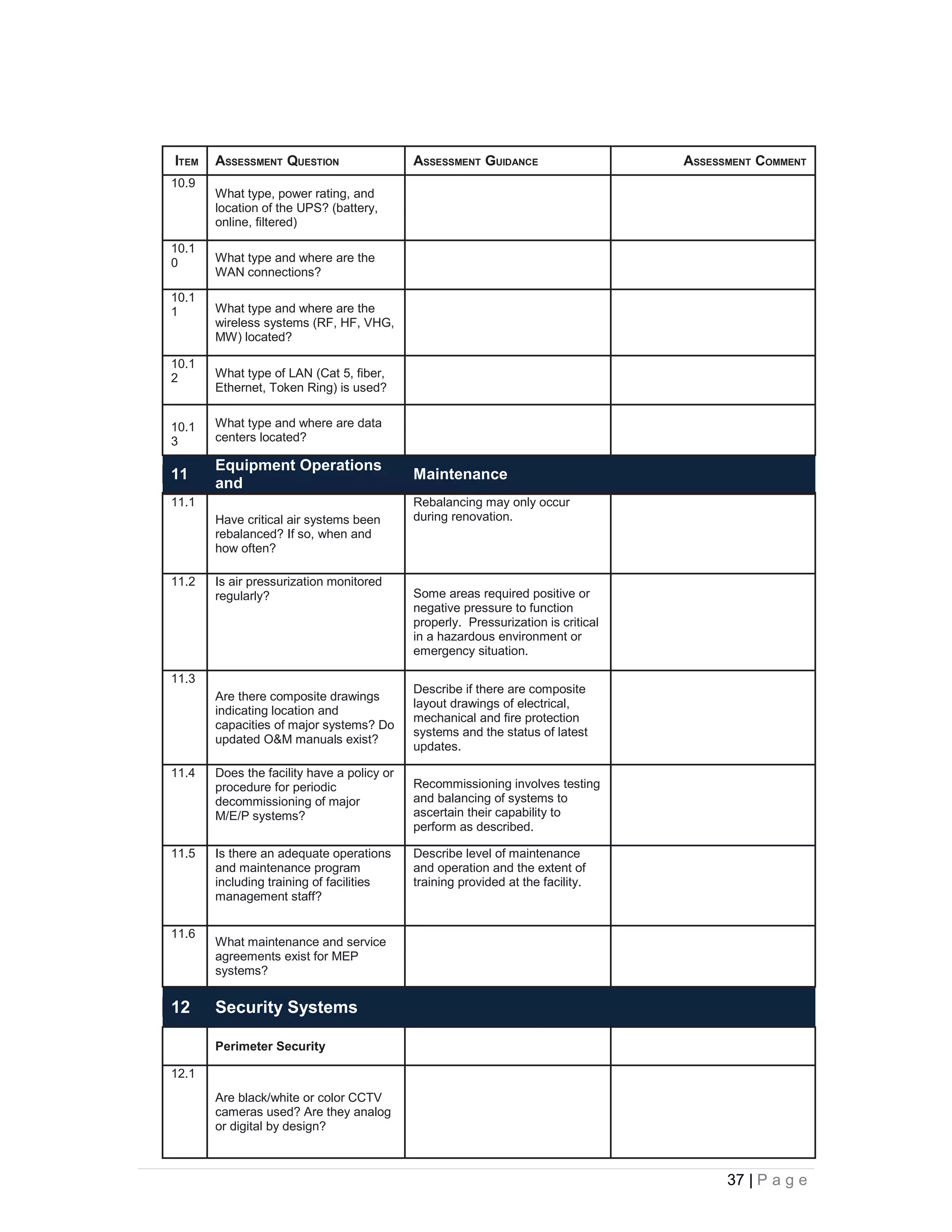
This document provides an overview of physical security best practices for protecting facilities and critical infrastructure. It discusses implementing a risk assessment and physical security program that identifies threats, assesses vulnerabilities, evaluates countermeasures, and manages risk through a continuous cycle. The document also outlines federal policies regarding critical infrastructure protection and the 18 identified critical infrastructure sectors. Key physical security technologies and an example design solution checklist for securing a data center are presented to illustrate applying security principles.