The document discusses the future of JavaScript and the ECMAScript 4 (ES4) specification. Some key points:
- ES4 will introduce classes, inheritance, and other object-oriented features to JavaScript to make it suitable for large applications.
- A new virtual machine called Tamarin is being developed by Adobe and will power future versions of JavaScript across browsers.
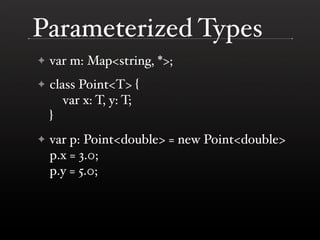
- Features like classes, packages, generics and operator overloading are described. The specification aims to make JavaScript more powerful while keeping it usable for small programs.
- The reference implementations of new JavaScript classes and features will be written in JavaScript itself, allowing the language to be self-hosting.



















![Function Types
✦ Only return specific types:
function isValid() : boolean { }
✦ Only be used on certain objects types:
function every( this: Array ) {
for ( var i = 0; i < this.length; i++ )
alert( this[i] );
}
every.call( [0,1,2] );
// alert(0); alert(1); alert(2);
every.call({a: “b”});
// ERROR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/future-of-js-130228085740-phpapp02/85/The-Future-of-JavaScript-Ajax-Exp-07-23-320.jpg)
![Rest Arguments
✦ function stuff( name, ...values ){
alert( values.length );
}
✦ stuff( “John”, 1, 2, 3, 4 );
// alert( 4 );
✦ function stuff( name : string, ...values :
[int] )
: void {
alert( values.length );
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/future-of-js-130228085740-phpapp02/85/The-Future-of-JavaScript-Ajax-Exp-07-24-320.jpg)




![“like”
✦ type Point = { x: int, y: int };
✦ if ( { x: 3, y: 5 } like Point )
alert( “That looks like a point to me!” );
✦ if ( !({ x: 3 } like Point) )
alert( “Not a point!” );
✦ // Loop over array-like things:
function every( a: like { length: int } ) {
for ( var i = 0; i < a.length; i++ )
alert( a[i] );
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/future-of-js-130228085740-phpapp02/85/The-Future-of-JavaScript-Ajax-Exp-07-29-320.jpg)


![let statements
✦ for ( let i = 0; i < a.length; i++ )
alert( a[i] );
typeof i == “undefined”
✦ Using block statements:
{
let x = 5;
{
let x = 6;
alert( x ); // 6
}
alert( x ); // 5
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/future-of-js-130228085740-phpapp02/85/The-Future-of-JavaScript-Ajax-Exp-07-33-320.jpg)






![Iteration
✦ class Fib {
private var a=0, b=1;
iterator function get(deep:boolean = false) : IteratorType.<int>
this
public function next(): int {
if ( b > 100 )
throw iterator::StopIteration;
[a,b] = [b,a+b];
return a;
}
}
✦ for ( let i in new Fib )
alert( i );](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/future-of-js-130228085740-phpapp02/85/The-Future-of-JavaScript-Ajax-Exp-07-40-320.jpg)
![For .. Each
✦ For each loops through values
✦ let s = “”;
for each ( let n in [“a”,”b”,”c”] )
s += n;
alert(s);
// “abc”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/future-of-js-130228085740-phpapp02/85/The-Future-of-JavaScript-Ajax-Exp-07-41-320.jpg)



