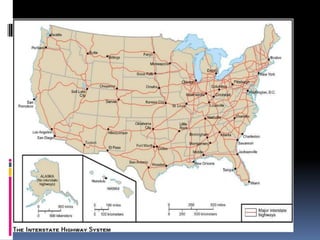
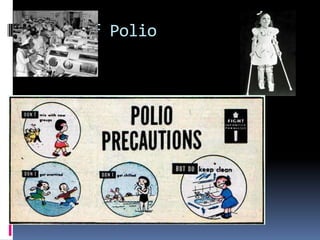
The document discusses the characteristics of life in the United States during the 1950s. It was a time of economic boom fueled by post-war prosperity. Suburban living became the norm as new highways and affordable housing developments like Levittown emerged. Television also rose to prominence during this period, influencing popular culture. However, tensions arose as new youth cultures like rock and roll music developed and rebelled against the conservative social values of the time.