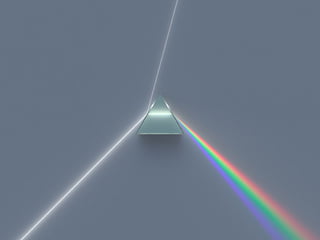
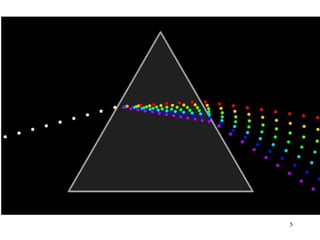
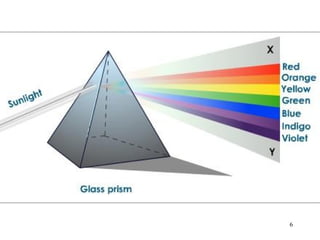
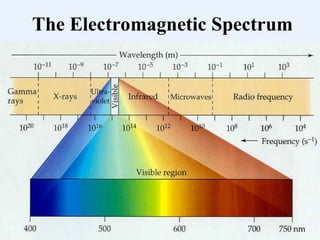
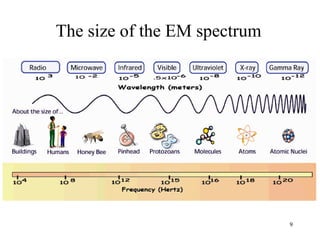
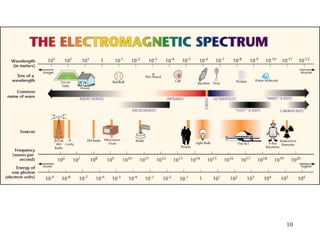
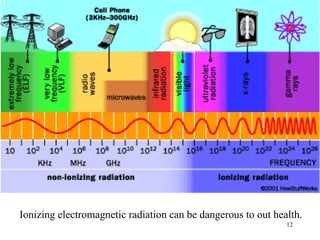
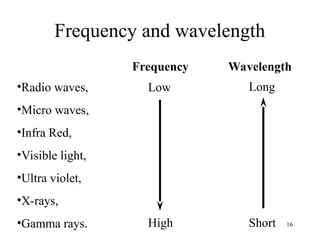
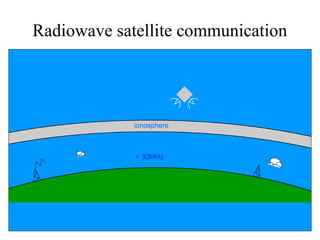
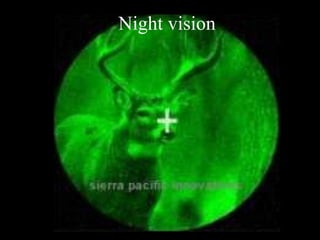
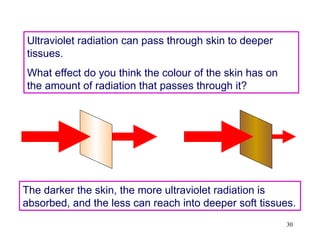
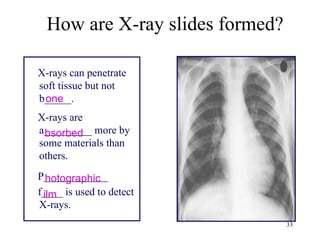
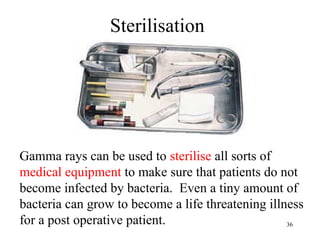
The document explains the electromagnetic spectrum, detailing that light is part of this spectrum which includes various types of radiation, all traveling at the same speed in a vacuum. It covers the order of the spectrum from radio waves to gamma rays, their properties, uses, and associated dangers. Additionally, it discusses the effects of different types of radiation, such as x-rays and gamma rays, on living organisms and their practical applications in technology and medicine.