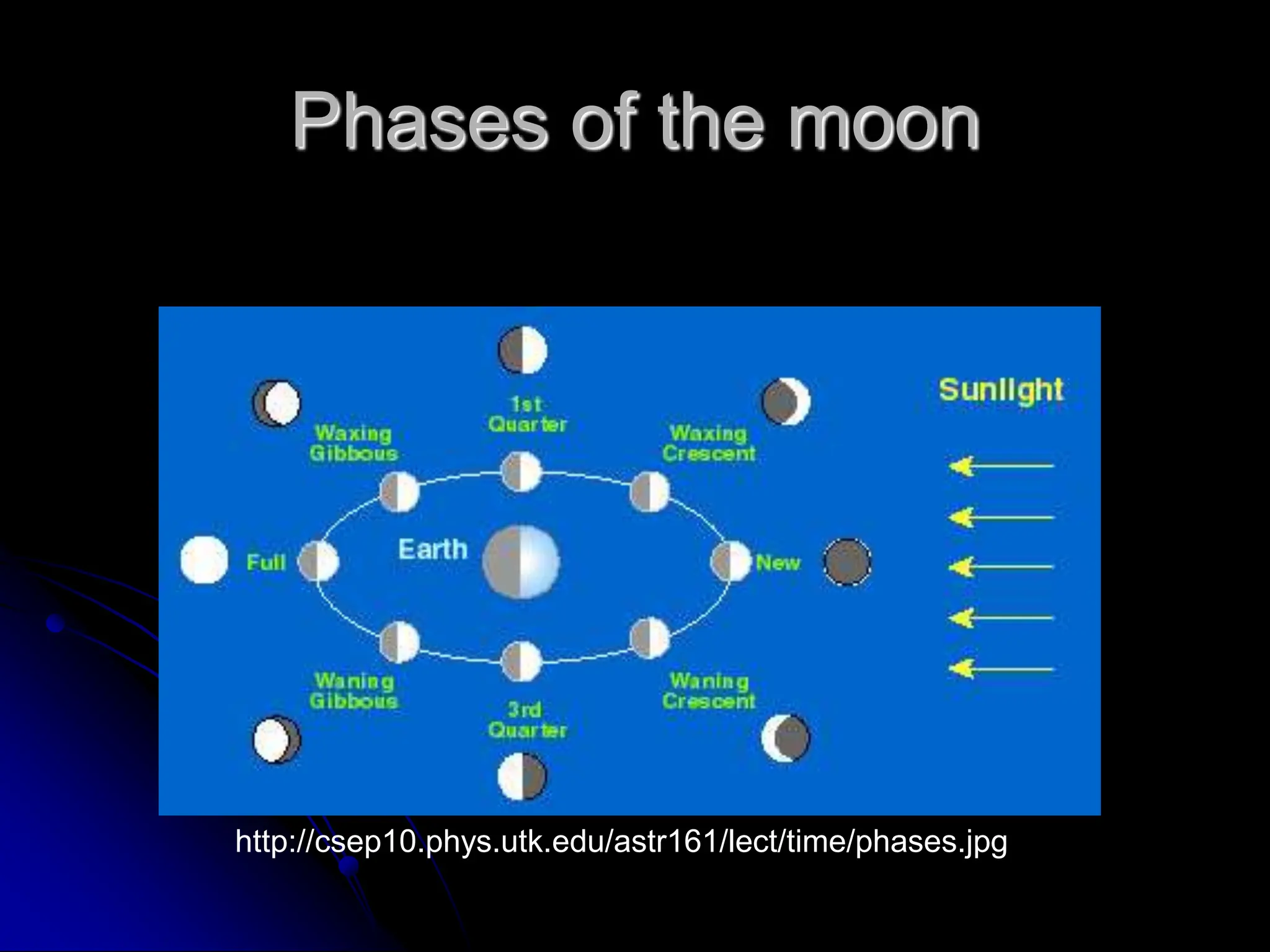
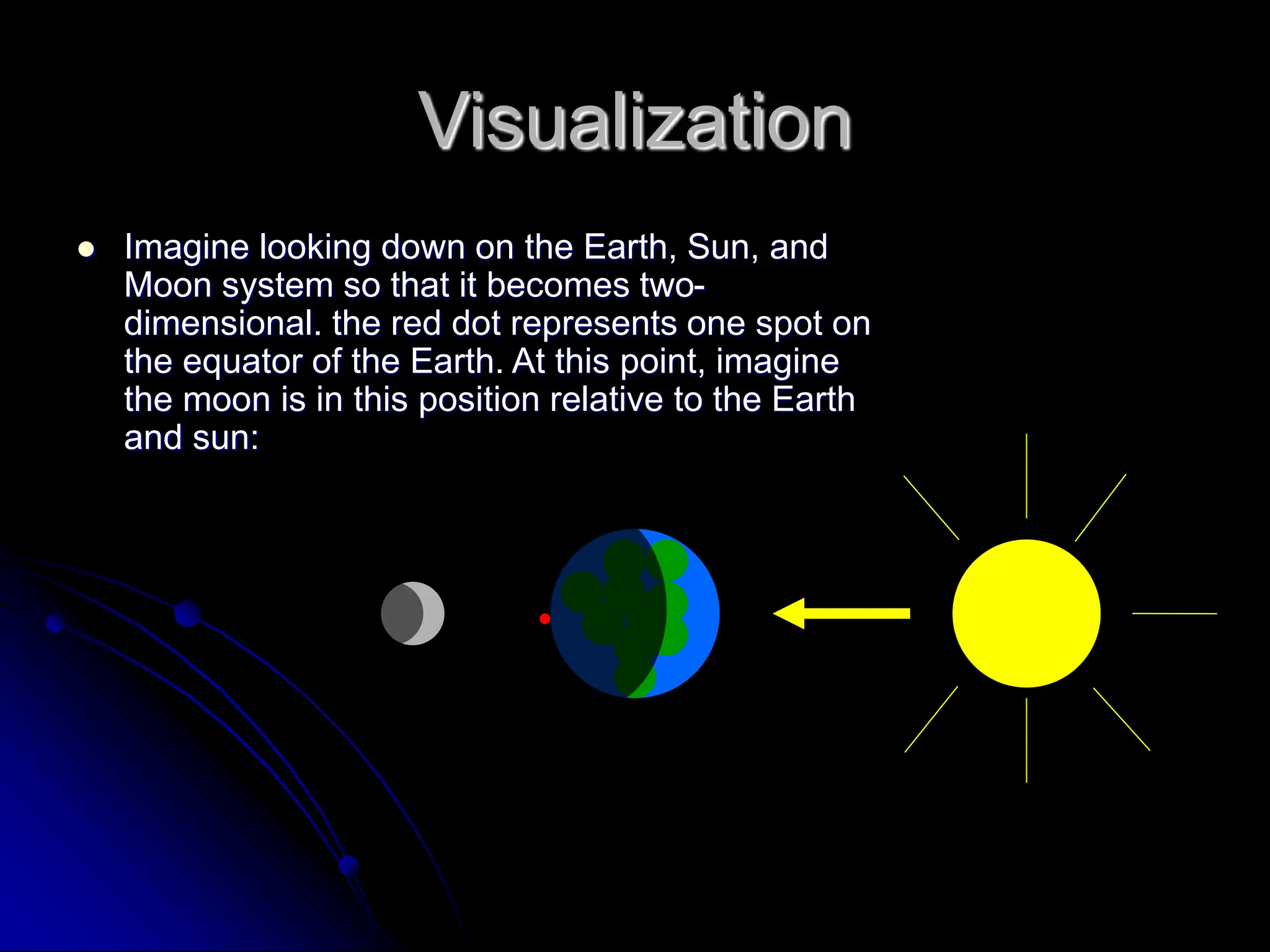
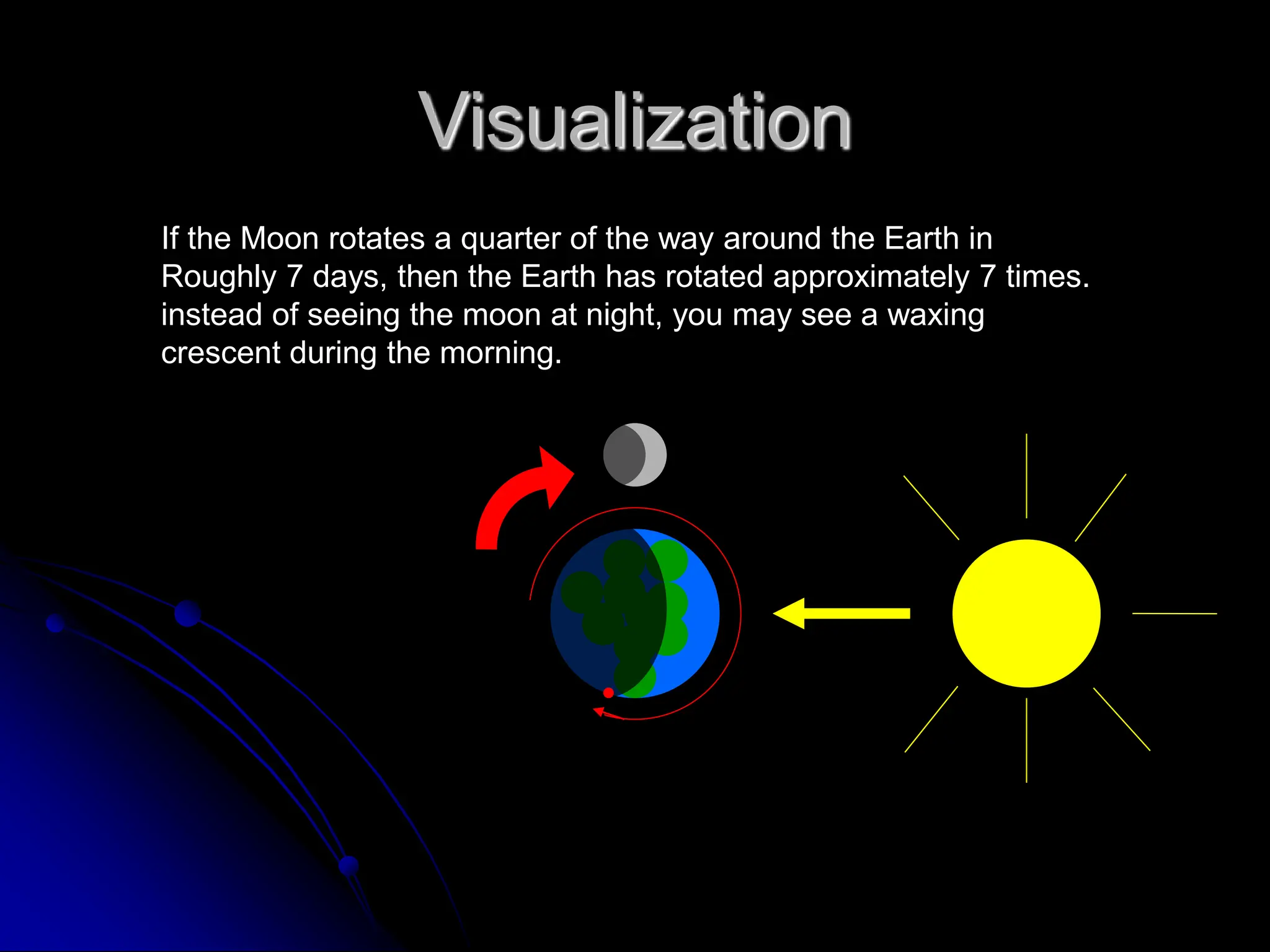
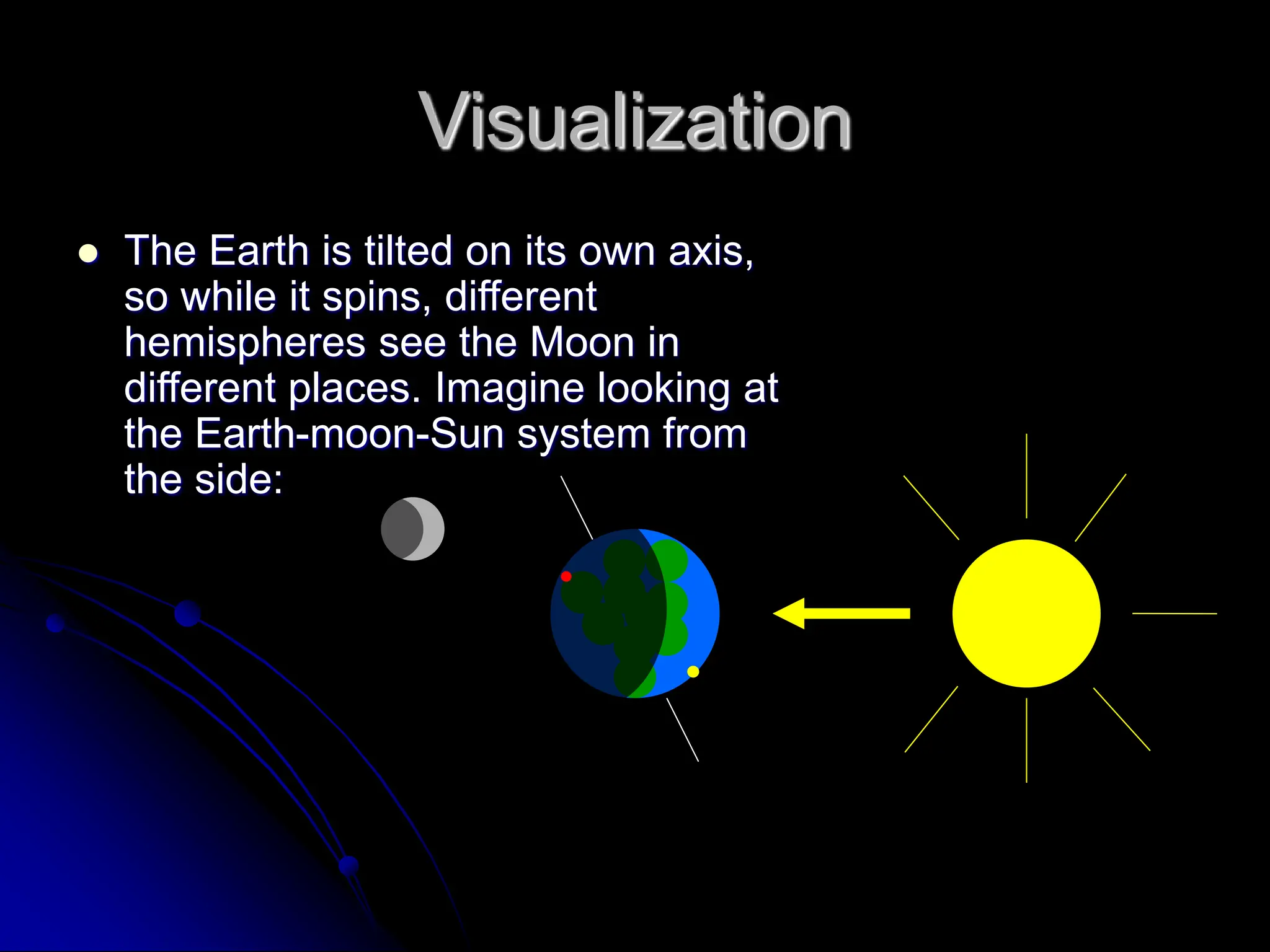
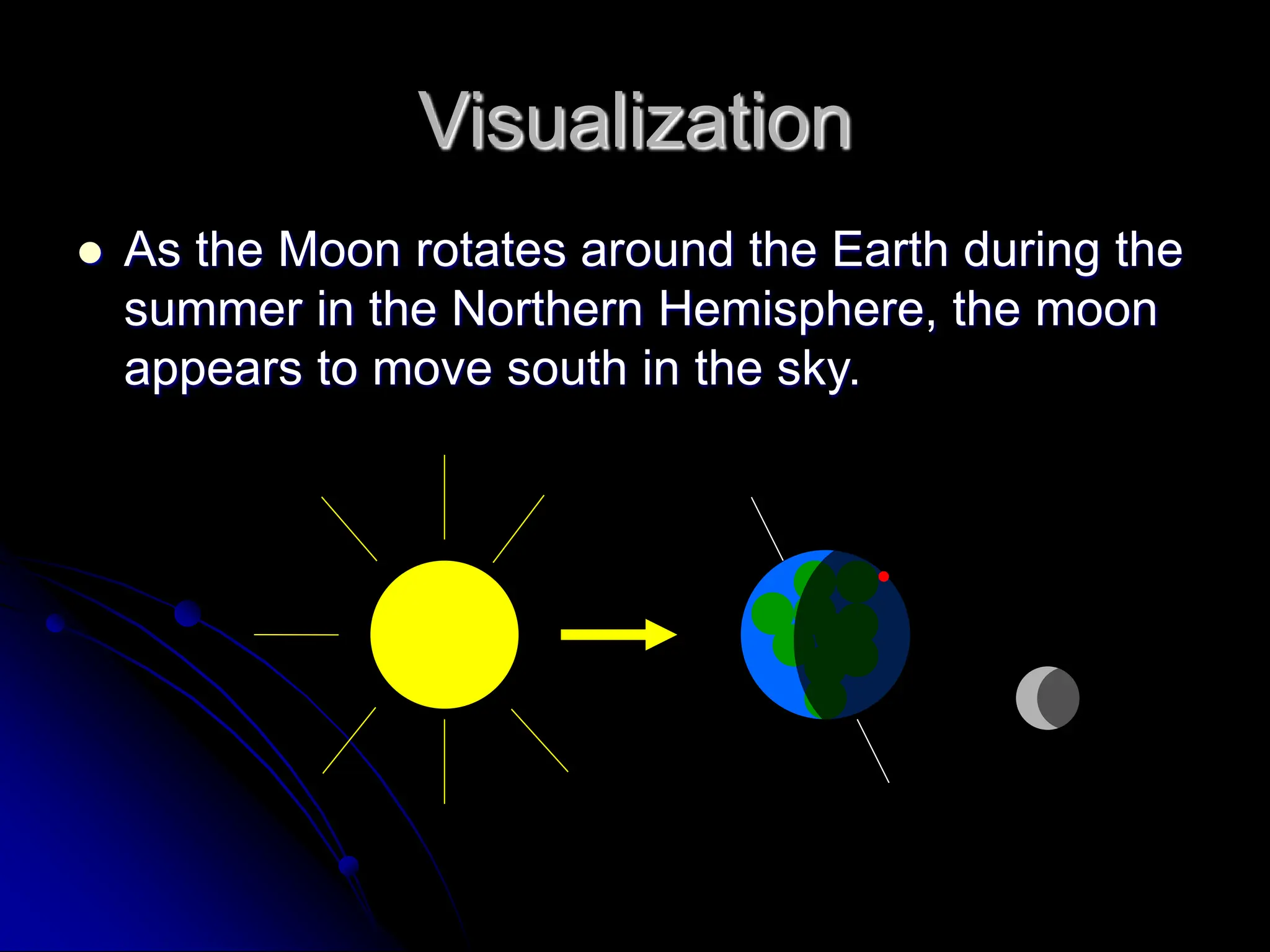
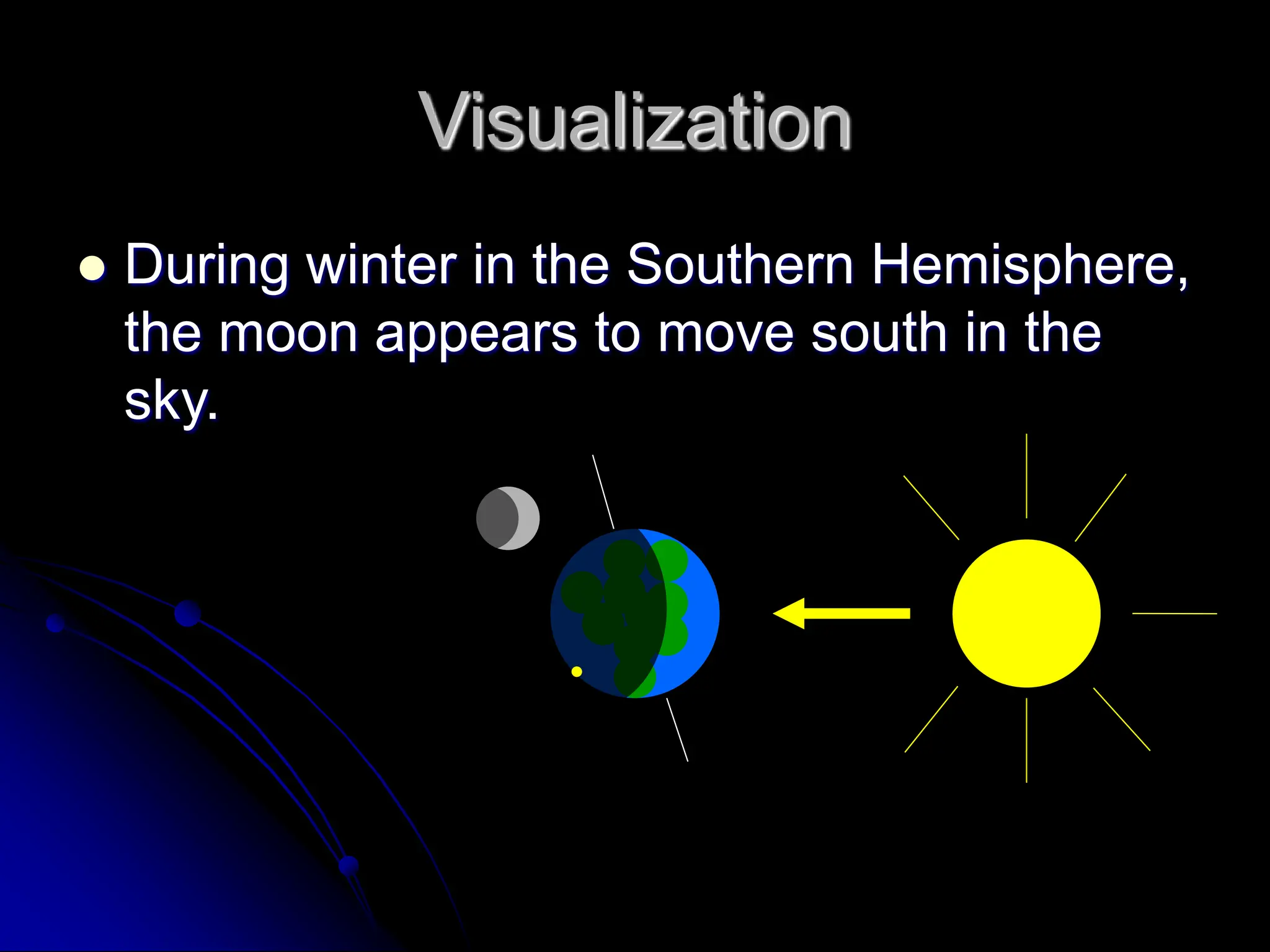
The document explains the cyclical phases of the moon, detailing how its rotation and orbit around the Earth relate to the Earth's rotation. It describes the moon's movement and the resulting phases: full moon, waxing crescent, new moon, and waning crescent, with phases occurring every 27.3 days. Additionally, it discusses how the moon's position in the sky changes with the seasons due to the tilt of the Earth's axis.