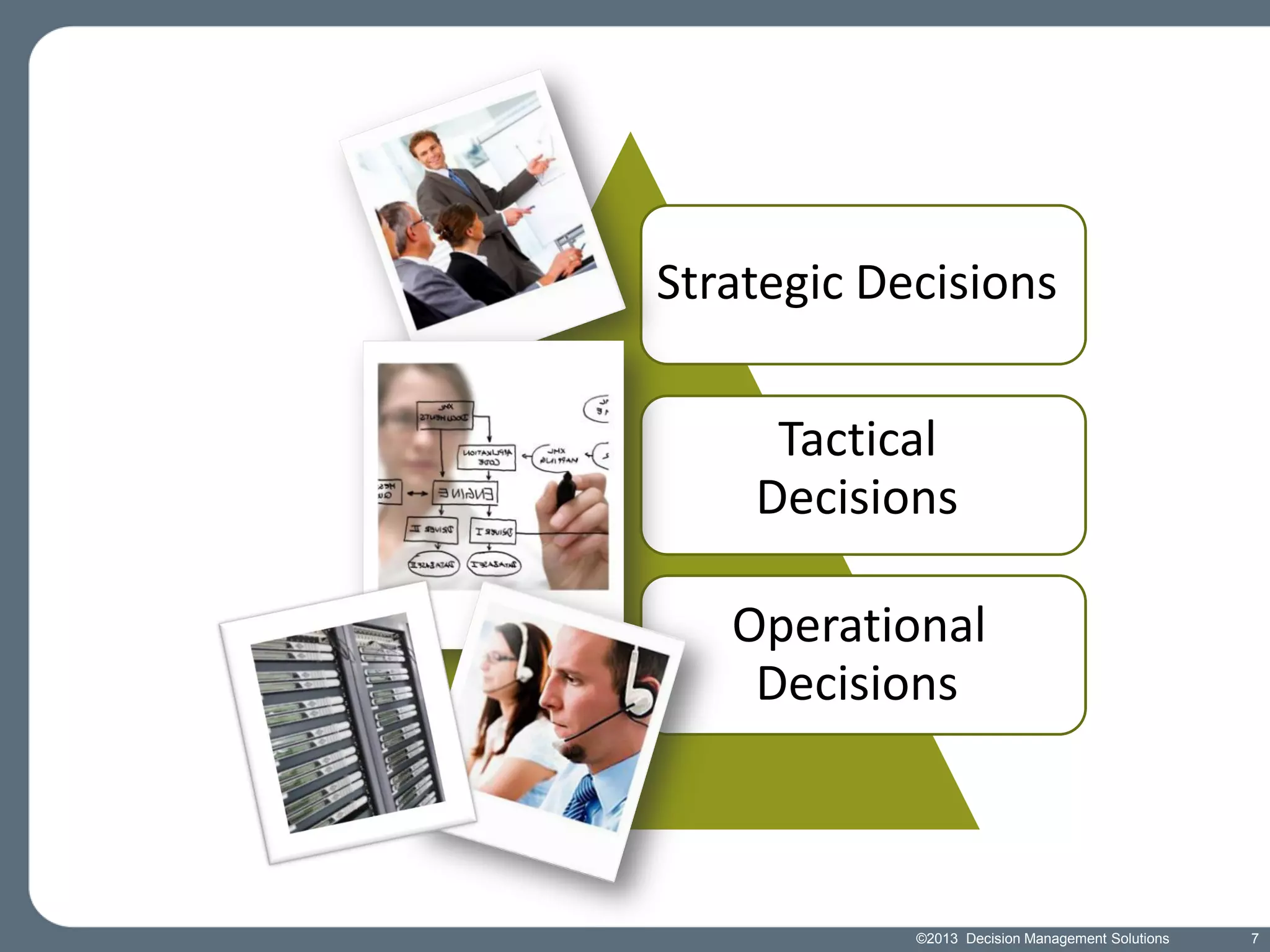
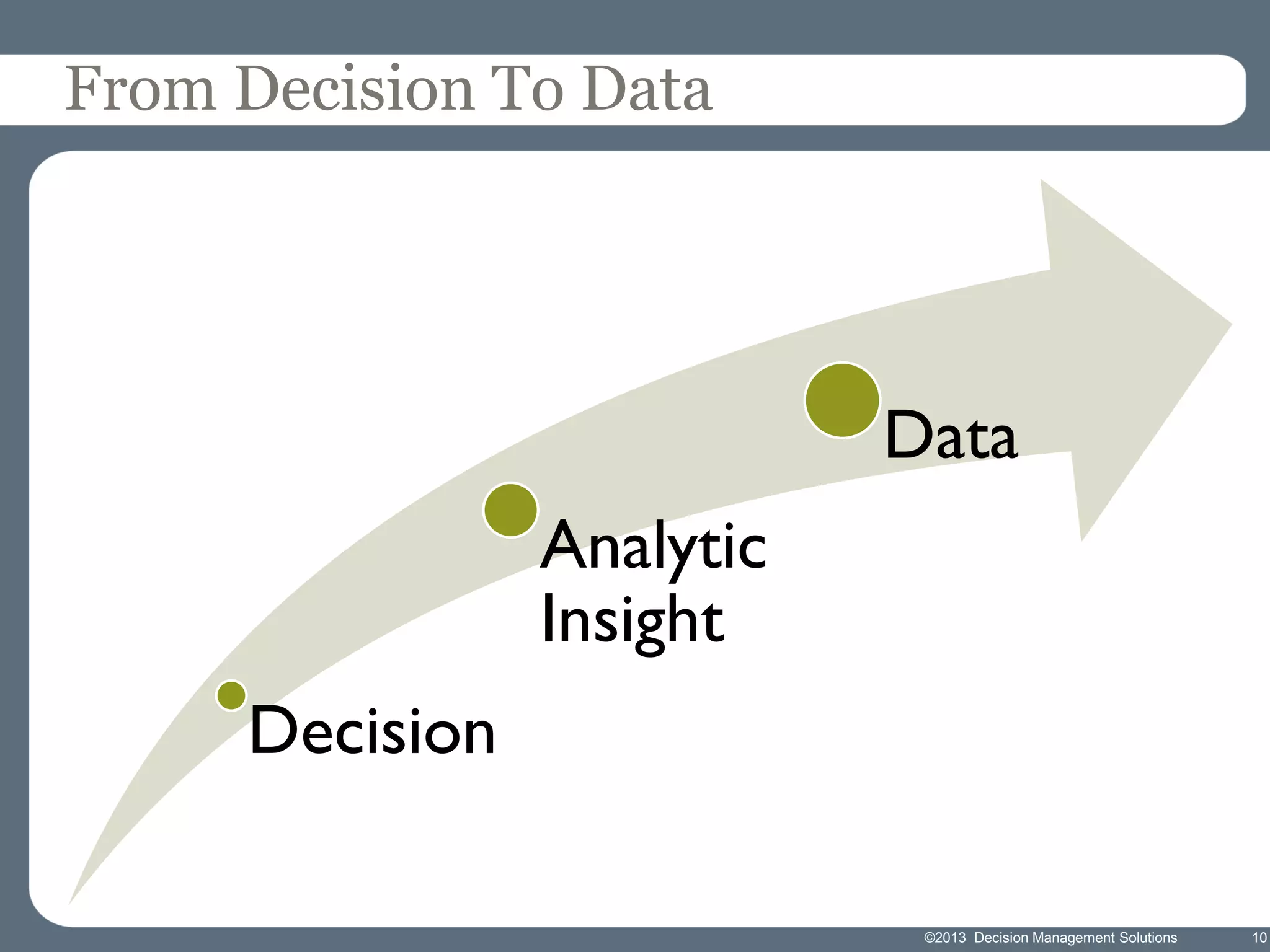
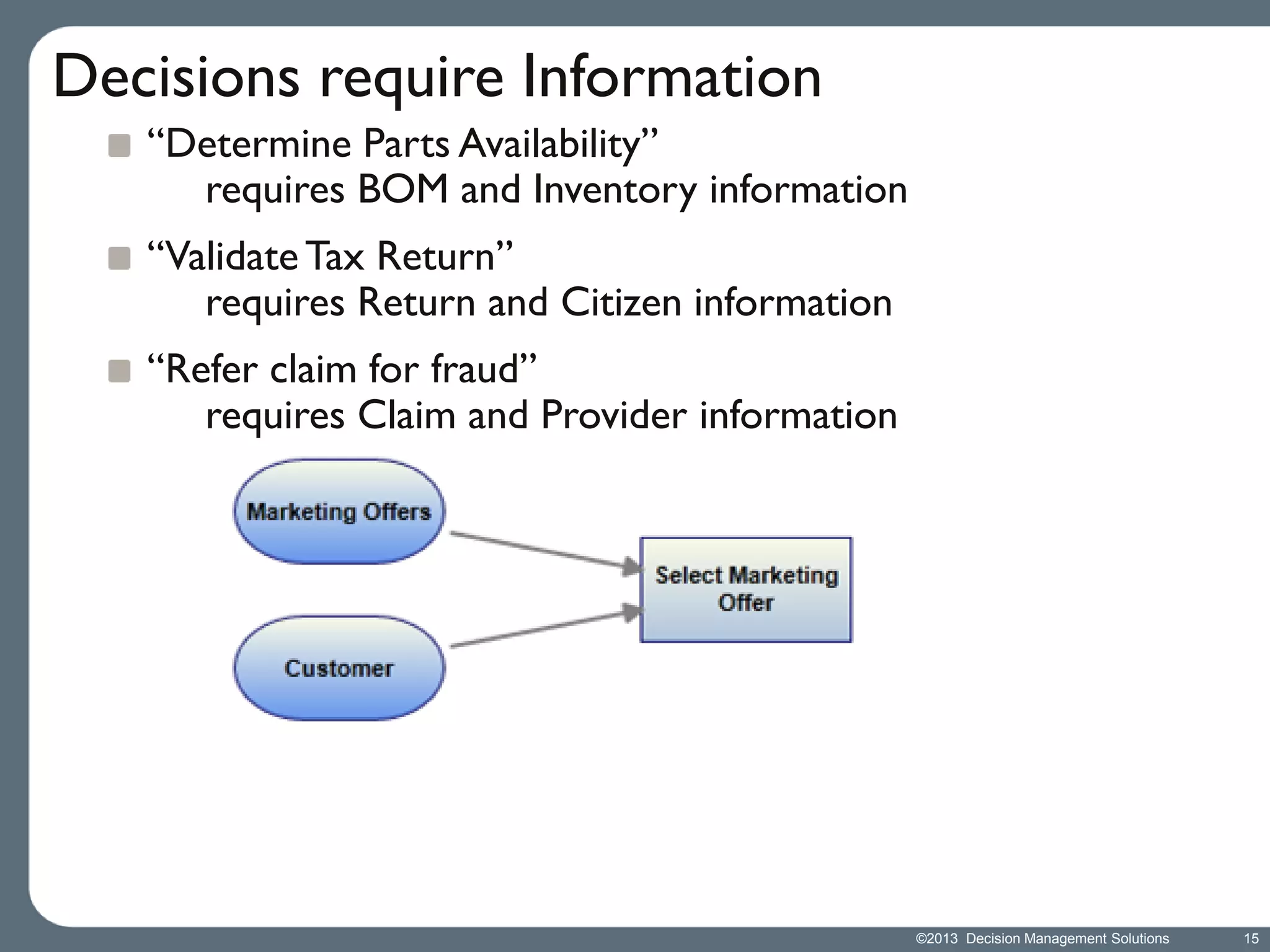
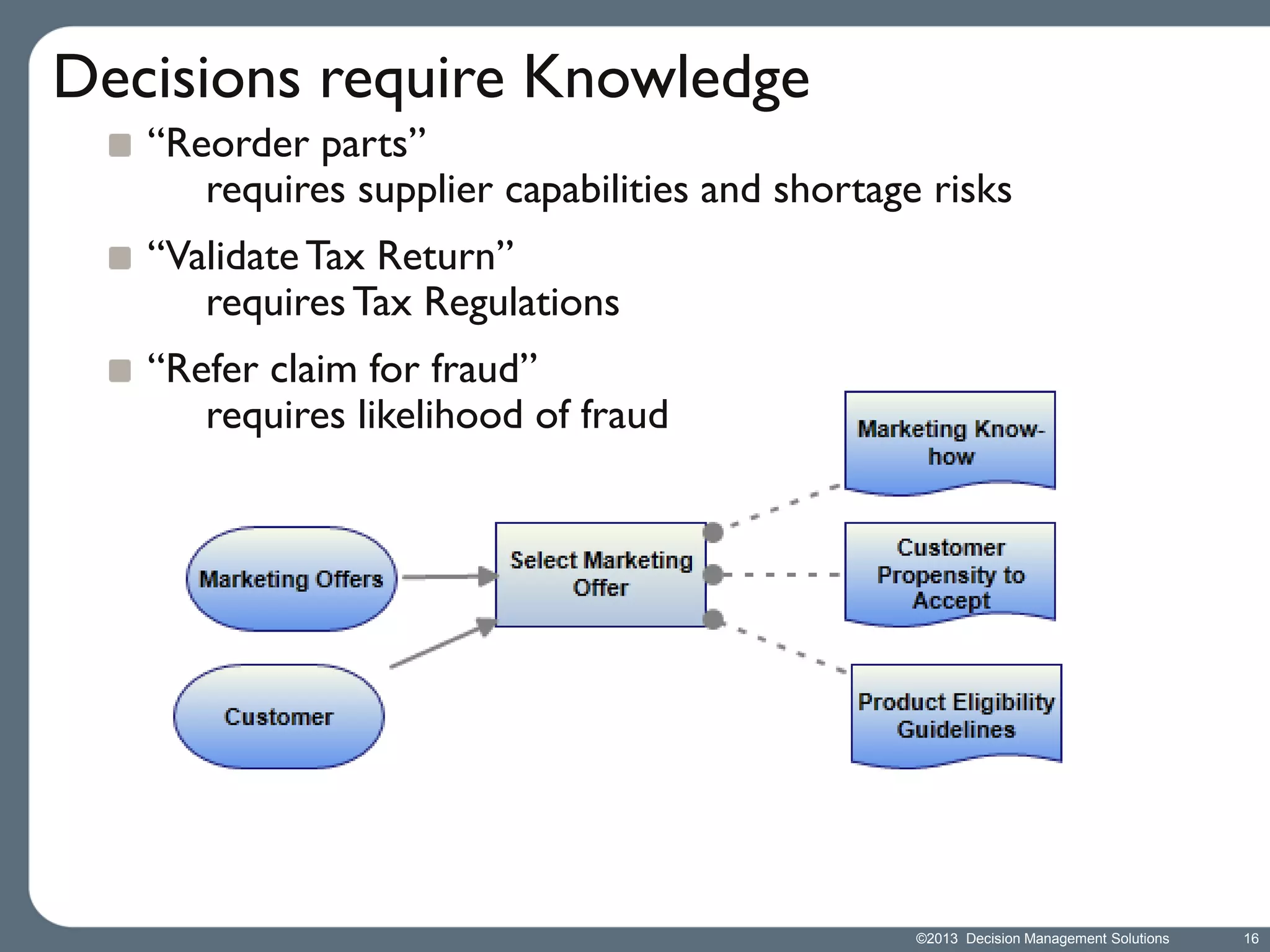
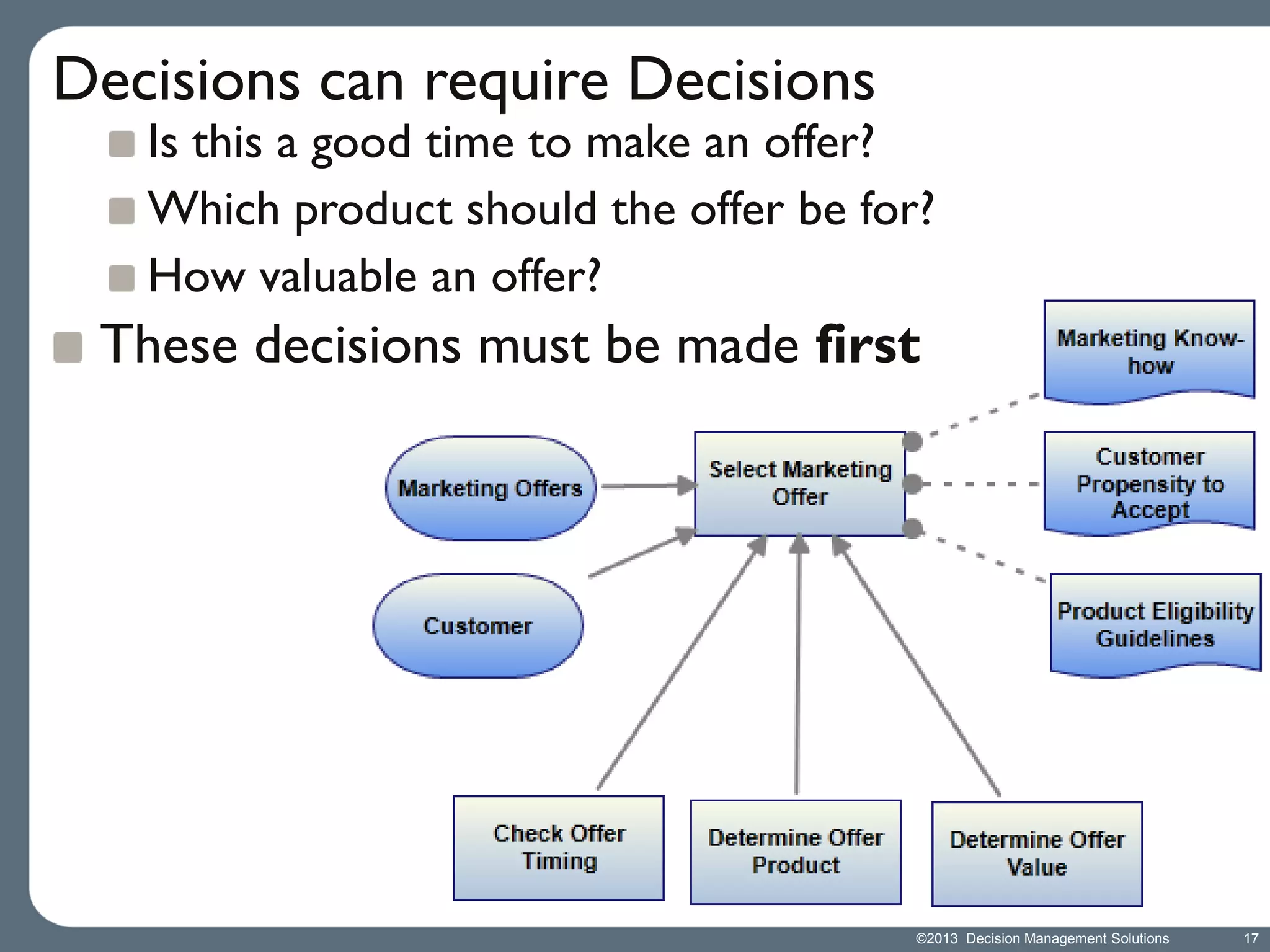
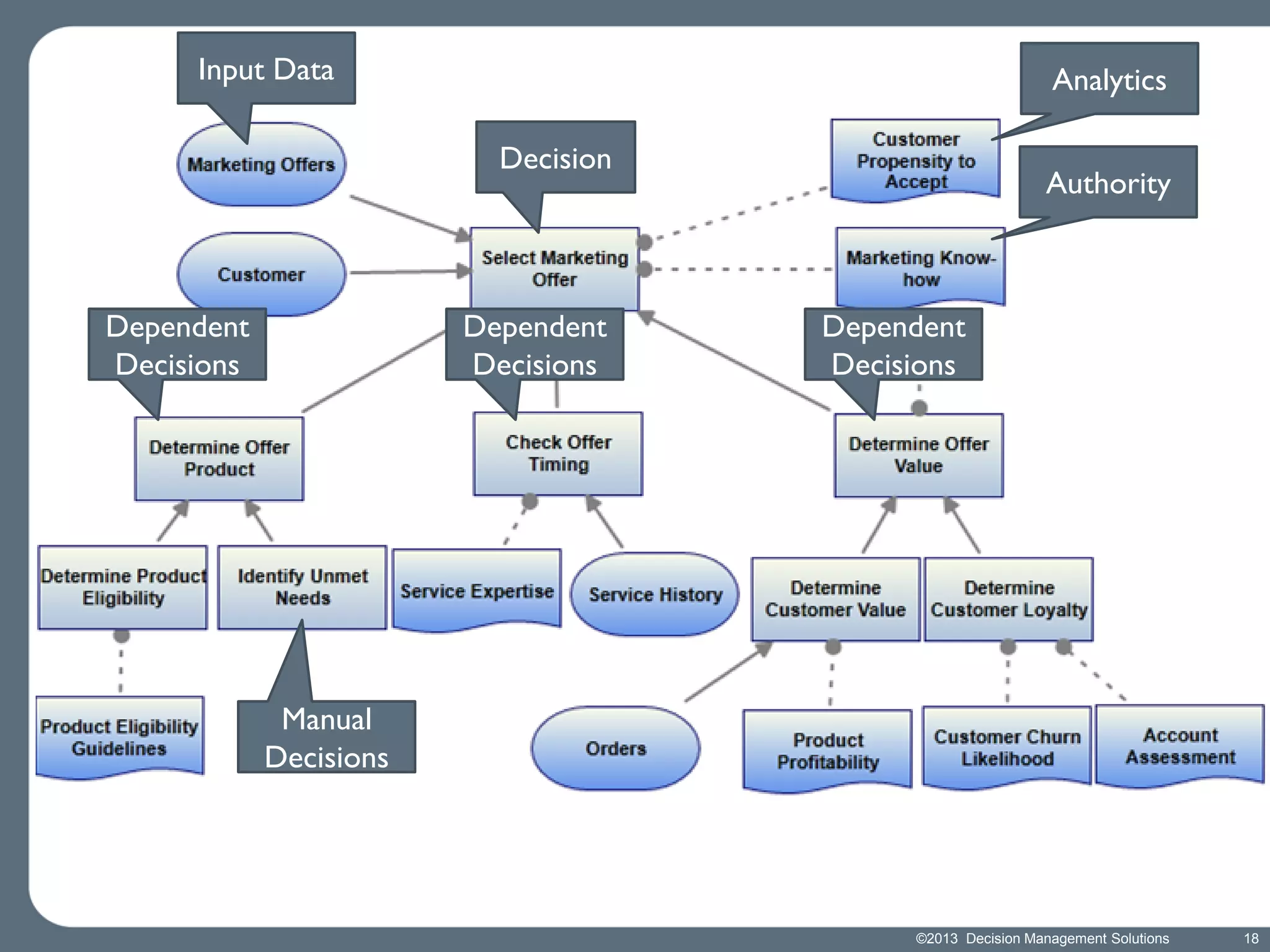
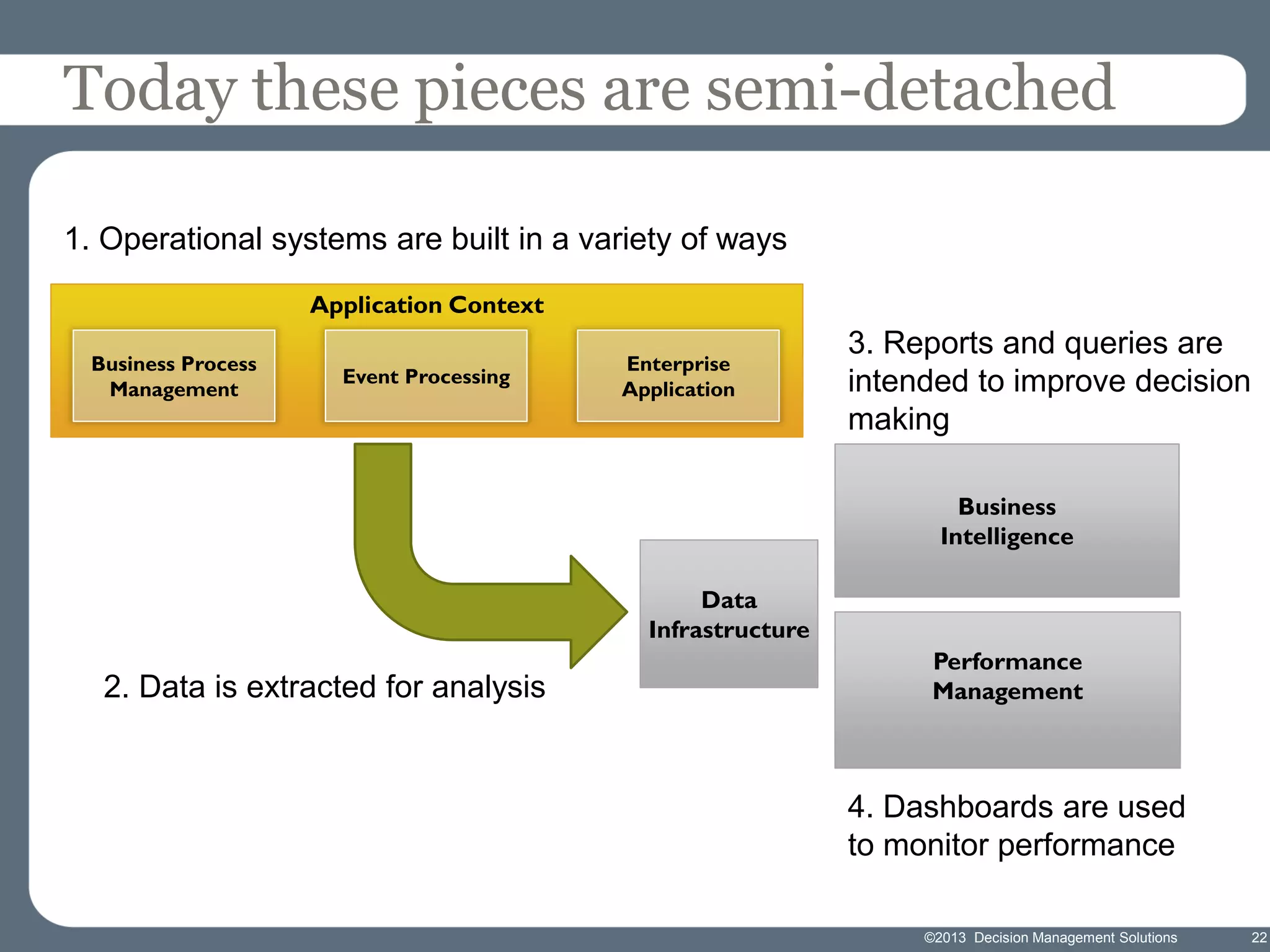
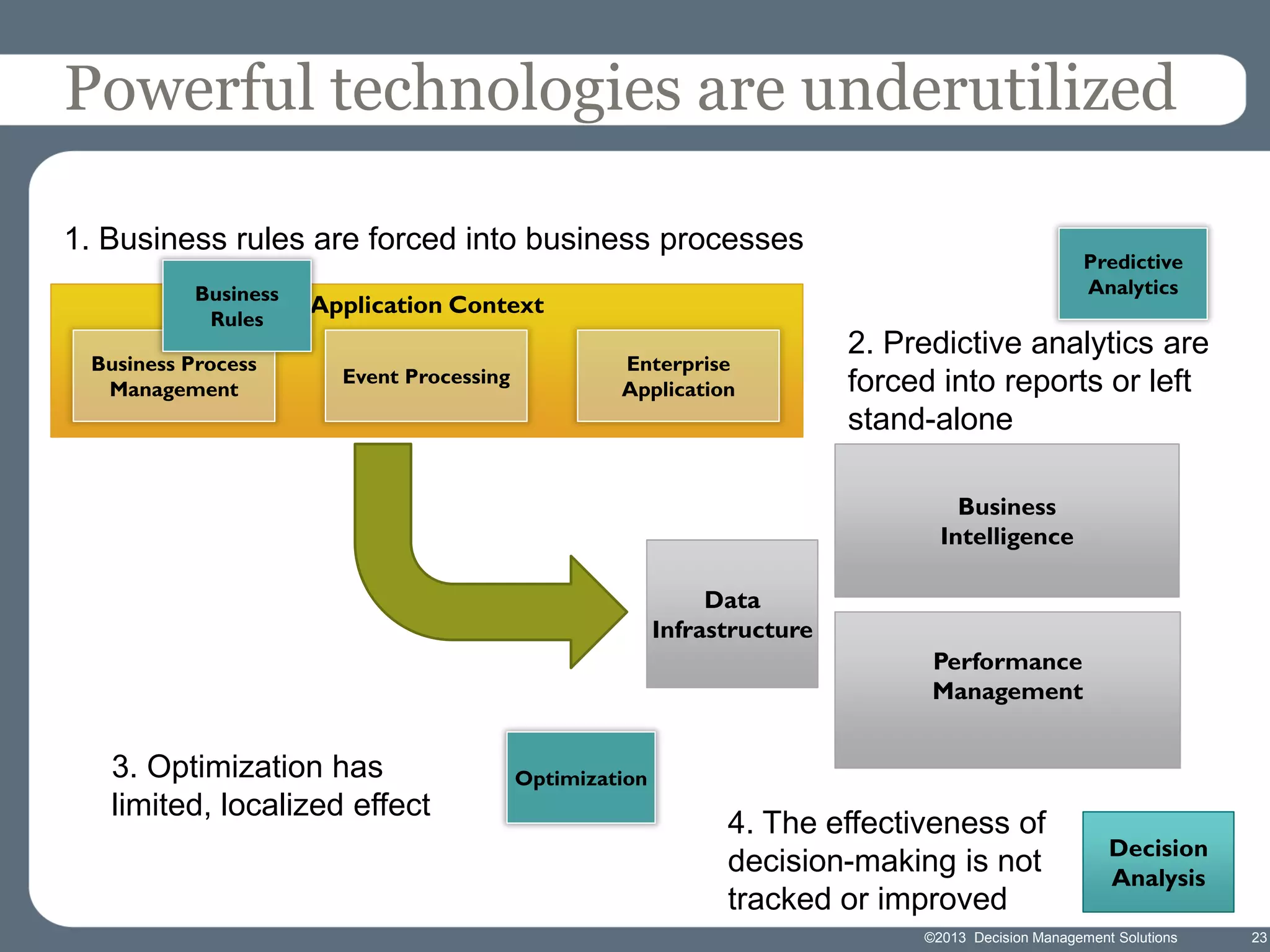
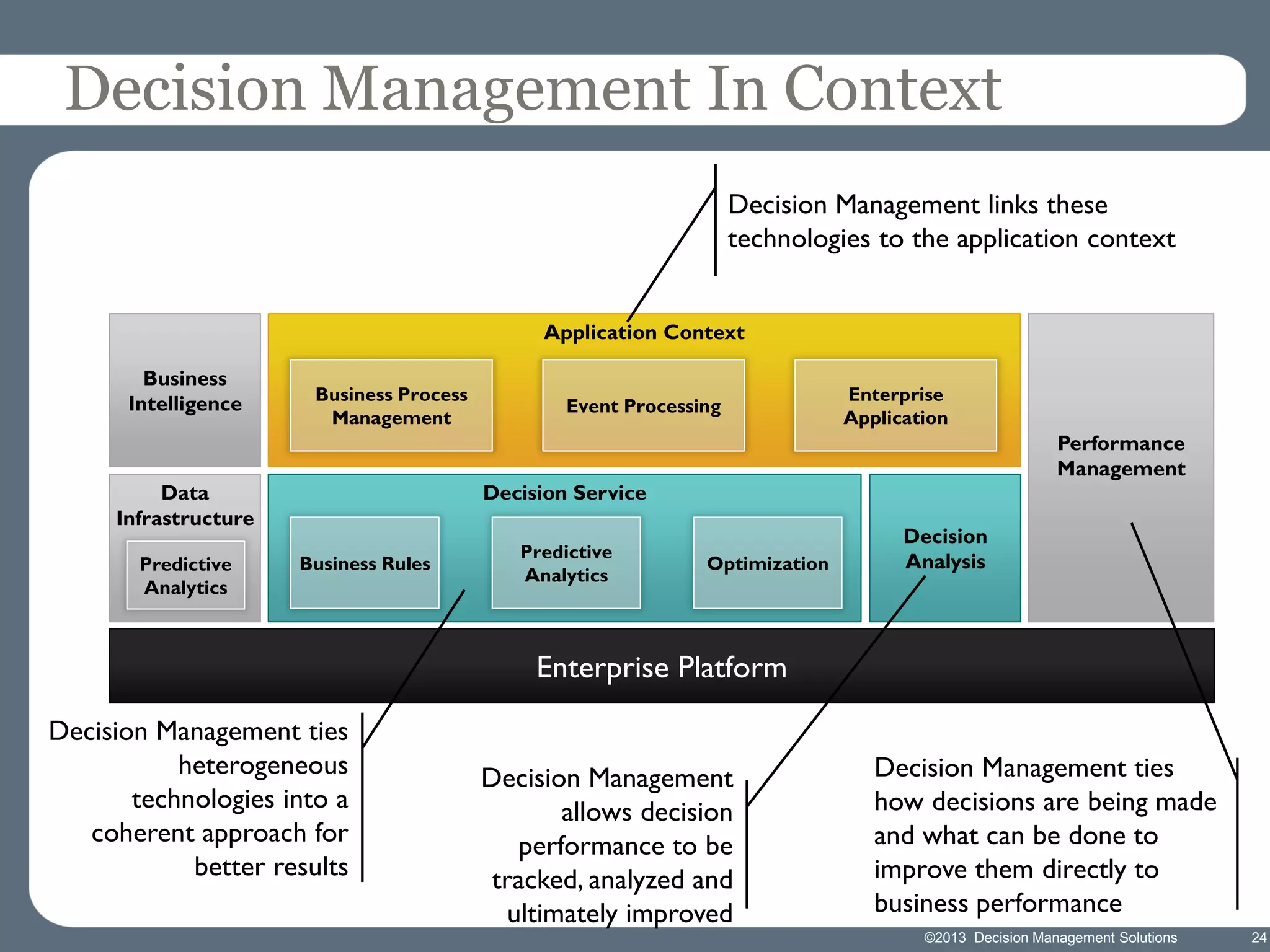
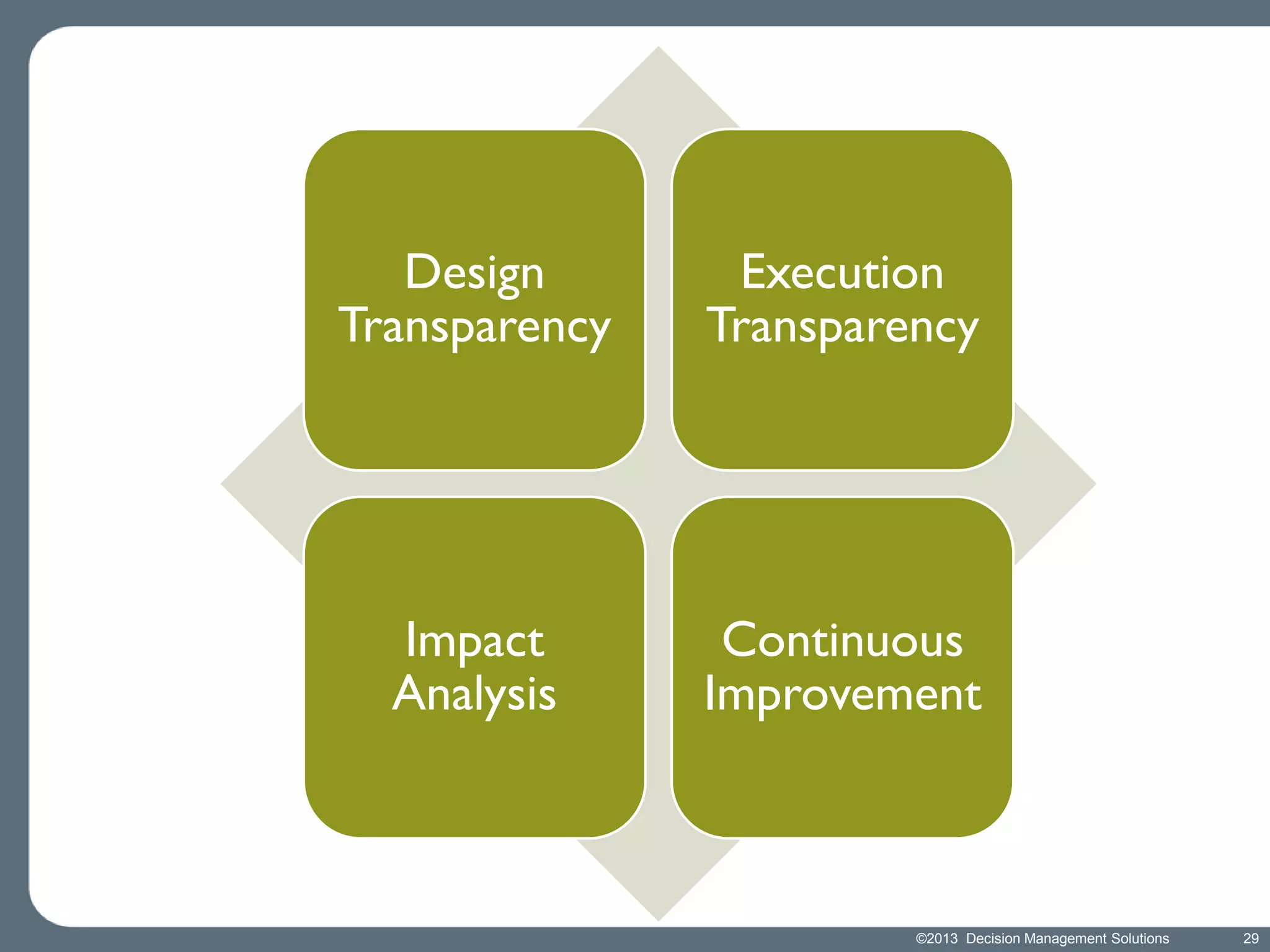
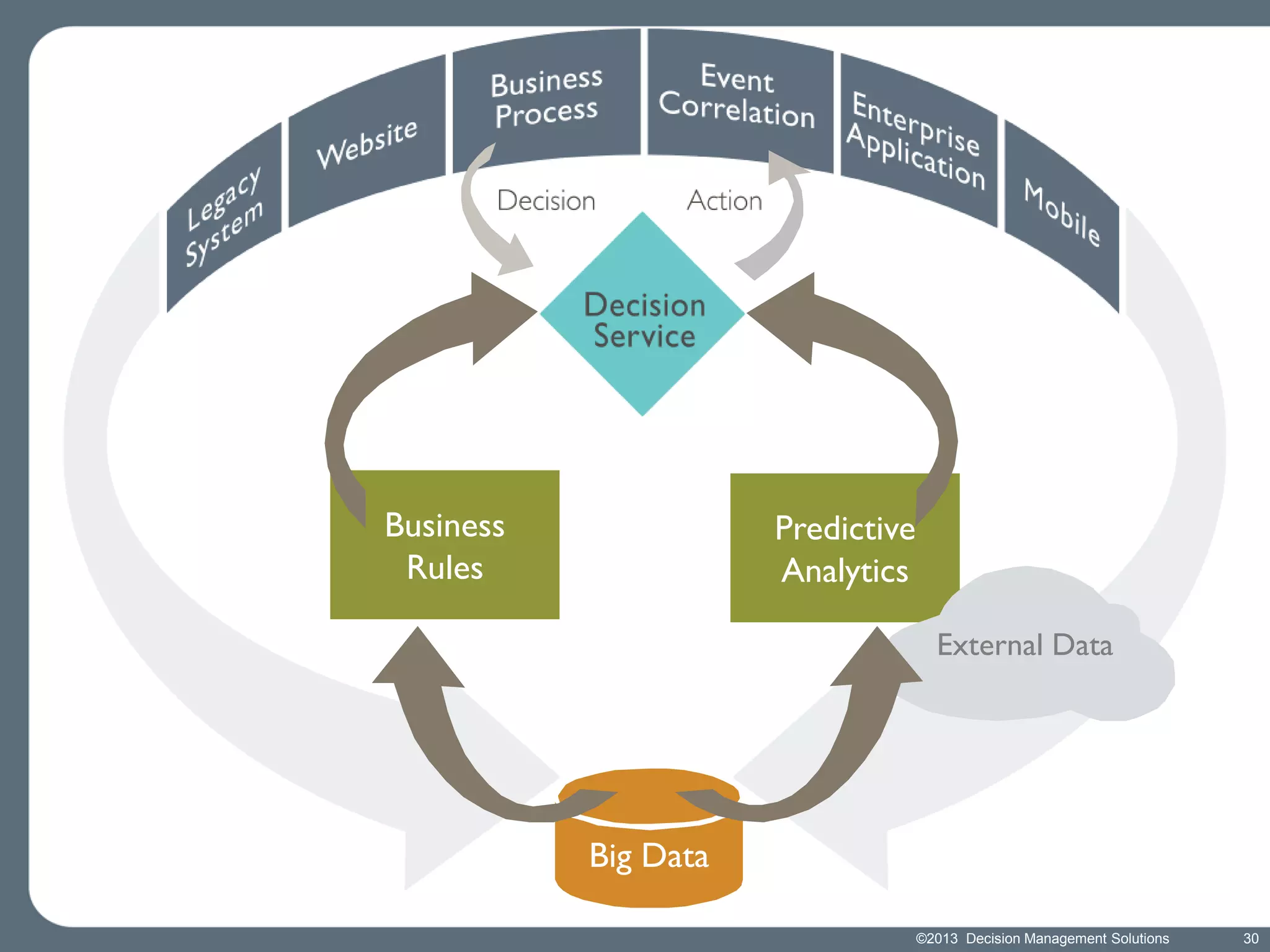
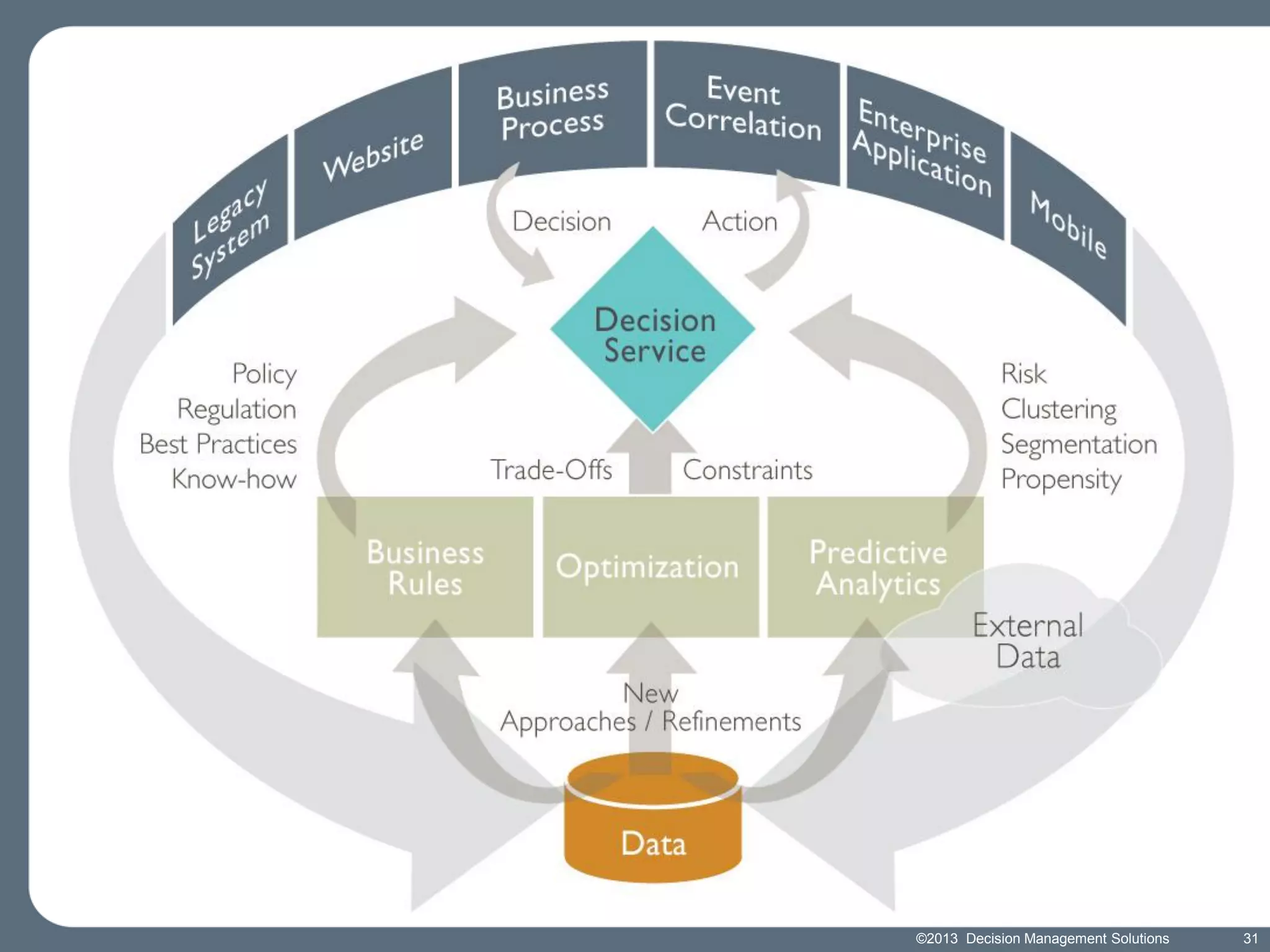
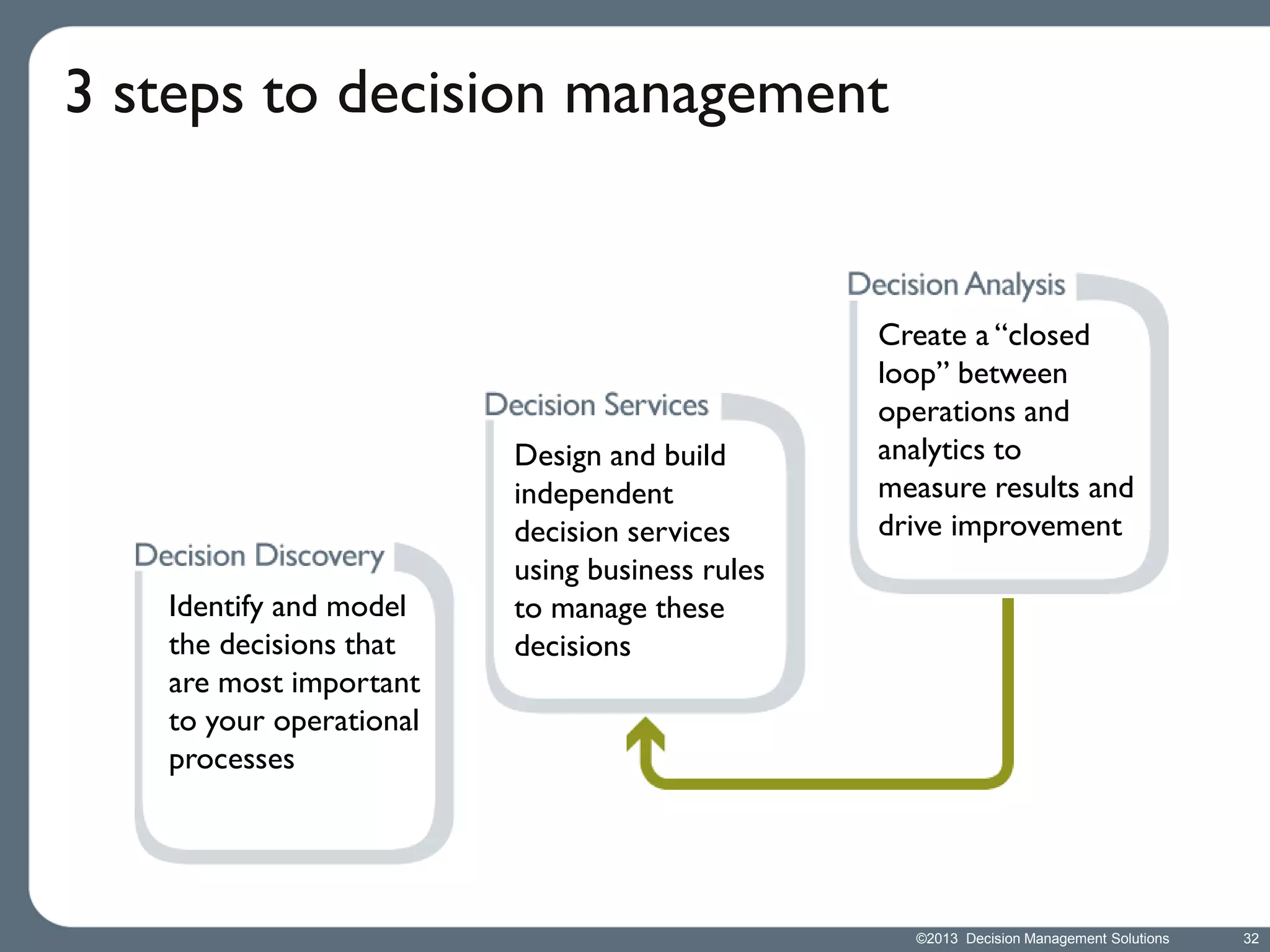
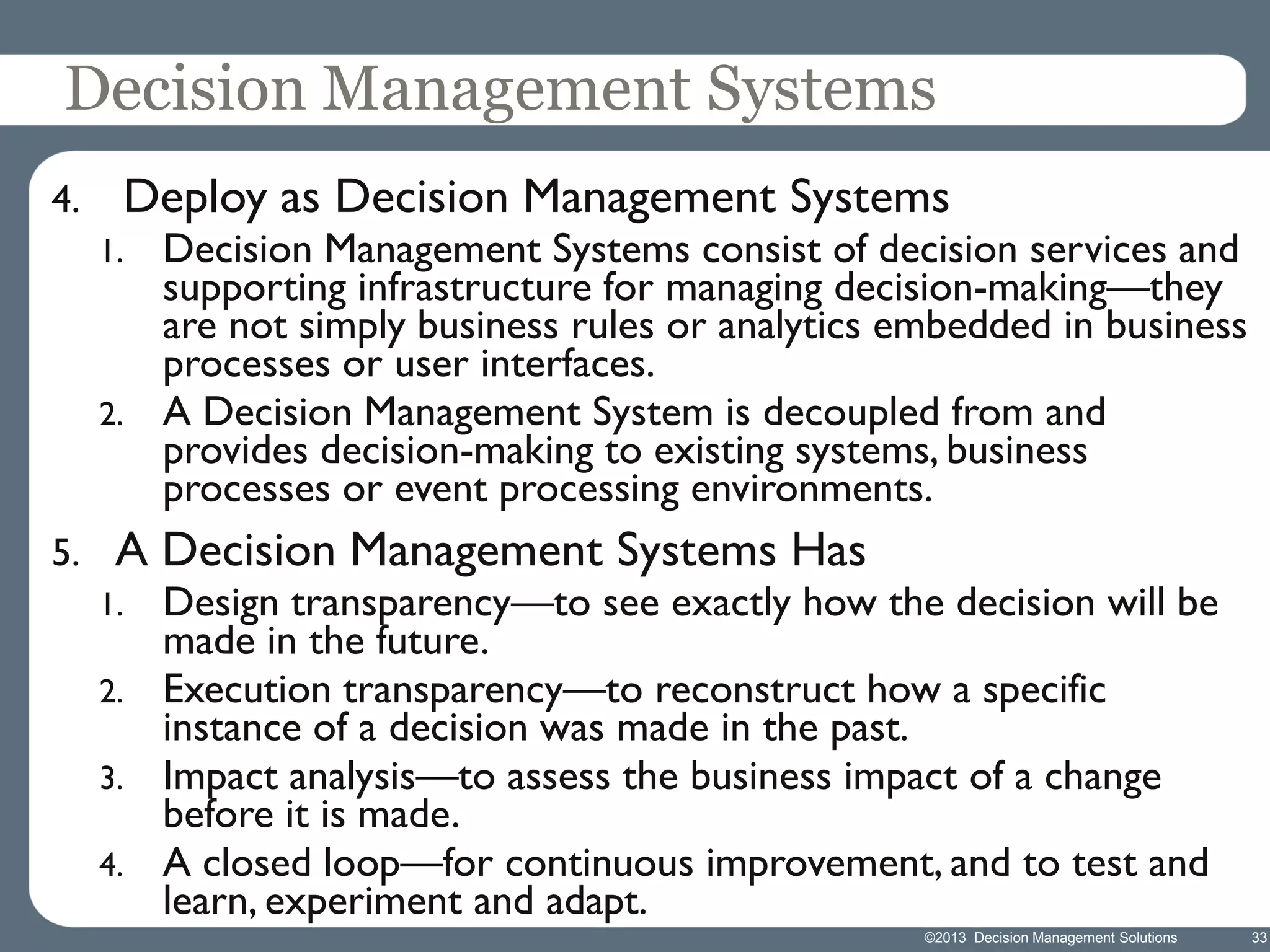
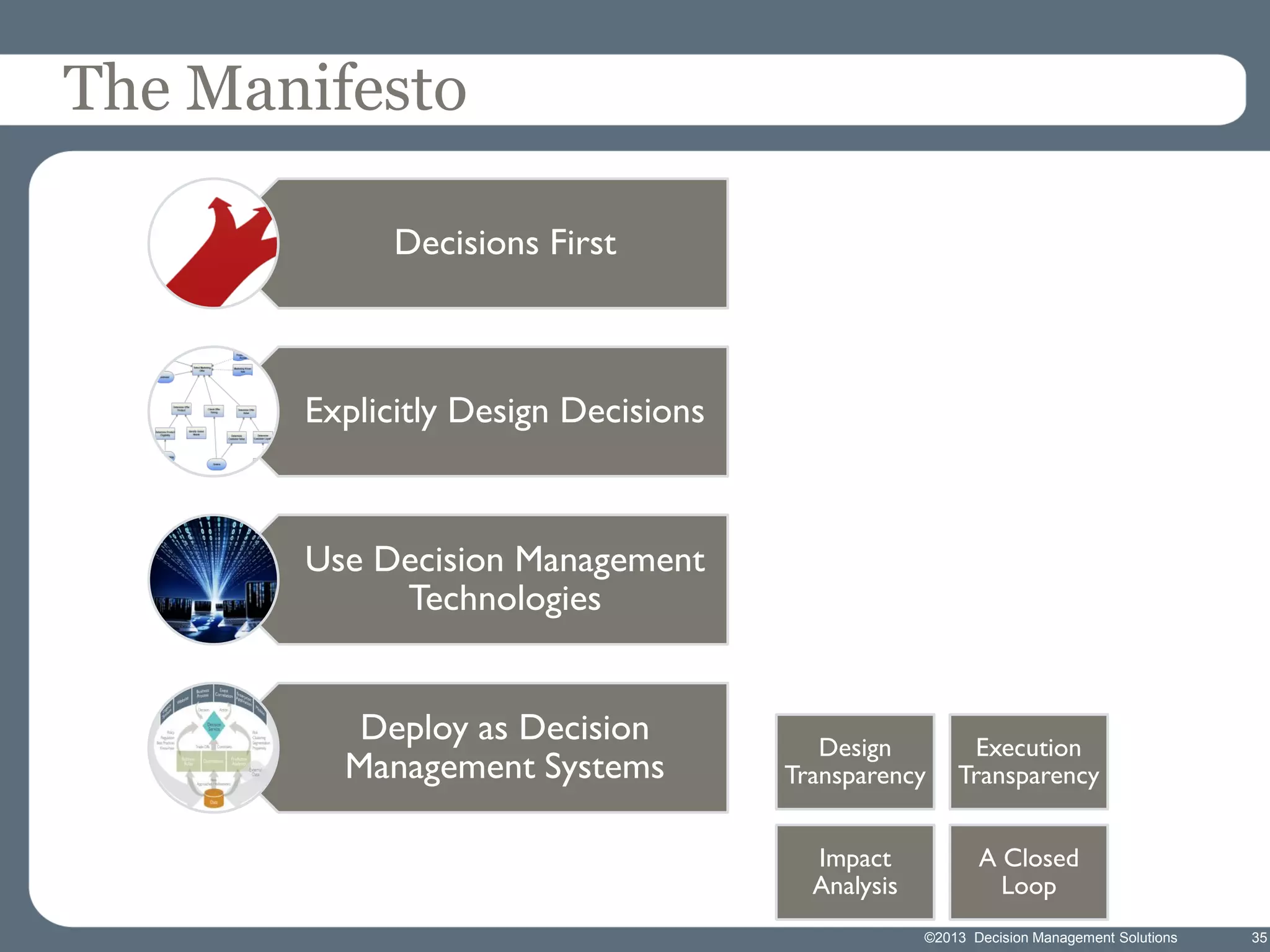
James Taylor presents the Decision Management Manifesto, outlining the need for a structured approach to decision-making that incorporates business rules, analytics, and technology. The manifesto advocates for explicit decision design and the use of decision management technologies to enhance business operations and improve decision quality. Key components include identifying critical decisions, deploying decision management systems, and ensuring transparency and continuous improvement in decision-making processes.