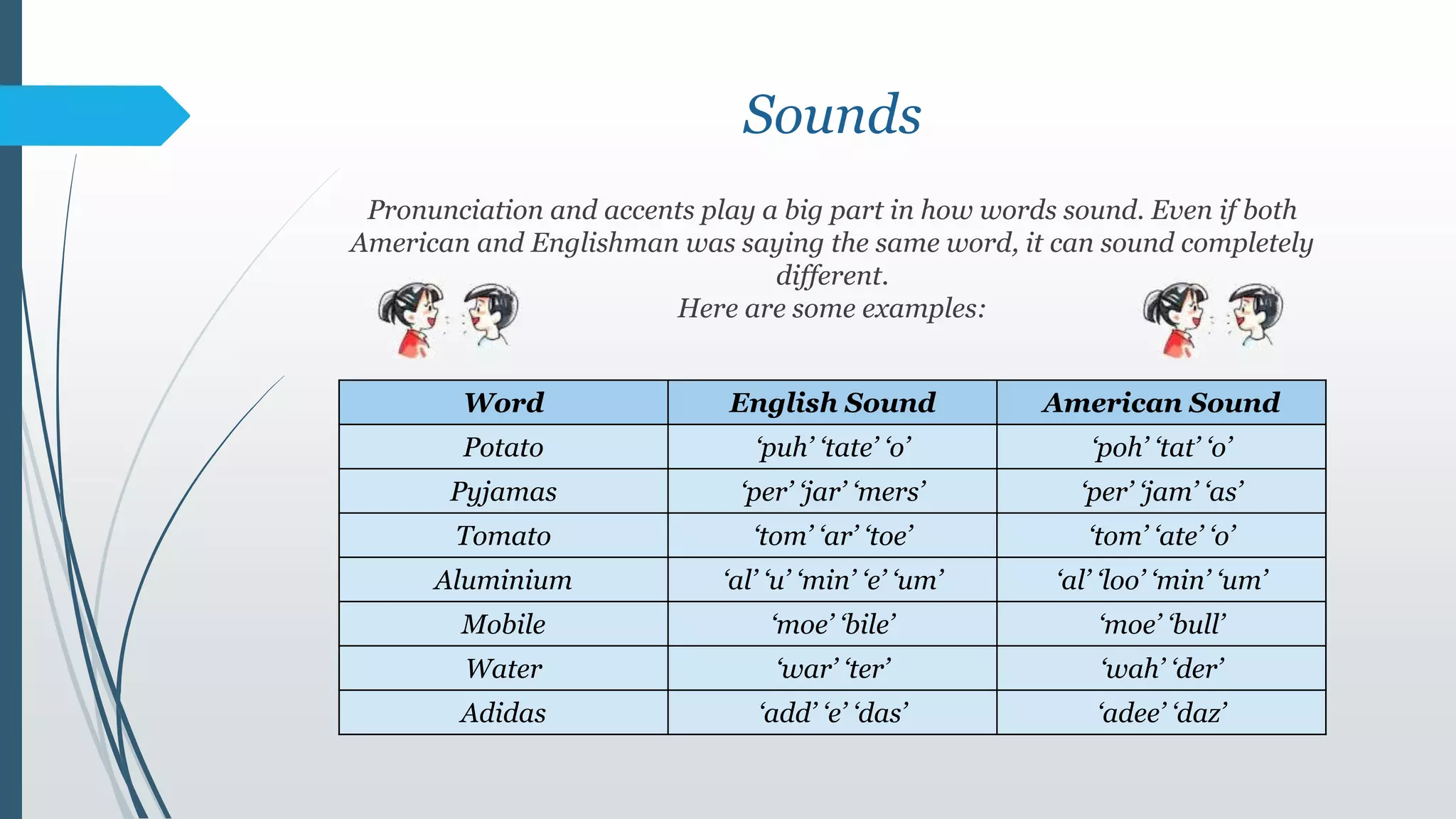
The colonization of North America began in the late 16th century with Walter Raleigh's expeditions and the first English settlement in 1607. By 1640, around 25,000 people had settled in Cape Cod. Various groups immigrated to the region, including the French, Dutch, and African slaves. The influx of immigrants from different language backgrounds influenced the development of a distinct American variety of English, with words and pronunciations from languages like Spanish, French, and West African dialects becoming incorporated. Factors like the isolation of colonial settlements and the mixing of various English accents contributed to changes in spelling, vocabulary, and pronunciation between American English and British English over time.