The document discusses the concept of big data and provides some key insights:
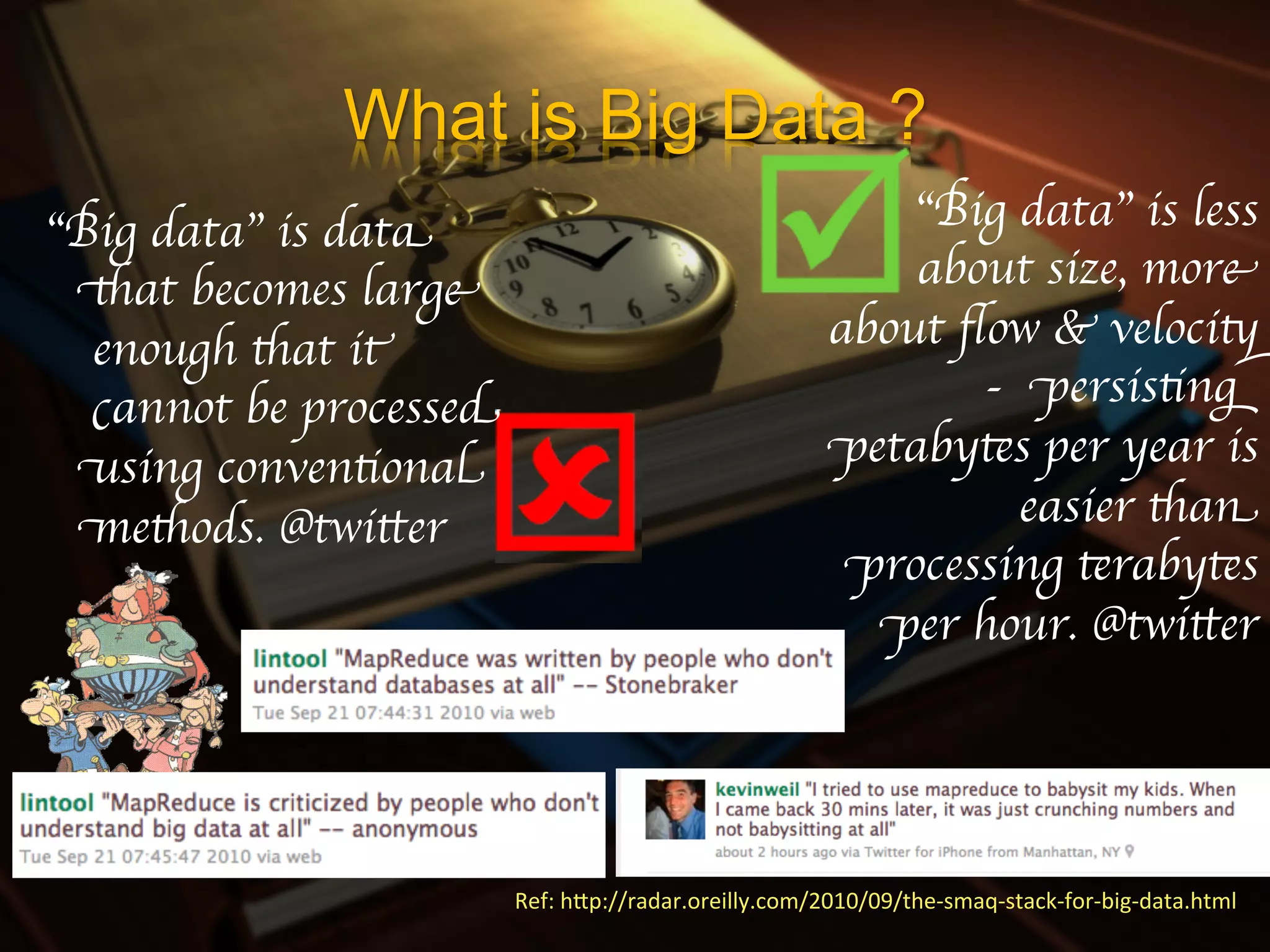
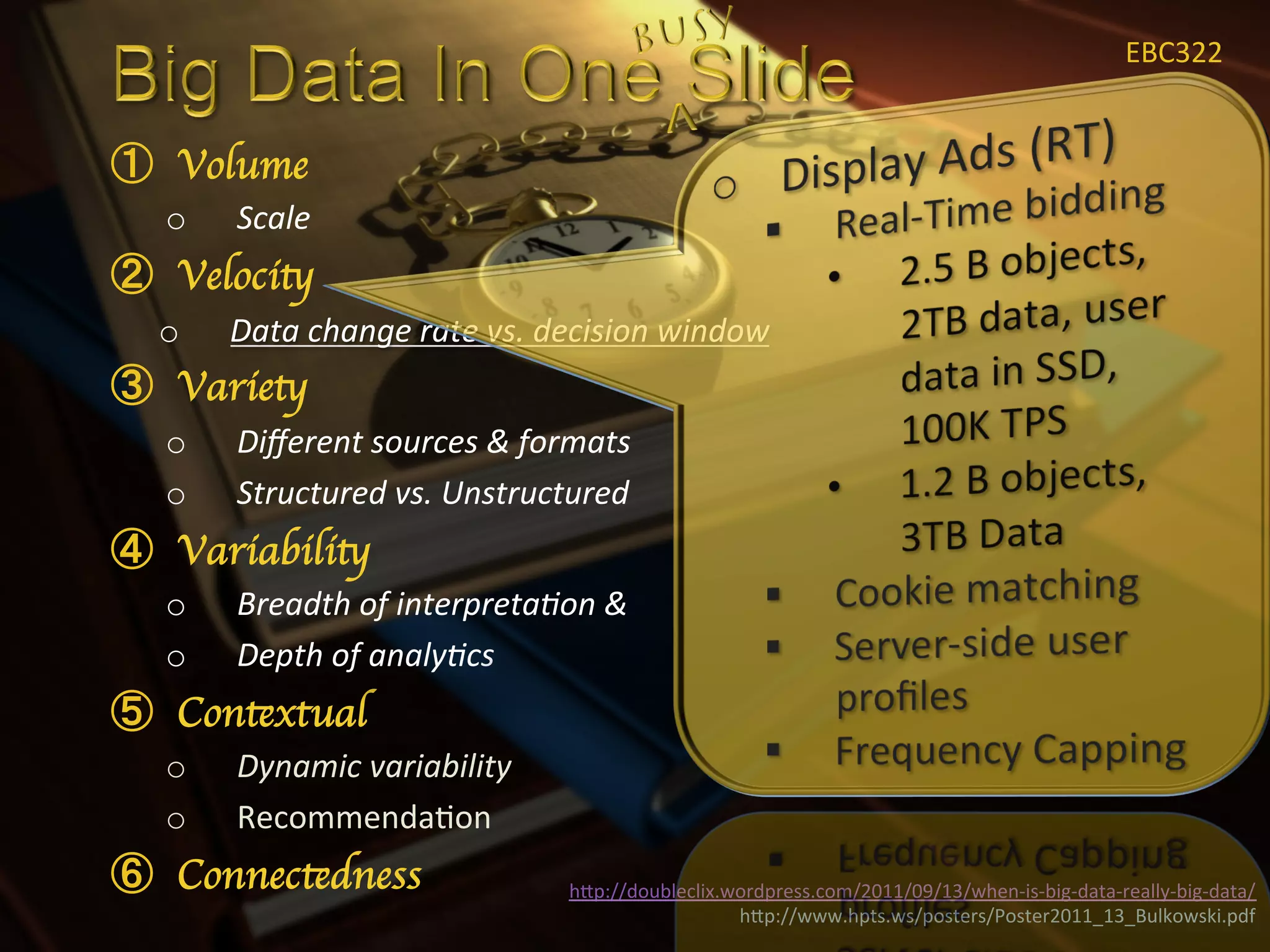
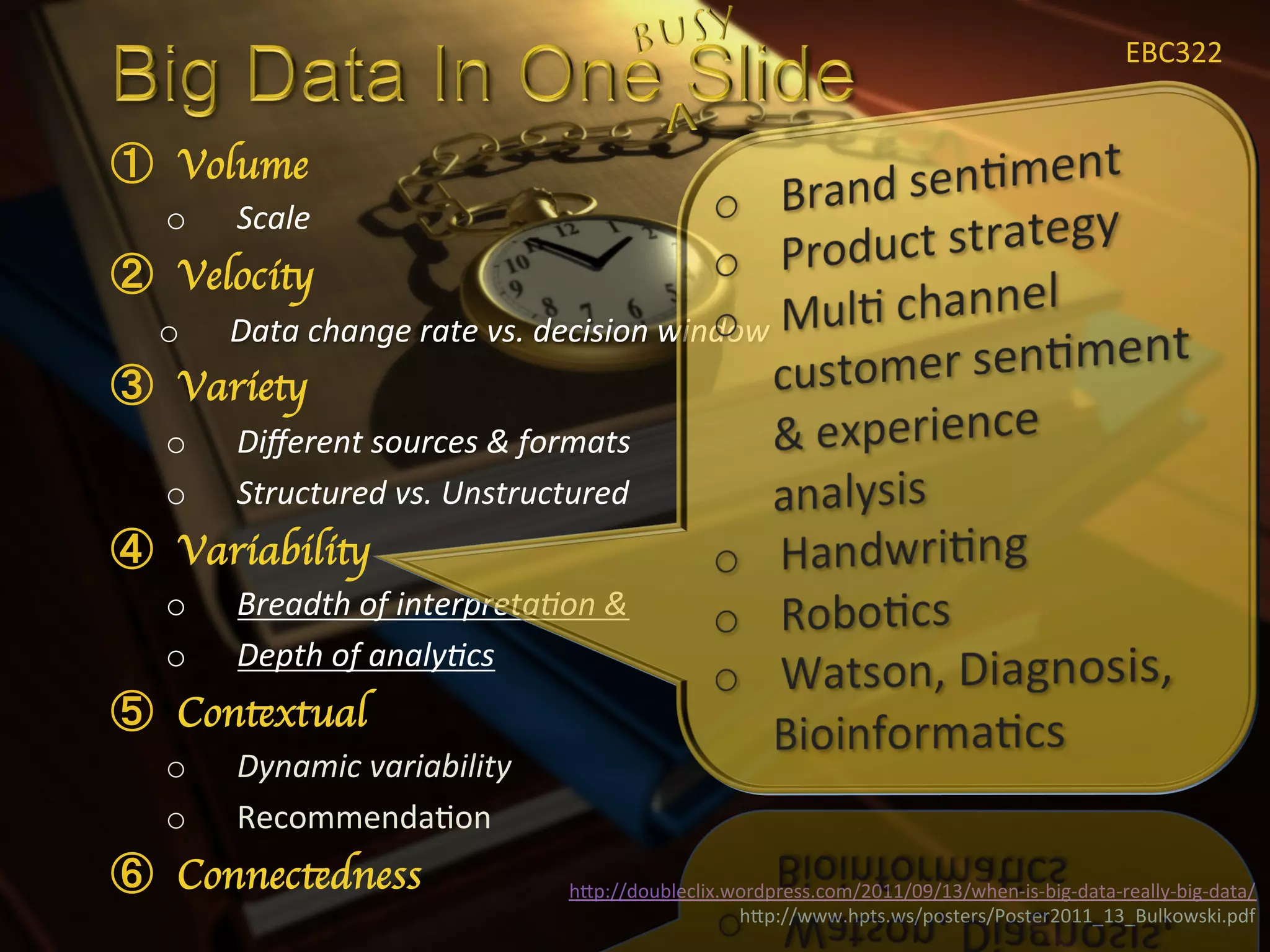
1) Big data refers to large data sets that cannot be processed by traditional software and hardware. It is characterized by high volume, velocity, and variety of data.
2) Examples of big data sources include social media firehoses from Twitter and large customer transaction logs from retailers.
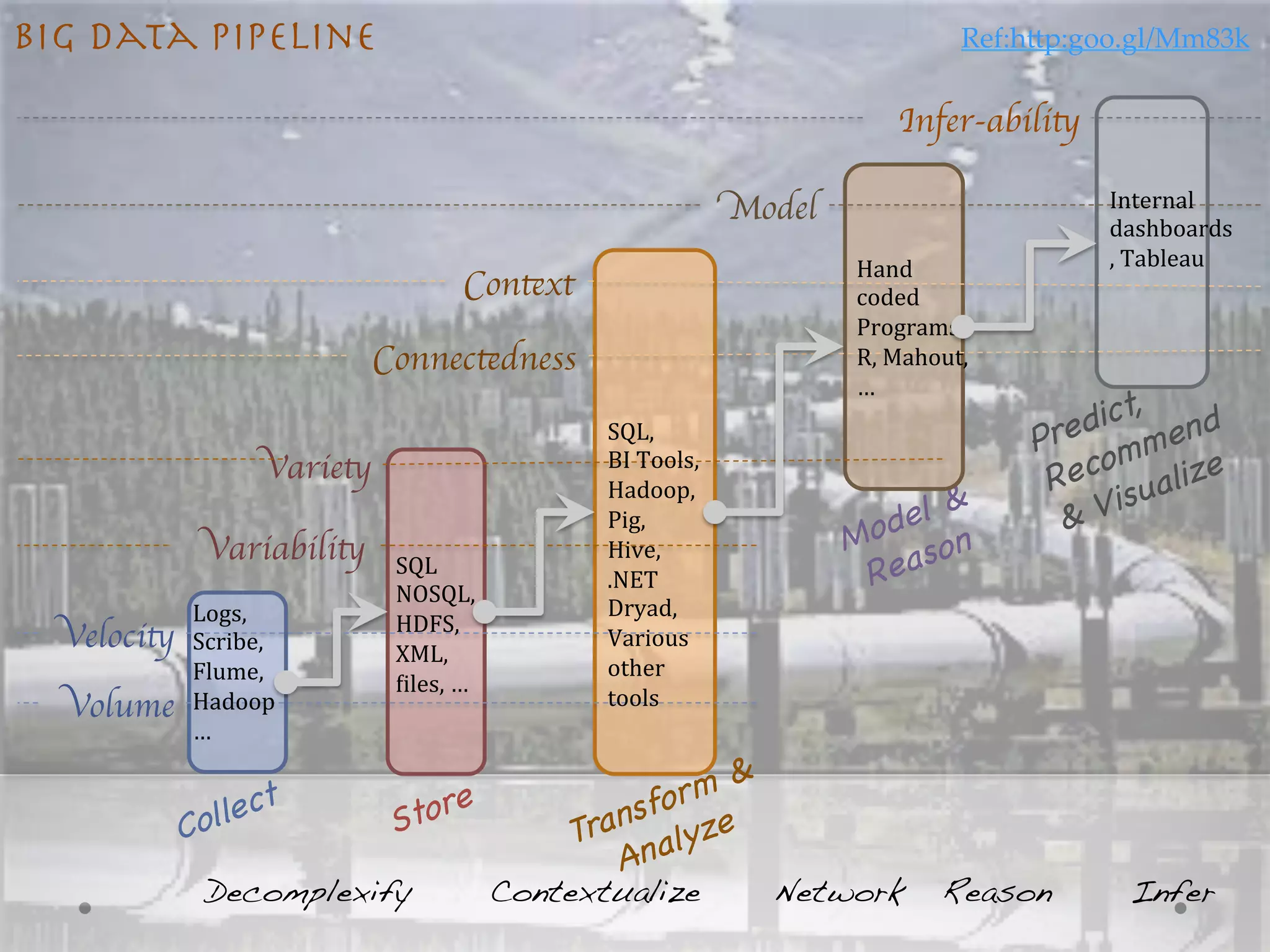
3) Analyzing big data requires specialized architectures and techniques to handle the scale, speed, and complexity of the data. Common approaches involve distributed file systems and map-reduce processing frameworks like Hadoop.
4) The goal of big data analytics is to extract useful insights, trends and patterns from these large and diverse data sets to help improve business

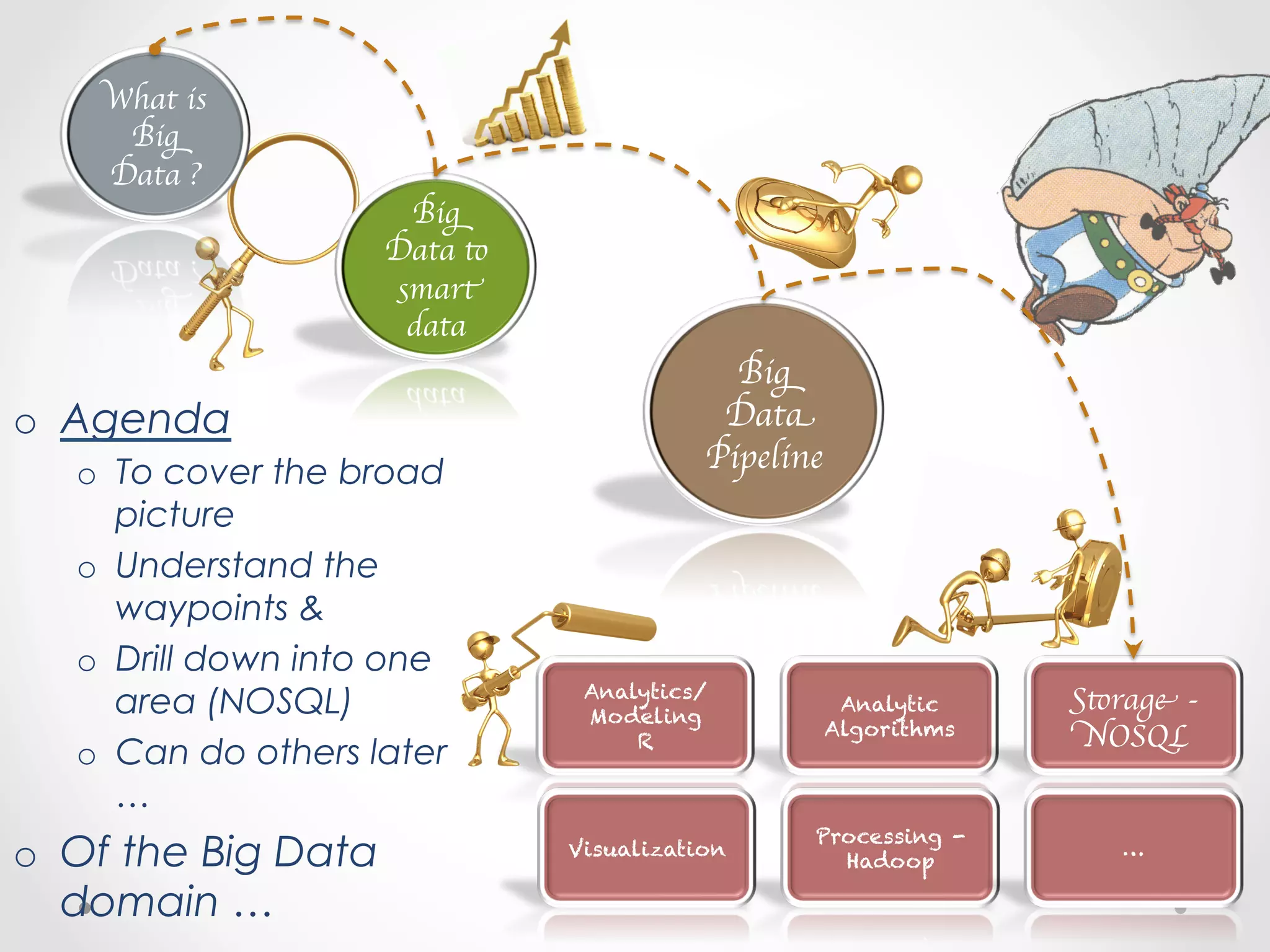












![Agenda
• Opening Gambit
– NOSQL
:
Toil,
Tears
&
Sweat
!
• The Pragmas
– ABCs
of
NOSQL
[ACID,
BASE
&
CAP]
• The Mechanics
– Algorithmics
&
Mechanisms
(For
reference)
Referenced Links @ http://doubleclix.wordpress.com/2010/06/20/nosql-talk-references/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-24-2048.jpg)
![What is NOSQL
Anyway ?
• NOSQL
!=
NoSQL
or
NOSQL
!=
(!SQL)
• NOSQL
=
Not
Only
SQL
• Can
be
traced
back
to
Eric
Evans[2]!
– You
can
ask
him
during
the
ayernoon
session!
• Unfortunate
Name,
but
is
stuck
now
• Non
RelaXonal
could
have
been
beIer
• Usually
OperaXonal,
Definitely
Distributed
• NOSQL
has
certain
semanXcs
–
need
not
stay
that
way](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-25-2048.jpg)
![NOSQL
Key
Value
Column
Document
Graph
In-‐memory
SimpleDB
CouchDB
Neo4j
Memcached
Google
MongoDB
FlockDB
BigTable
Disk
Based
HBase
Lotus
Domino
InfiniteGraph
Redis
Cassandra
Riak
Tokyo
Cabinet
Dynamo
HyperTable
Voldemort
Azure
TS
Ref:
[22,51,52]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-26-2048.jpg)

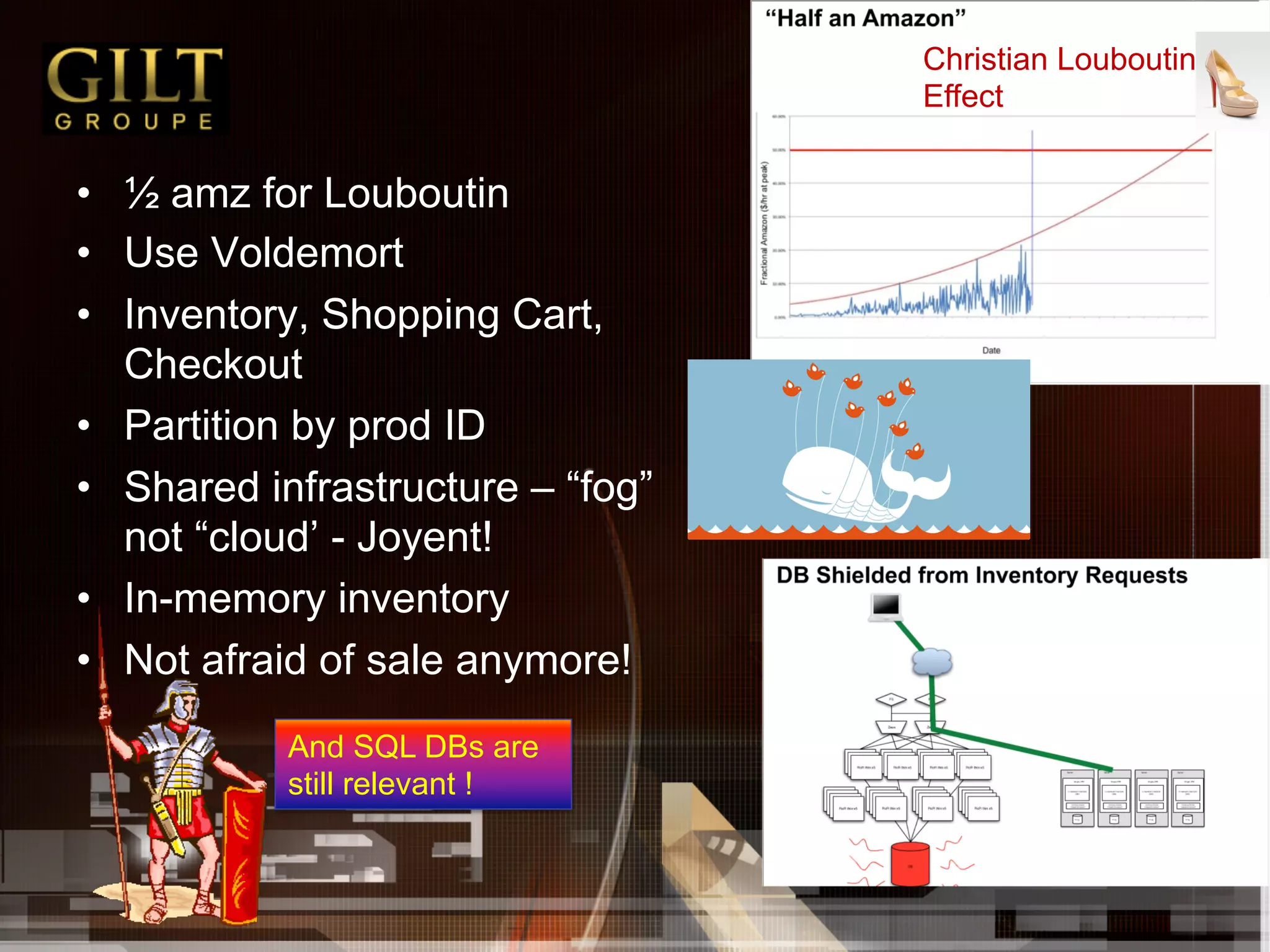
![• Designer Augmenting RDBMS with a Distributed key
Value Store[40 : A good talk by Geir]
• Invitation only designer brand sales
• Limited inventory sales – start at 12:00, members have
10 min to grab them. 500K mails every day
• Keeps brand value, hidden from search
• Interesting load properties
• Each item a row in DB-BUY NOW reserves it
– Can't order more
• Started out as a Rails app
– shared nothing
• Narrow peaks – half of revenue](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-28-2048.jpg)
![Typical NOSQL Example Bit.ly
• Bit,ly URL shortening service, uses MongoDB
• User, title, URL, hash, labels[I-5], sort by time
• Scale – ~50M users, ~10K concurrent, ~1.25B shortens
per month
• Criteria:
– Simple, Zippy FAST, Very Flexible, Reasonable Durability, Low
cost of ownership
• Sharded by userid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-30-2048.jpg)
![• New kind of “dictionary” a word repository, GPS for
English – context, pronunciations, twitter … developer
API
• Characteristics[I-6,Tony Tam’s presentation]
– RO-centric, 10,000 reads for every write
– Hit a wall with MySQL (4B rows)
– MongoDB read was so good that memcached layer was not
required
– MongoDB used 4 times MySQL storage
• Another example :
– Voldemort – Unified Communications, IP-Phone data stored
keyed off of phone number. Data relatively stable](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-31-2048.jpg)
![Large Hadron Collider@CERN
• DAS is part of giant data management
enterprise (cms)
– Polygot Persistence (SQL + NOSQL, Mongo, Couch,
memcache, HDFS, Luster, Oracle, mySQL, …)
• Data Aggregation System [I-1,I-2,I-3,I-4]
– Uses MongoDB
– Distributed Model, 2-6 pb data
– Combine info. from different metadata sources, query
without knowing their existence, user has domain
knowledge – but shouldn’t deal with various formats,
interfaces and query semantics
– DAS aggregates, caches and presents data as JSON
documents – preserving security & integrity
And SQL DBs are
still relevant !](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-32-2048.jpg)

![• Digg
– RDBMS places burden on reads than writes[I-8]
– Looked at NOSQL, selected Cassandra
• Colum oriented, so more structure than key-value
• Heard from noSQL Boston[http://twitter.com/
#search?q=%23nosqllive]
– Baidu: 120 node HyperTable cluster managing
600TB of data
– StumbleUpon uses HBase for Analytics
– Twitter’s Current Cassandra cluster: 45 nodes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-34-2048.jpg)
![• Adob is a HBase shop • BBC is a CouchDB shop
[I-10,I-11,2] [I-13]
• Adobe SaaS Infrastructure – • Sweet spot:
tagging, content aggregation, • Multi-master, multi
search, storage and so forth datacenter replication
• Dynamic schema & huge
number of records[I-5]
• 40 million records in 2008 to
1 billion with 50 ms response • Interactive Mediums
• NOSQL not mature in 2008, • Old data to CouchDB
now good enough • Thus free up DB to do
• Prod Analytics:40 nodes, work!
largest has 100 nodes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-35-2048.jpg)
![• Cloudkick is a Cassandra shop[I-12]
• Cloudkick offers cloud management services
• Store metrics data
• Linear scalability for write load
• Massive write performance
• Memory table & serial commit log
• Low operational costs
• Data Structure
– Metrics, Rolled-up data, Statuses at time slice : all indexed by
timestamp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-36-2048.jpg)
![• Guardian/UK
– Runs on Redis[I-14] !
– “Long-term The Guardian is looking
towards the adoption of a schema-free
database to sit alongside its Oracle
database and is investigating CouchDB.
… the relational database is now just a
component in the overall data
management story, alongside data
caching, data stores, search engines
And SQL DBs are
etc.
still relevant !
– NOSQL can increase performance of "The evil that SQL
relational data by offloading specific DBs do lives after
data and tasks them; the good is
oft interred with
their bones...",](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-37-2048.jpg)

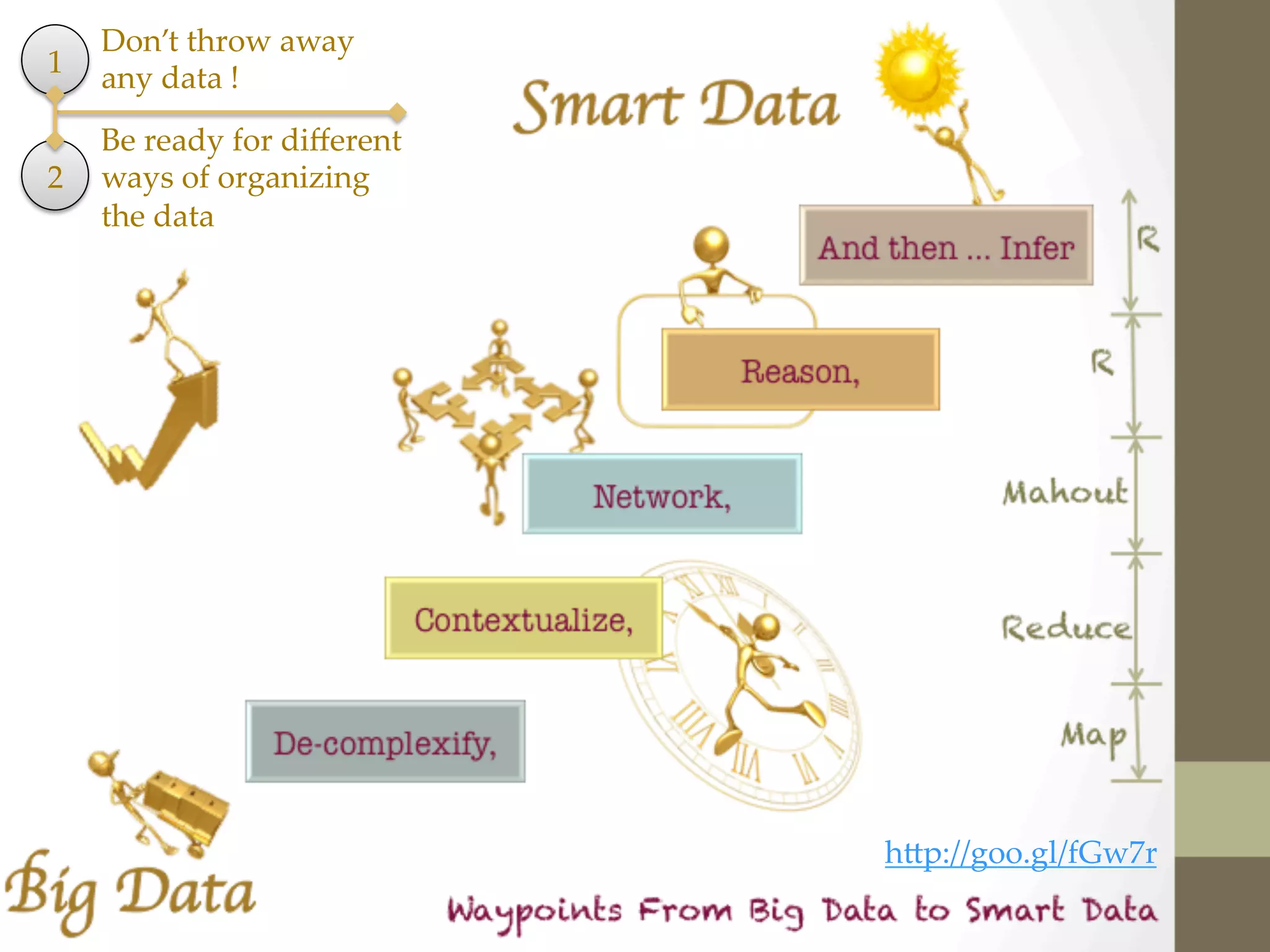
![21 NOSQL Themes
• Web
Scale
• Scale
Incrementally/conXnuous
growth
• Oddly
shaped
&
exponenXally
connected
• Structure
data
as
it
will
be
used
–
i.e.
read,
query
• Know
your
queries/updates
in
advance[96],
but
you
can
change
them
later
• Compute
aIributes
at
run
Xme
• Create
a
few
large
enXXes
with
opXonal
parts
– NormalizaXon
creates
many
small
enXXes
• Define
Schemas
in
models
(not
in
databases)
• Avoid
impedance
mismatch
• Narrow
down
&
solve
your
core
problem
• Solve
the
right
problem
with
the
right
tool
Ref:
[I-‐8]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-40-2048.jpg)
![21 NOSQL Themes
• ExisXng
soluXons
are
clunky[1]
(in
certain
situaXons)
• Scale
automaXcally,
“becoming
prohibiXvely
costly
(in
terms
of
manpower)
to
operate”
TwiIer[I-‐9]
• DistribuXon
&
parXXoning
are
built-‐in
NOSQL
• RDBMS
distribuXon
&
sharding
not
fun
and
is
expensive
– Lose
most
funcXonality
along
the
way
• Data
at
the
center,
Flexible
schema,
Less
joins
• The
value
of
NOSQL
is
in
flexibility
as
much
as
it
is
in
“Big
Data”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-41-2048.jpg)
![21 NOSQL Themes
• Requirements[3]
– Data
will
not
fit
in
one
node
• And
so
need
data
parXXon/distribuXon
by
the
system
– Nodes
will
fail,
but
data
needs
to
be
safe
–
replicaXon!
– Low
latency
for
real-‐Xme
use
• Data
Locality
– Row
based
structures
will
need
to
read
whole
row,
even
for
a
column
– Column
based
structures
need
to
scan
for
each
row
• SoluXon
:
Column
storage
with
Locality
– Keep
data
that
is
read
together,
don’t
read
what
you
don’t
care
• For
example
friends
–
other
data
Ref:
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-42-2048.jpg)
![CAP Principle
“CAP
Principle
→
Strong
Consistency,
High
Availability,
Consistency
Par::on-‐resilience:
Pick
at
most
2”[37]
Availability Partition
Which
feature
to
discard
depends
on
the
nature
of
your
system[41]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-44-2048.jpg)
![CAP Principle
“CAP
Principle
→
Strong
Consistency,
High
Availability,
Consistency
Par::on-‐resilience:
Pick
at
most
2”[37]
C-‐A
No
P
→
Single
DB
server,
no
network
par::on
Availability Partition
Which
feature
to
discard
depends
on
the
nature
of
your
system[41]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-45-2048.jpg)
![CAP Principle
“CAP
Principle
→
Strong
Consistency,
High
Availability,
Consistency
Par::on-‐resilience:
Pick
at
most
2”[37]
C-‐P
No
A
→
Block
transac:on
in
case
of
par::on
failure
Availability Partition
Which
feature
to
discard
depends
on
the
nature
of
your
system[41]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-46-2048.jpg)
![CAP Principle
Interesting (& controversial) from
“CAP
Principle
→
NOSQL perspective
Strong
Consistency,
High
Availability,
Consistency
Par::on-‐resilience:
Pick
at
most
2”[37]
A-‐P
No
C
→
Expira:on
based
caching,
vo:ng
majority
Availability Partition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-47-2048.jpg)
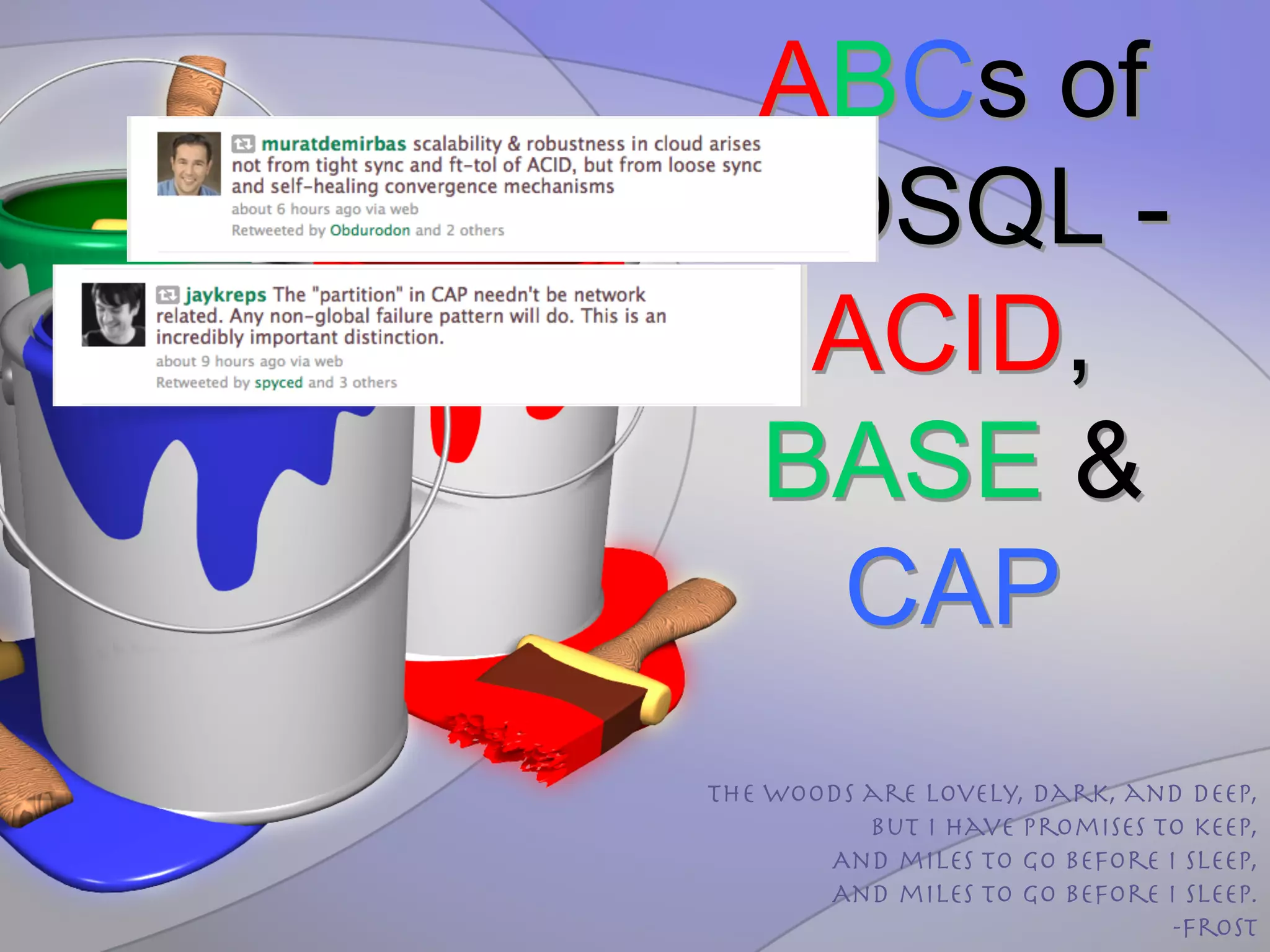
![ABCs
of
NOSQL
• ACID
o Atomicity,
Consistency,
IsolaXon
&
Durability
–
fundamental
properXes
of
SQL
DBMS
• BASE[35,39]
o Basically
Available
Soy
state(Scalable)
Eventually
Consistent
• CAP[36,39]
o Consistency,
Availability
&
ParXXoning
o This
C
is
~A+C
• i.e.
Atomic
Consistency[36]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-48-2048.jpg)
![CAP
Pragmas
• PrecondiXons
o The
domain
is
scalable
web
apps
o Low
Latency
For
real
Xme
use
o A
small
sub-‐set
of
SQL
FuncXonality
o Horizontal
Scaling
• PritcheI[35]
talks
about
relaxing
consistency
across
funcXonal
groups
than
within
funcXonal
groups
• Idempotency
to
consider
o Updates
inc/dec
are
rarely
idempotent
o Order
preserving
trx
are
not
idempotent
either
o MVCC
is
an
answer
for
this
(CouchDB)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-50-2048.jpg)
![Consistency
• Strict
Consistency
o Any
read
on
Data
X
will
return
the
most
recent
write
on
X[42]
• SequenXal
Consistency
o Maintains
sequenXal
order
from
mulXple
processes
(No
menXon
of
Xme)
• Linearizability
o Add
Xmestamp
from
loosely
synchronized
processes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-51-2048.jpg)
![Consistency
• Write
availability,
not
read
availability[44]
• Even
load
distribuXon
is
easier
in
eventually
consistent
systems
• MulX-‐data
center
support
is
easier
in
eventually
consistent
systems
• Some
problems
are
not
solvable
with
eventually
consistent
systems
• Code
is
someXmes
simpler
to
write
in
strongly
consistent
systems](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-52-2048.jpg)
![CAP
EssenXals
–
1
of
3
• “CAP
Principle
→
Strong
Consistency,
High
Availability,
ParXXon-‐resilience:
Pick
at
most
2”[37]
o C-‐A
No
P
→
Single
DB
server,
no
network
parXXon
o C-‐P
No
A
→
Block
transacXon
in
case
of
parXXon
failure
o A-‐P
No
C
→
ExpiraXon
based
caching,
voXng
majority
• Which
feature
to
discard
depends
on
the
nature
of
your
system[41]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-53-2048.jpg)
![CAP
EssenXals
–
2
of
3
• Yield
vs.
Harvest[37]
o Yield
→
Probability
of
compleXng
a
request
o Harvest
→
FracXon
of
data
reflected
in
the
response
• Some
systems
tolerate
<
100%
harvest
(e.g
search
i.e.
approximate
answers
OK)
others
need
100%
harvest
(e.g.
Trx
i.e.
correct
behavior
=
single
well
defined
response)
• For
sub-‐systems
that
tolerate
harvest
degradaXon,
CAP
makes
sense](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-54-2048.jpg)
![CAP
EssenXals
–
3
of
3
• Trading
Harvest
for
yield
–
AP
• ApplicaXon
decomposiXon
&
use
NOSQL
in
appropriate
sub-‐systems
that
has
state
management
and
data
semanXcs
that
match
the
opera<onal
feature
&
impedance
o Hence
NotOnly
SQL
not
No
SQL
o Intelligent
homing
to
tolerate
parXXon
failures[44]
o MulX
zones
in
a
region
(150
miles
-‐
5
ms)
o TwiIer
tweets
in
Cassandra
&
MySQL
o BBC
using
MongoDB
for
offloading
DBMS
o Polygot
persistence
at
LHC@CERN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-55-2048.jpg)
![CAP
EssenXals
–
3
of
3
• Trading
Harvest
for
yield
–
AP
• ApplicaXon
decomposiXon
&
use
NOSQL
in
appropriate
sub-‐systems
that
has
state
management
and
data
semanXcs
that
match
the
opera<onal
feature
&
impedance
o Hence
NotOnly
SQL
not
No
SQL
o Intelligent
homing
to
tolerate
parXXon
failures[44]
o MulX
zones
in
a
region
(150
miles
-‐
5
ms)
o TwiIer
tweets
in
Cassandra
and
MySQL
Most important
o BBC
using
MongoDB
for
offloading
DBMS
point in the whole
o Polygot
persistence
at
LHC@CERN
presentation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-56-2048.jpg)
![Eventual
Consistency
&
AMZ
• DistribuXon
Transparency[38]
• Larger
distributed
systems,
network
parXXons
are
given
• Consistency
Models
o Strong
o Weak
• Has
an
inconsistency
window
before
update
and
guaranteed
view
o Eventual
• If
no
new
updates,
all
will
see
the
value,
eventually](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-57-2048.jpg)
![Eventual
Consistency
&
AMZ
• Guarantee
variaXons[38]
o Read-‐Your-‐writes
o Session
consistency
o Monotonic
Read
consistency
• Access
will
not
return
previous
value
o Monotonic
Write
consistency
• Serialize
write
by
the
same
process
• Guarantee
order
(vector
clocks,
mvcc)
o Example
:
Amz
Cart
merger
(let
cart
add
even
with
parXal
failure)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-58-2048.jpg)
![Eventual
Consistency
&
AMZ
-‐
SimpleDB
• SimpleDB
strong
consistency
semanXcs
[49,50]
o UnXl
Feb
2010,
SimpleDB
only
supported
eventual
consistency
i.e.
GetAIributes
ayer
PutAIributes
might
not
be
the
same
for
some
Xme
(1
second)
o On
Feb
24,
AWS
Added
ConsistentRead=True
aIribute
for
read
o Read
will
reflect
all
writes
that
got
200OK
Xll
that
Xme!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-59-2048.jpg)
![Eventual
Consistency
&
AMZ
-‐
SimpleDB
• SimpleDB
strong
consistency
semanXcs
[49,50]
o Also
added
condiXonal
put/delete
o Put
aIribute
has
a
specified
value
(Expected.1.Value=)
or
(Expected.
1.Exists
=
true/false)
o Same
condiXonal
check
capability
for
delete
also
o
Only
on
one
aIribute
!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-60-2048.jpg)

![!SQL
?
• “We
conclude
that
the
current
RDBMS
code
lines,
while
aIempXng
to
be
a
“one
size
fits
all”
soluXon,
in
fact,
excel
at
nothing.
Hence,
they
are
25
year
old
legacy
code
lines
that
should
be
reXred
in
favor
of
a
collecXon
of
“from
scratch”
specialized
engines.”[43]
• “Current
systems
were
built
in
an
era
where
resources
were
incredibly
expensive,
and
every
compuXng
system
was
watched
over
by
a
collecXon
of
wizards
in
white
lab
coats,
responsible
for
the
care,
feeding,
tuning
and
opXmizaXon
of
the
system.
In
that
era,
computers
were
expensive
and
people
were
cheap”
• “The
1970
-‐
1985
period
was
a
<me
of
intense
debate,
a
myriad
of
ideas,
&
considerable
upheaval.
We
predict
the
next
fiUeen
years
will
have
the
same
feel
“](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-62-2048.jpg)
![Further
deliberaXon
• Daniel
Abadi[45],Mike
Stonebreaker[46],
James
Hamilton[47],
Pat
Hilland[48]
are
all
good
read
for
further
deliberaXons](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-63-2048.jpg)


![Consistent
Hashing
• Origin:
web
caching
“To
decrease
‘hot
spots’
• Three
goals[87]
– Smooth
evoluXon
• When
a
new
machine
joins,
minimum
rebalance
work
and
impact
– Spread
• Objects
assigned
to
a
min
number
of
nodes
– Load
• #
of
disXnct
objects
assigned
to
a
node
is
small](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-67-2048.jpg)



![AnX-‐entropy
• Merge
and
reconciliaXon
operaXons
– Operate
on
two
states
and
return
a
new
state[86]
• Merkle
Trees
– Dynamo
use
of
Merkle
trees
to
detect
inconsistencies
between
replicas
– AnXEntropy
in
Cassandra
exchanges
Merkle
trees
and
if
they
disagree,
range
repair
via
compacXon
[91,92]
– Cassandra
uses
the
ScuIlebuI
ReconciliaXon[86]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-71-2048.jpg)
![Gossip
• Membership
&
Failure
detecXon
• Based
on
emergence
without
rigidity
–
pulse
coupled
oscillators,
biological
systems
like
fireflies
![90]
• Also
used
for
state
propagaXon
– Used
in
Dynamo/Cassandra](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-72-2048.jpg)

![Membership
&
Failure
detecXon
• Consensus
&
Atomic
Broadcast
-‐
impossible
to
solve
in
a
distributed
system[88,89]
– Cannot
differenXate
between
an
slow
system
and
a
crashed
system
• Completeness
– Every
system
that
crashed
will
be
eventually
detected
• Correctness
– A
correct
process
is
never
suspected
• In
short,
if
you
are
dead
somebody
will
no<ce
it
and
if
you
are
alive,
nobody
will
mistake
you
for
dead
!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-74-2048.jpg)
![Ø
Accrual
Failure
Detector
• Not
Boolean
value
but
a
probabilisXc
number
that
“accrues”
over
an
exponenXal
scale
• Captures
the
degree
of
confidence
that
a
corresponding
monitored
process
has
crashed[94]
– Suspicion
Level
– Ø
=
1
-‐>
prob(error)
10%
– Ø
=
2
-‐>
prob(error)
1%
– Ø
=
3
-‐>
prob(error)
0.1%
• If
process
is
dead,
– Ø
is
monotonically
increasing
&
Ø→α
as
t
→α
• If
process
is
alive
and
kicking,
Ø=0
• Account
for
lost
messages,
network
latency
and
actual
crash
of
system/process
• Well
known
heartbeat
period
Δi,
then
network
latency
Δtr
can
be
tracked
by
inter-‐arrival
Xme
modeling](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-75-2048.jpg)

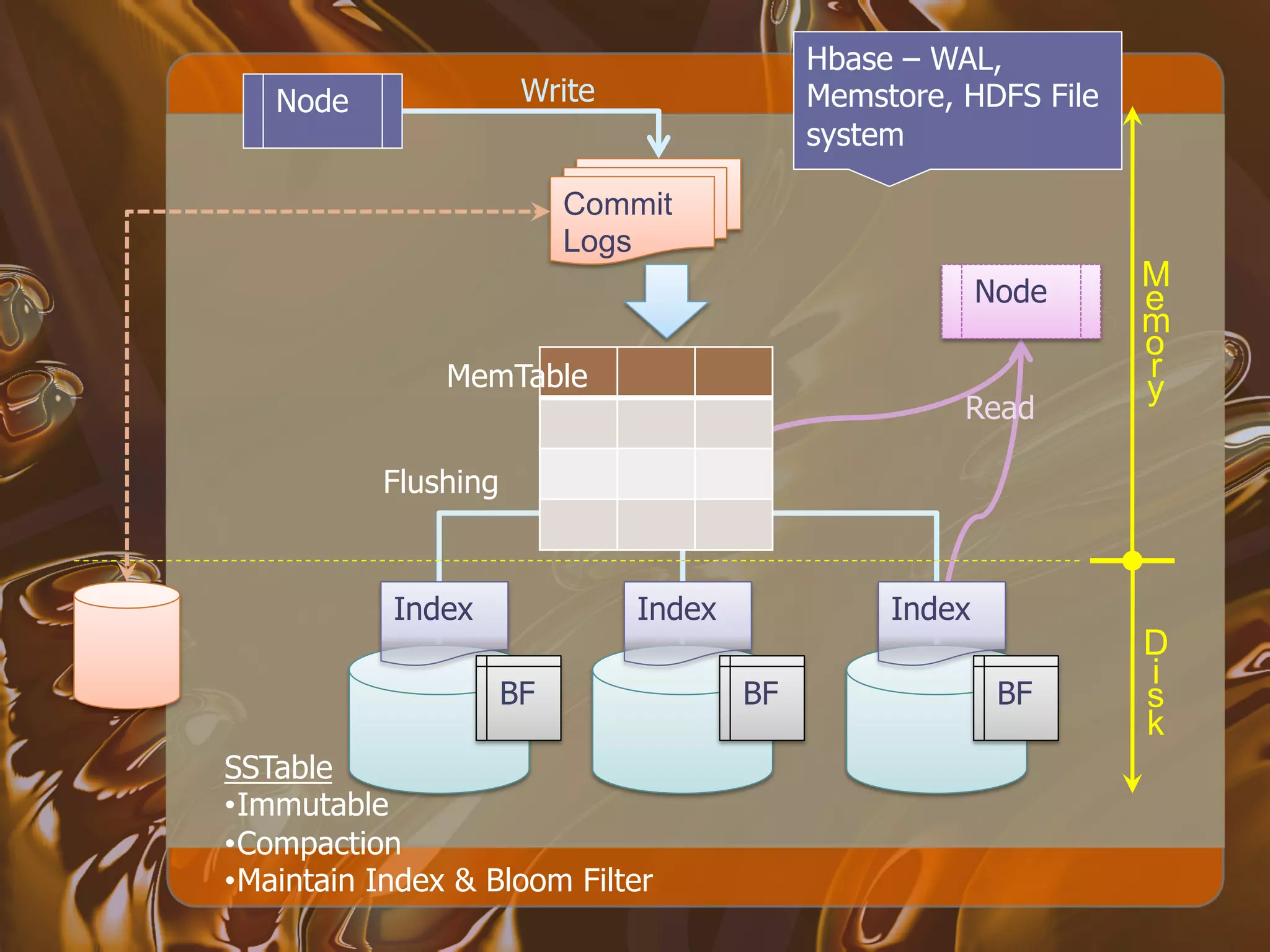
![Bloom
Filter
• The
BloomFilter
answers
the
quesXon
• “Might
there
be
data
for
this
key
in
this
SSTable?”
[Ref:
Cassandra/Hbase
mailer]
– “Maybe"
or
–
“Definitely
not“
– When
the
BloomFilter
says
"maybe"
we
have
to
go
to
disk
to
check
out
the
content
of
the
SSTable
• Depends
on
implementaXon
– Redone
in
Cassandra
– Hbase
0.20.x
removed,
will
be
back
in
0.90
with
a
“jazzy”
implementaXon](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nps-06-111124185334-phpapp01/75/The-Art-of-Big-Data-79-2048.jpg)

