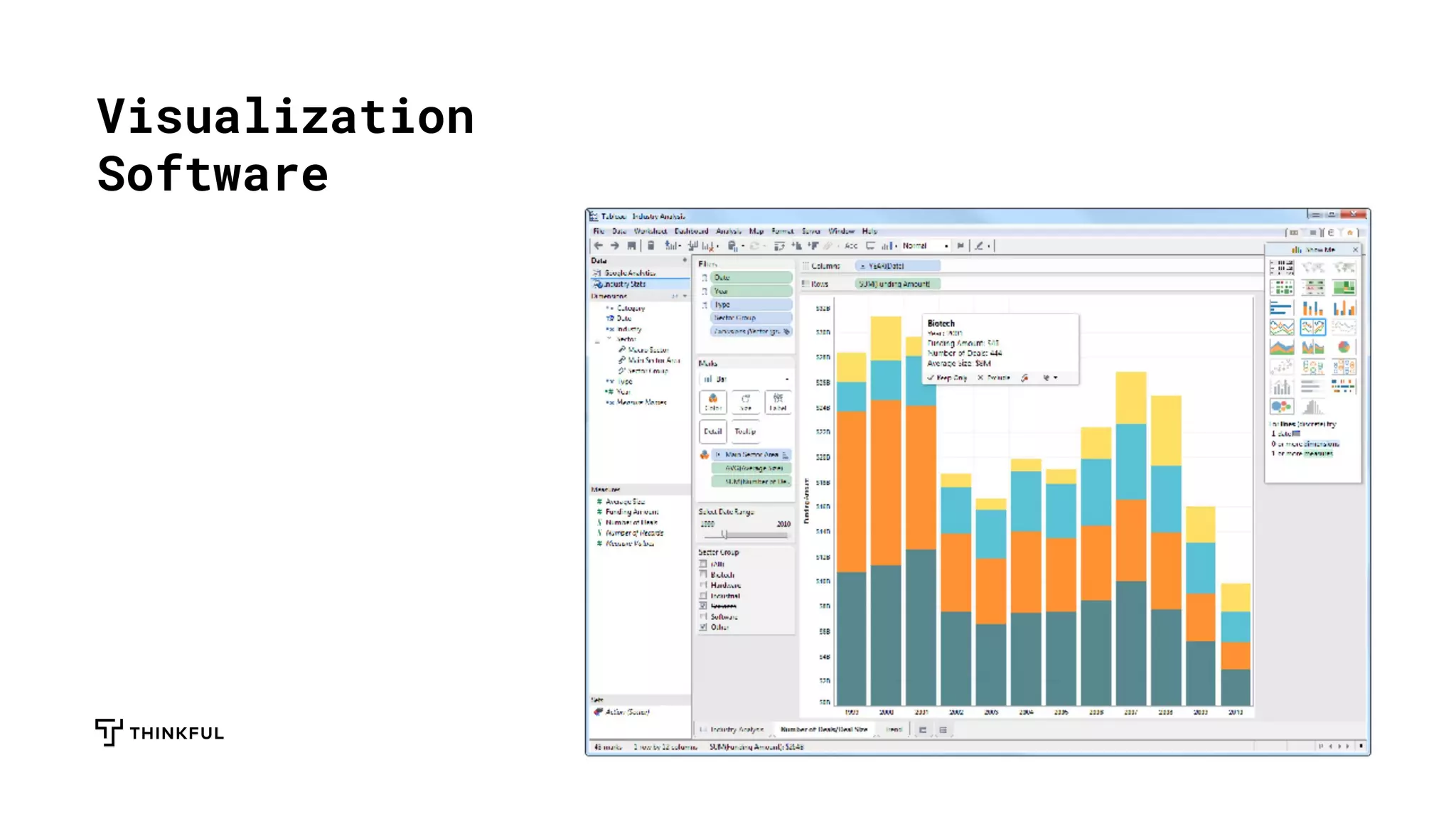
This document provides an overview of data science and the role of data scientists. It discusses how data scientists work with large datasets to solve problems, highlights example use cases at companies like LinkedIn and Uber, and outlines the data science process. Tools commonly used by data scientists like SQL, machine learning algorithms, and Python are also explained. The document concludes by discussing opportunities and challenges in the field and how to get started learning data science through programs like Thinkful.




![“[LinkedIn] was like arriving at a conference
reception and realizing you don’t know anyone. So
you just stand in the corner sipping your drink —
and you probably leave early.”
— LinkedIn Manager, June 2006
Example:
LinkedIn
2006](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tf-gsds-180807203226/75/Tf-gsds-5-2048.jpg)