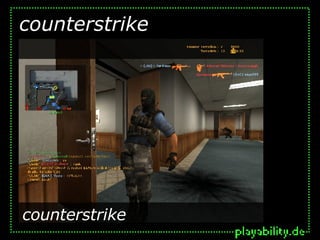
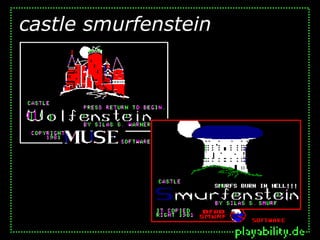
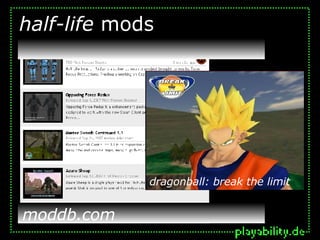
This document discusses the topic of modding, or modifying digital games. It defines modding as changing games' representational or gameplay aspects, ranging from minor tweaks to total conversions. The document then briefly outlines the history of modding, including early examples from the 1980s and prolific modding of games from the 1990s like Doom and Half-Life. It notes modding allows the blending of games and other popular culture works, and helps establish games as "intertextual commodities". Finally, it states modding highlights games' new media aspects like fluid texts and distributed authorship.