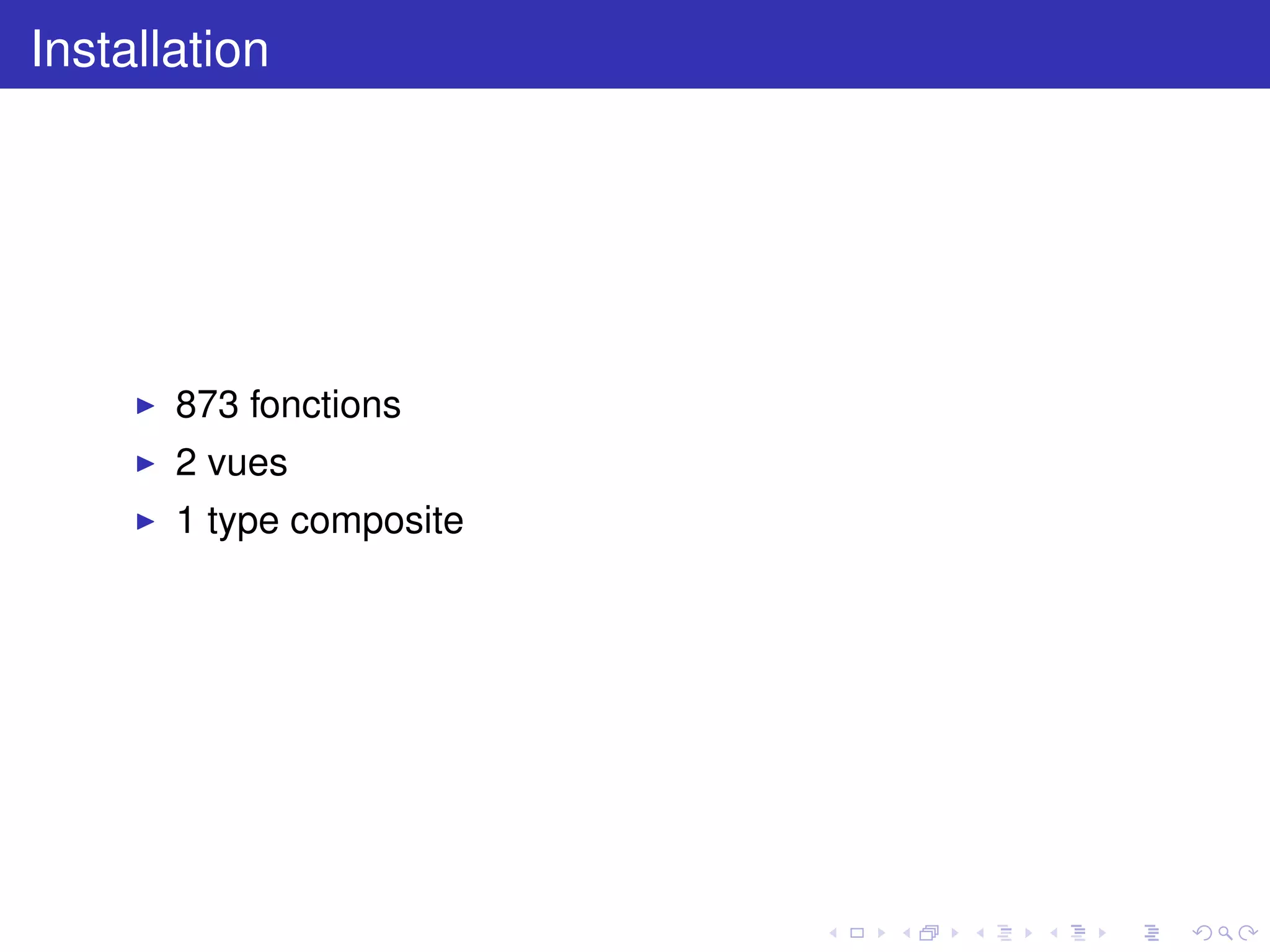
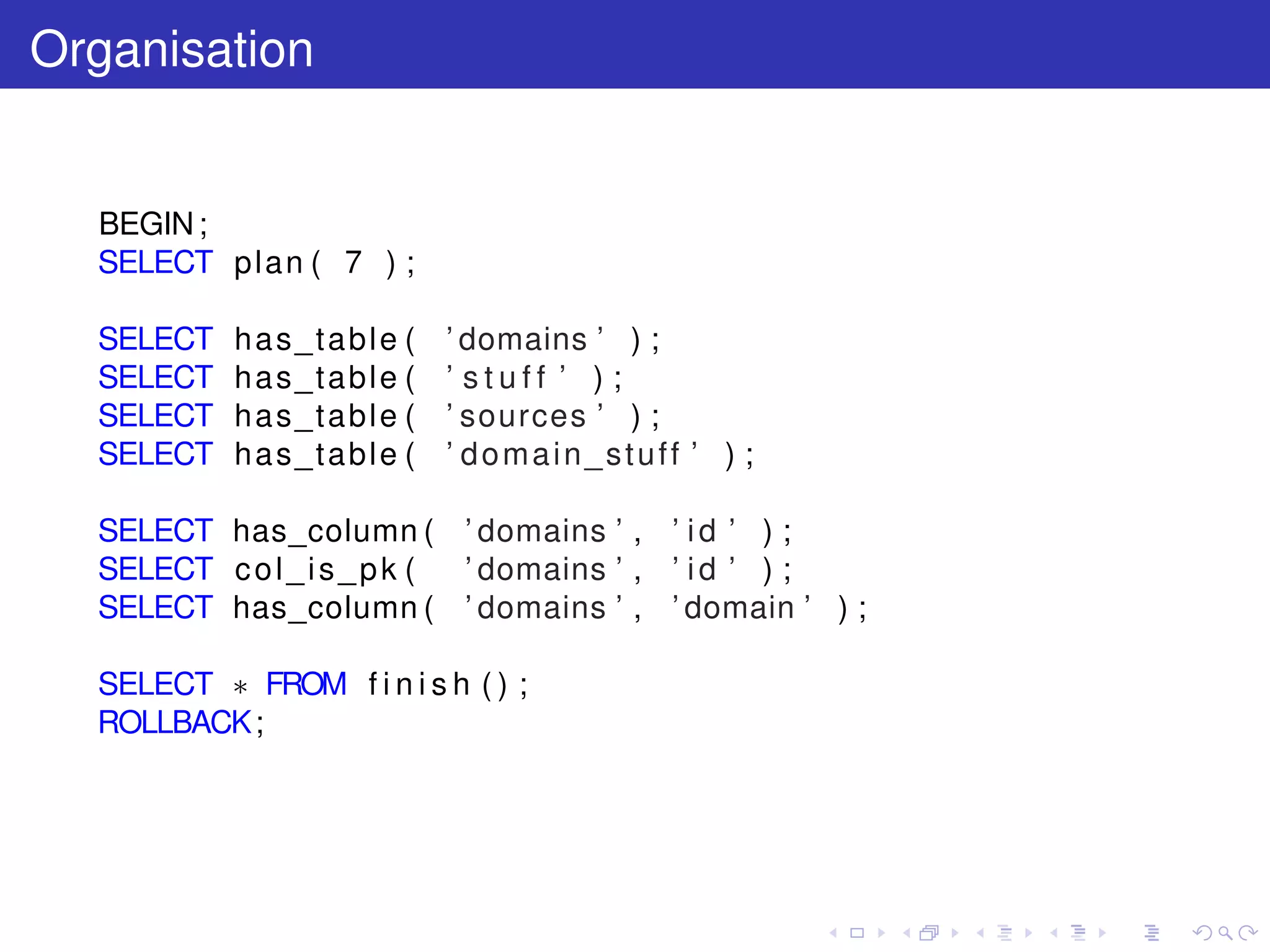
The document discusses pgtap, a unit testing framework for PostgreSQL, and its functionalities, including various testing functions and schema validation methods. It details installation steps and examples of tests conducted, highlighting successes and failures in various assertions. The author, Rodolphe Quiédeville, provides insights into their experience with PostgreSQL and the importance of unit testing in software development.














![CAST everywhere
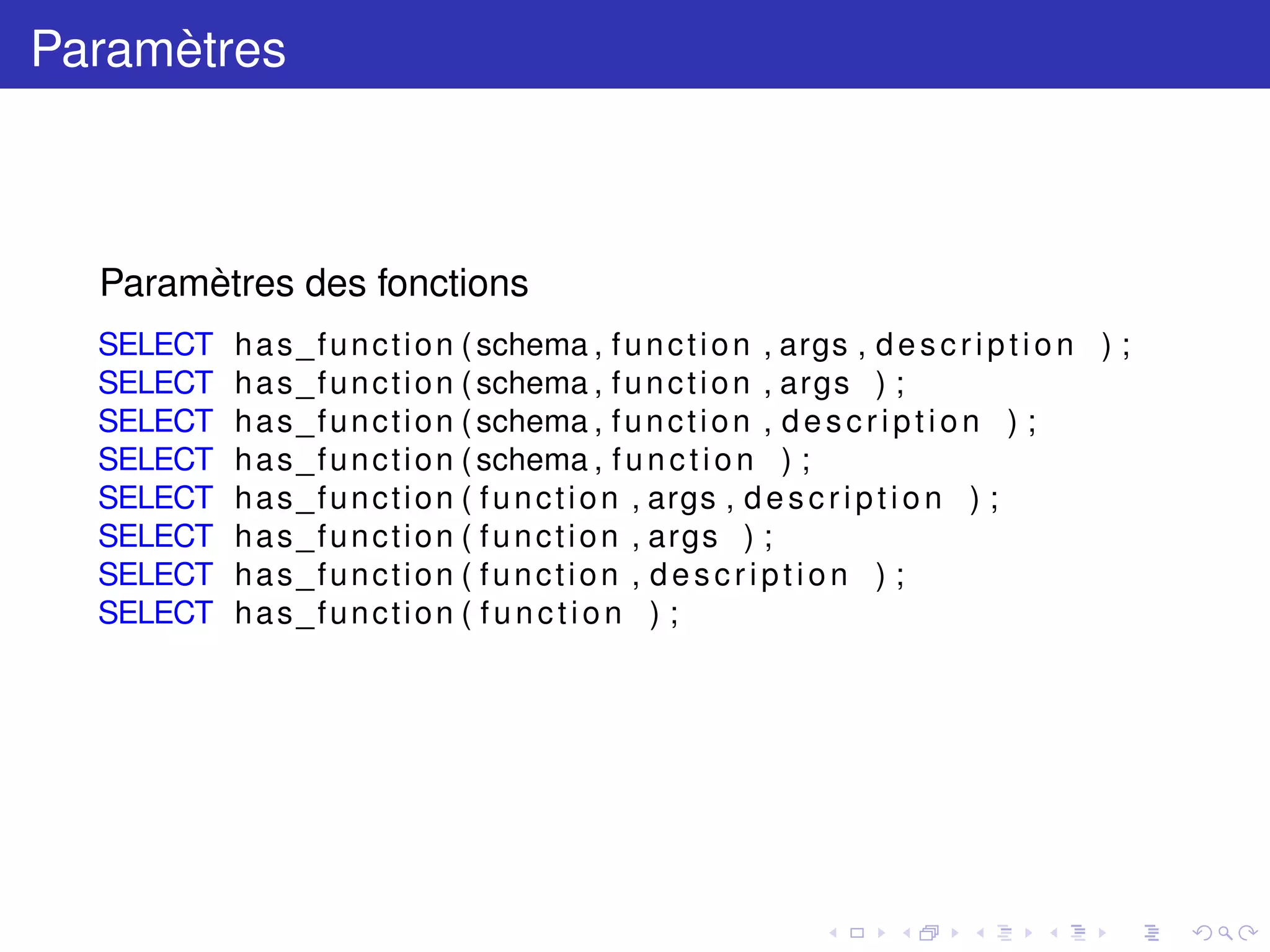
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+--------------+------------------+--------------------------+--------
public | has_function | text | name | normal
public | has_function | text | name, name | normal
public | has_function | text | name, name[] | normal
public | has_function | text | name, name, name[] | normal
public | has_function | text | name, name, name[], text | normal
public | has_function | text | name, name, text | normal
public | has_function | text | name, name[], text | normal
public | has_function | text | name, text | normal
(8 rows)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meetnantes-3-160623073635/75/Tests-unitaires-pour-PostgreSQL-avec-pgTap-17-2048.jpg)



![CAST everywhere
PREPARE count_site AS
SELECT count ( ∗ )
FROM s i t e
WHERE id < 0;
SELECT results_eq (
’ count_site ’ ,
ARRAY[ 0 ] ,
’ check s i t e name ’ ) ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meetnantes-3-160623073635/75/Tests-unitaires-pour-PostgreSQL-avec-pgTap-21-2048.jpg)


![CAST everywhere
SELECT results_eq (
’ count_site ’ ,
ARRAY[ 0 : : b i g i n t ] ,
’ check s i t e name ’ ) ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meetnantes-3-160623073635/75/Tests-unitaires-pour-PostgreSQL-avec-pgTap-24-2048.jpg)




![Cas classique
PREPARE create_site AS
INSERT INTO s i t e
( id , fqdn , sitename , uuid )
VALUES
(−1, ’www. foo . bar ’ , ’ foobar ’ , uuid_generate_v4 ( ) ) ,
(−2, ’www. biz .com ’ , ’ Bizcom ’ , uuid_generate_v4 ( ) ) ;
PREPARE check_site AS
SELECT sitename
FROM s i t e
WHERE id = −1;
SELECT lives_ok ( ’ create_site ’ , ’ [ SetUp ] create s i t e s ’ ) ;
SELECT results_eq ( ’ check_site ’ ,
ARRAY[ ’ foobar ’ : : t e x t ] ,
’ check s i t e name ’ ) ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meetnantes-3-160623073635/75/Tests-unitaires-pour-PostgreSQL-avec-pgTap-30-2048.jpg)



![Pourquoi tout écrire
rodo@roz-desktop:~/$ pg_tapgen -d rodo
rodo@roz-desktop:~/$ cat schema.sql
SELECT views_are(’public’, ARRAY[
’pg_all_foreign_keys’,
’tap_funky’
]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meetnantes-3-160623073635/75/Tests-unitaires-pour-PostgreSQL-avec-pgTap-36-2048.jpg)



