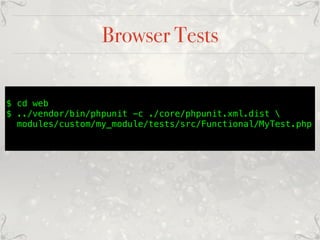
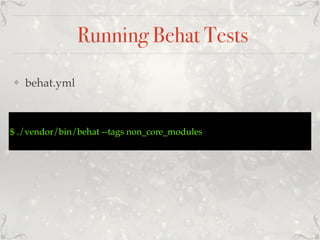
The document presents a comprehensive overview of automated testing for Drupal 8, detailing various testing methods including unit tests, kernel tests, functional tests, browser tests, javascript tests, and behavioral tests. It emphasizes the importance of automated testing in improving efficiency and reliability in the development process, while contrasting the benefits and challenges of manual testing. Additional resources and best practices for implementing these testing strategies are provided, ensuring developers can better manage and execute tests within their projects.











![public function __construct() {
$this->httpClient = Drupal::service('httpd_client');
$this->logger = Drupal::logger('apod');
$this->config = Drupal::config('apod.api_config');
}
public function getAstronomyPictureOfTheDay() {
$uri = $this->addQueryString(
$this->url, ['query' => [
'api_key' => $this->config->get(‘api_key')
]]);
$response = $this->httpClient->request('GET', $uri);
return $this->handleResponse($response);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testyourmodules-180409151553/85/Test-your-modules-12-320.jpg)