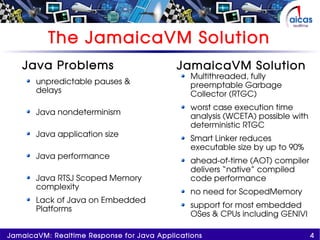
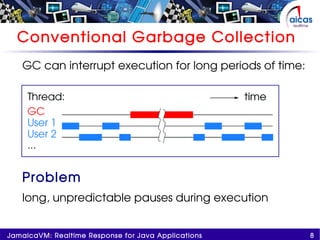
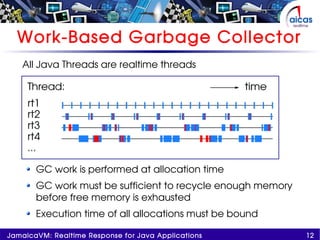
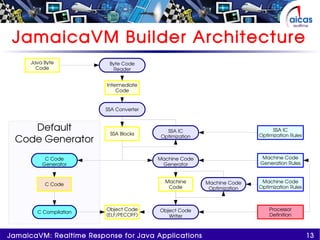
The document discusses JamaicaVM, a virtual machine that provides real-time response capabilities for Java applications, addressing challenges like unpredictable pauses and non-determinism. It highlights features such as a multithreaded, preemptable garbage collector, deterministic runtime performance, and compliance with real-time specification for Java (RTSJ). Ultimately, JamaicaVM aims to enhance Java's reliability in embedded and critical applications while maintaining safety and reducing memory management issues.