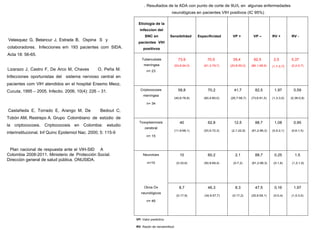
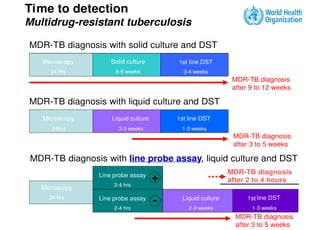
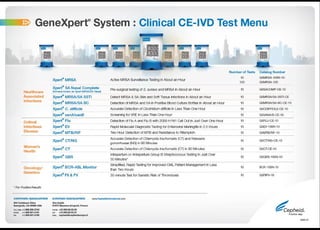
This document discusses techniques for diagnosing tuberculous meningitis. It describes direct diagnostic techniques that detect the causal agent and indirect techniques that detect the host's immune response. Adenosine deaminase (ADA) is an indirect diagnostic technique discussed in detail. ADA levels are often elevated in tuberculosis and other diseases. The document outlines the principle, definition, and determination of the ADA technique. Studies comparing ADA to polymerase chain reaction and examining ADA cutoff levels for diagnosing tuberculous meningitis in cerebrospinal fluid are summarized.