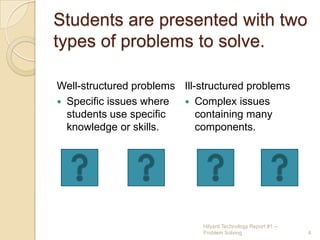
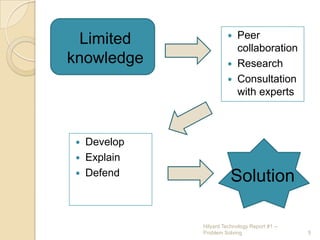
This report discusses using problem solving as an instructional strategy. It defines problem solving as placing students in an active role to solve real-world problems. Students are presented with well-structured problems that use specific skills or knowledge, and ill-structured complex problems with many components. When problem solving, students engage in peer collaboration, research, and consultation with experts to develop, explain, and defend a solution. Problem solving is advantageous as it engages students and provides context for learning, but it can be difficult to create problems and requires time to implement. Problem solving can integrate a variety of content areas and lead to students gaining content knowledge and collaborative skills.