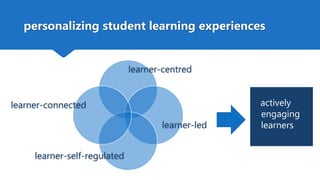
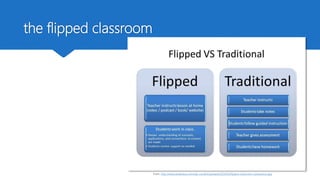
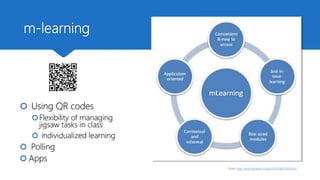
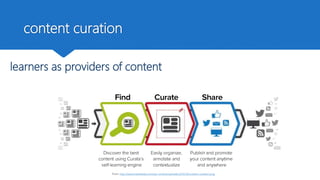
The document discusses how technology can be used to give learners a voice in higher education. It presents the DigCompEdu framework for digital competencies in education and describes four types of learner-centered tasks that empower students: learner-centered, learner-led, learner-connected, and learner-self-regulated. These tasks actively engage students and help personalize their learning experiences by allowing them more freedom and ownership over their education. The document argues that technologies can help educators implement new pedagogical approaches that focus on developing students' creativity, critical thinking, collaboration, and communication skills.