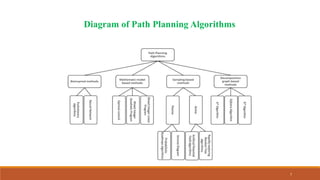
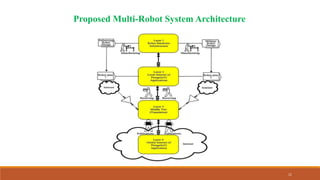
This document provides a summary of a technical seminar presentation on multi-robot systems for space applications. The presentation covered topics including what space robots are, why they are used, examples of multi-robot systems, how path planning algorithms work, the key technologies used in space robots, a proposed multi-robot system architecture, the importance of space robots, types of space robots, and future space missions that will utilize robotics. The presentation provided information on space robots through diagrams, flow charts, and explanations of concepts like sensing, planning, control and execution in multi-robot systems.